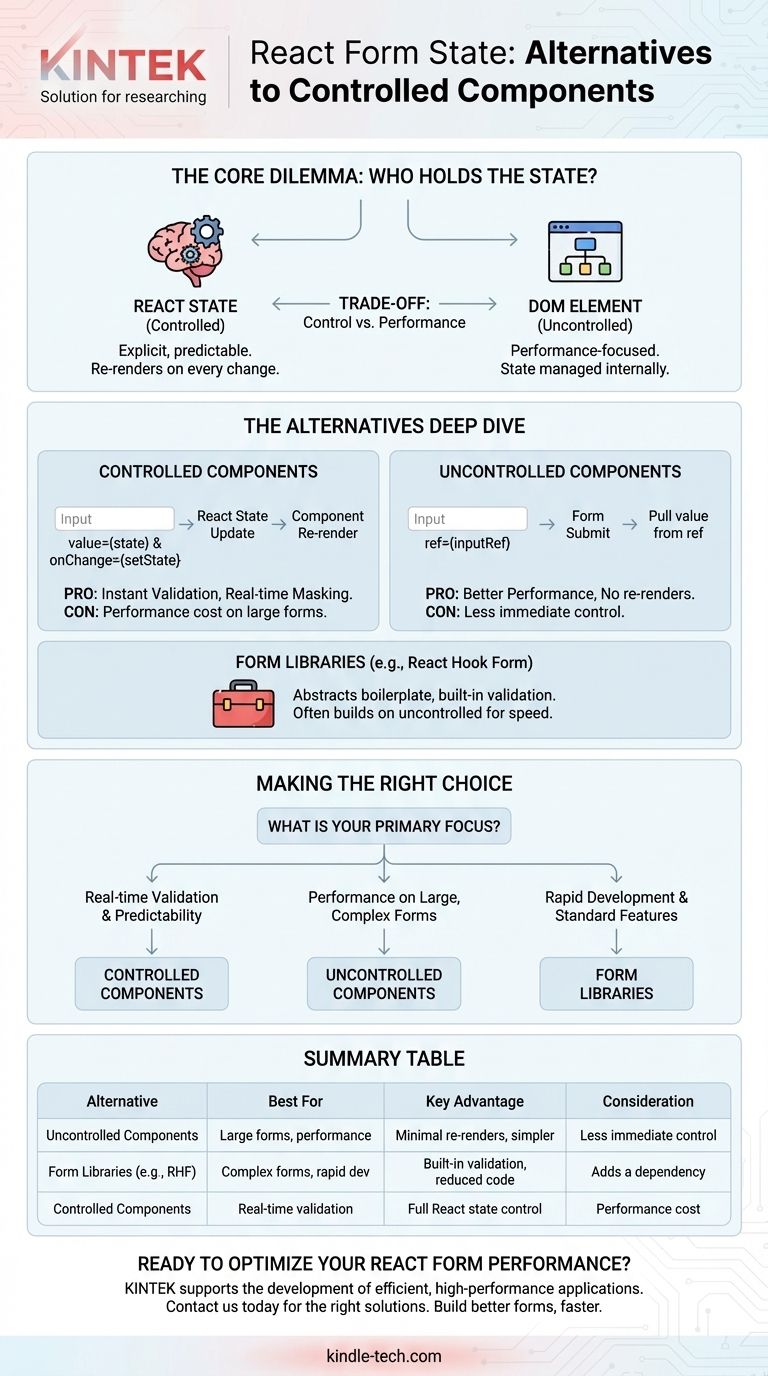
When managing form state in React, the most direct alternative to a controlled component is an uncontrolled component. While controlled components keep their state within React itself, uncontrolled components let the browser's DOM manage the state internally. For more complex scenarios, dedicated form libraries or global state managers offer a higher-level alternative to managing form logic manually.
The choice between controlled and uncontrolled components is not about which is universally "better," but a fundamental trade-off. You are choosing between the explicit, predictable state management of React versus the performance and simplicity of letting the DOM handle the work.
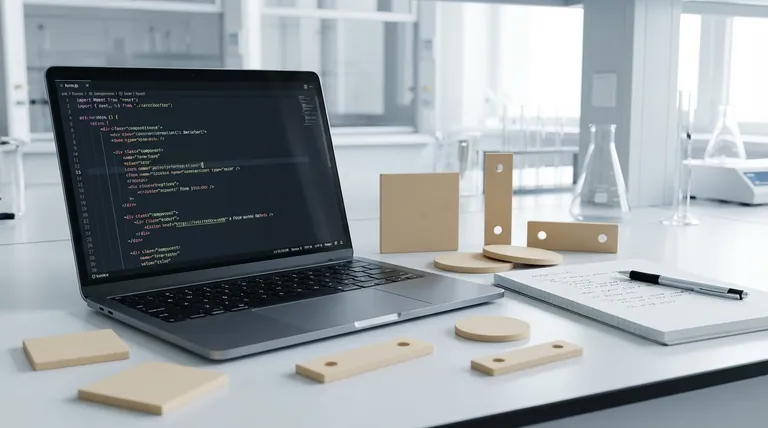

The Core Dilemma: Who Holds the State?
