The primary advantage of ceramics over metals is their superior performance in extreme environments characterized by high temperatures, extreme wear, or corrosive chemicals. While metals deform and fail under such conditions, engineering ceramics maintain their structural integrity, hardness, and chemical resistance.
Choosing between ceramic and metal isn't about which is fundamentally "better," but about understanding a critical trade-off. You are trading the toughness and forgiveness of metal for the exceptional hardness and environmental resilience of ceramic.

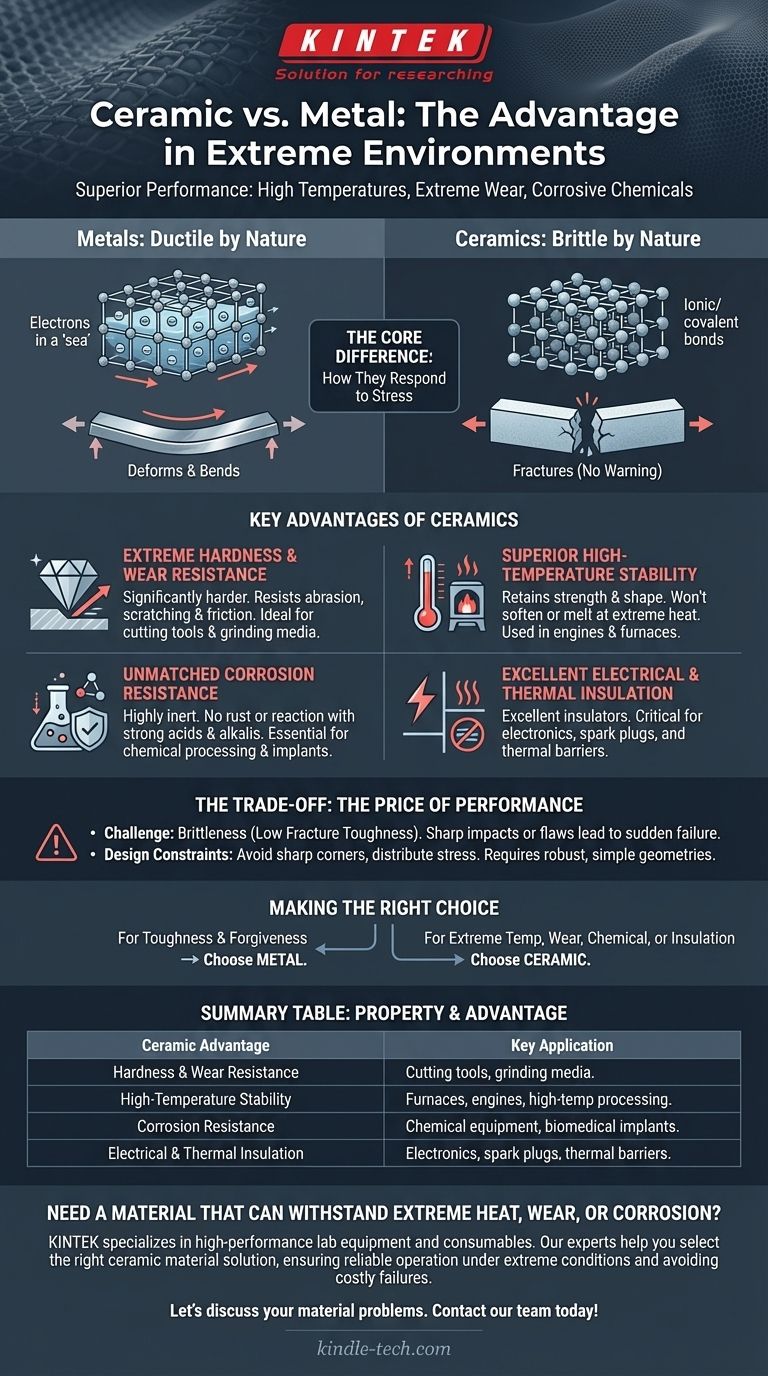
The Core Difference: How They Respond to Stress
The most significant distinction between these materials lies in their atomic bonds, which dictates how they behave under load.
Metals: Ductile by Nature
Metals possess metallic bonds, where electrons are shared in a "sea," allowing atoms to slip past one another without the structure failing.
This atomic arrangement gives metals their signature ductility. When overloaded, they bend, stretch, and deform before they ultimately break.
Ceramics: Brittle by Nature
Ceramics have strong ionic and covalent bonds that lock atoms rigidly in place. These bonds resist stress exceptionally well up to a certain point.
However, once that limit is exceeded, the bonds break catastrophically rather than deforming. This property is known as brittleness. They do not provide a warning by bending; they simply fracture.
Key Advantages of Ceramics Over Metals
This fundamental difference in bonding gives ceramics a unique set of properties that make them ideal where metals would quickly fail.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
Ceramics are significantly harder than most metals. This makes them incredibly resistant to abrasion, scratching, and friction.
This is why they are used for cutting tools, industrial grinding media, and wear-resistant coatings.
Superior High-Temperature Stability
The strong atomic bonds in ceramics require enormous energy to break, giving them exceptionally high melting points.
They retain their strength and shape at temperatures that would cause even high-performance metal alloys to soften, deform, or melt entirely.
Unmatched Corrosion Resistance
Ceramics are highly inert and do not react with most chemicals, including strong acids and alkalis.
Unlike metals, they do not rust or corrode, making them essential for chemical processing equipment and biomedical implants.
Excellent Electrical and Thermal Insulation
While metals are defined by their ability to conduct electricity and heat, most ceramics are excellent insulators.
This property is critical for electronic components, spark plugs, and thermal barriers in engines and furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Price of Performance
The unique advantages of ceramics come with significant design and engineering challenges that must be respected.
The Challenge of Brittleness
The primary disadvantage of ceramics is their low fracture toughness. A sharp impact or a hidden microscopic flaw can lead to sudden, complete failure without warning.
Unlike a metal part that might dent or bend, a ceramic component can shatter.
Design and Manufacturing Constraints
You cannot design a ceramic part the same way you design a metal one. Because ceramics cannot deform to redistribute localized stress, the design itself must prevent it.
This requires avoiding sharp corners, ensuring forces are applied over large, smooth surfaces, and generally favoring simple, robust geometries to prevent stress concentrations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary operational goal and the working environment.
- If your primary focus is toughness and forgiveness: Choose metal. Its ability to absorb impacts and deform without failing makes it a safer choice for general structural applications.
- If your primary focus is performance at extreme temperatures or high wear: Choose ceramic. Its stability and hardness are unmatched, but you must invest in a design that caters to its brittle nature.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance or electrical insulation: Choose ceramic. Its inherent inertness and insulative properties are far superior to metals for these specific tasks.
Ultimately, the right material is the one whose properties best solve the specific problem you are facing.
Summary Table:
| Property | Ceramic Advantage | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness & Wear Resistance | Superior to metals, resists abrasion | Cutting tools, grinding media |
| High-Temperature Stability | Maintains strength, won't soften or melt | Furnaces, engines, high-temp processing |
| Corrosion Resistance | Inert, does not rust or react | Chemical equipment, biomedical implants |
| Electrical & Thermal Insulation | Excellent insulator, unlike conductive metals | Electronics, spark plugs, thermal barriers |
Need a material that can withstand extreme heat, wear, or corrosion?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Whether your application requires the unmatched temperature stability of a ceramic furnace tube or the superior wear resistance of ceramic components for your processing needs, our experts can help you select the right material solution.
We provide value by:
- Supplying durable, high-purity ceramic parts designed for demanding laboratory and industrial environments.
- Offering expert guidance to ensure your equipment operates reliably and efficiently under extreme conditions.
- Helping you avoid costly downtime and material failure by matching the right ceramic properties to your specific challenge.
Let's discuss how ceramics can solve your toughest material problems. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
People Also Ask
- How is alumina ceramic made? A Guide to Manufacturing Methods and Material Properties
- What is the effect of heating rate on sintering? Achieve Uniform Density and Avoid Defects
- At what temperature does ceramic melt? A Guide to Ceramic Heat Resistance
- Can ceramics withstand high temperatures? Discover Their Exceptional Heat Resistance
- Can ceramic withstand high temperatures? Discover the Superior Materials for Extreme Heat
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits
- Is silicon carbide used in high temperature applications? Master Extreme Heat with SiC
- What is the effect of sintering temperature on density and hardness? Optimize Your Material's Properties



