At the heart of this decision is a single question: should your React code be the "single source of truth" for an input's value, or should the DOM element itself?
Understanding Controlled Components
A controlled component is the conventional React approach. The value of the form element is driven entirely by React state.
You achieve this by passing a value prop to the input and an onChange handler to update that state with every change. React state is the ultimate authority.
This creates a clear, predictable data flow. Every keystroke triggers a state update, which causes the component to re-render, ensuring the UI and the state are always in sync.
The Alternative: Uncontrolled Components
An uncontrolled component works more like traditional HTML. The form data is handled by the DOM itself, not by React state.
Instead of writing an event handler for every state update, you use a ref to create a direct reference to the DOM element.
You can then pull the input's current value from that ref when you need it, such as when the user submits the form. React doesn't "know" the input's value until you explicitly ask for it.
Beyond the Basics: Form Management Libraries
For forms with significant complexity, managing state manually with either pattern can become tedious and error-prone. This is why specialized libraries exist.
The Role of Libraries
Libraries like Formik and React Hook Form abstract away the boilerplate code for managing values, validation, and submission states.
They provide a structured framework, saving you from reinventing the wheel for common form functionalities like error handling and tracking whether a field has been touched.
Key Library Approaches
Interestingly, these libraries often build upon the core patterns. React Hook Form, for example, is built on the principle of uncontrolled components and refs to maximize performance by minimizing re-renders. This makes it an excellent alternative when performance is a key concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither approach is a silver bullet. Your choice has direct consequences for performance, features, and code complexity.
When Controlled Components Shine
The strength of controlled components is explicit control. Because the value lives in React state, you can implement features like instant validation, real-time input masking (e.g., for phone numbers), or dynamically disabling a submit button with ease.
The Cost of Control
This control comes at a performance cost. For large forms with many inputs, re-rendering the entire form component on every single keystroke can lead to noticeable input lag and a sluggish user experience.
When Uncontrolled Components are Better
Uncontrolled components generally offer better performance, especially in complex forms, because they avoid the re-render cycle on each input change. They are also simpler to set up for basic forms and integrate more easily with non-React UI libraries.
The Drawback of Uncontrolled
The trade-off is a loss of immediate control. Implementing real-time validation or conditional logic is more complex because you don't have the input's current value readily available in state. You must manually pull it from the DOM.
Making the Right Choice for Your Form
Choosing the correct pattern depends entirely on the specific requirements of the form you are building.
- If your primary focus is real-time validation and predictable state: Controlled components give you the most direct and declarative control over your form's data.
- If your primary focus is performance on large, complex forms: Uncontrolled components, especially when paired with a library like React Hook Form, will prevent performance bottlenecks.
- If your primary focus is rapid development with standard features: A dedicated form library abstracts away these low-level decisions so you can focus on building features.
Ultimately, understanding this fundamental trade-off between direct control and DOM-managed simplicity is the key to building efficient and maintainable forms.
Summary Table:
| Alternative | Best For | Key Advantage | Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Uncontrolled Components | Large forms, performance | Minimal re-renders, simpler setup | Less immediate control |
| Form Libraries (e.g., React Hook Form) | Complex forms, rapid development | Built-in validation, reduced boilerplate | Adds a dependency |
| Controlled Components | Real-time validation, predictable state | Full React state control | Performance cost on large forms |
Ready to Optimize Your React Form Performance?
Struggling with form state management in your React applications? Whether you're building a simple contact form or a complex data-entry system, choosing the right approach is crucial for performance and user experience.
At KINTEK, we understand the challenges developers face when managing form logic. Our expertise in providing robust lab equipment and consumables extends to supporting the development of efficient, high-performance applications. Let us help you streamline your workflow and enhance your lab's digital tools.
Contact us today via our contact form to discuss how we can support your project with the right solutions and expertise. Build better forms, faster.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Ceramic Sheet
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Side Window Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the properties of ceramic surfaces? Discover Their Extreme Hardness and Stability
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- What is the maximum temperature for ceramics? Find the Right Material for Your High-Temp Application
- What are the high temperature properties of alumina? Discover Its Stability, Strength, and Limits
- Does nanomaterials have potential hazards to human health? Understanding the Risks and Safe Handling







