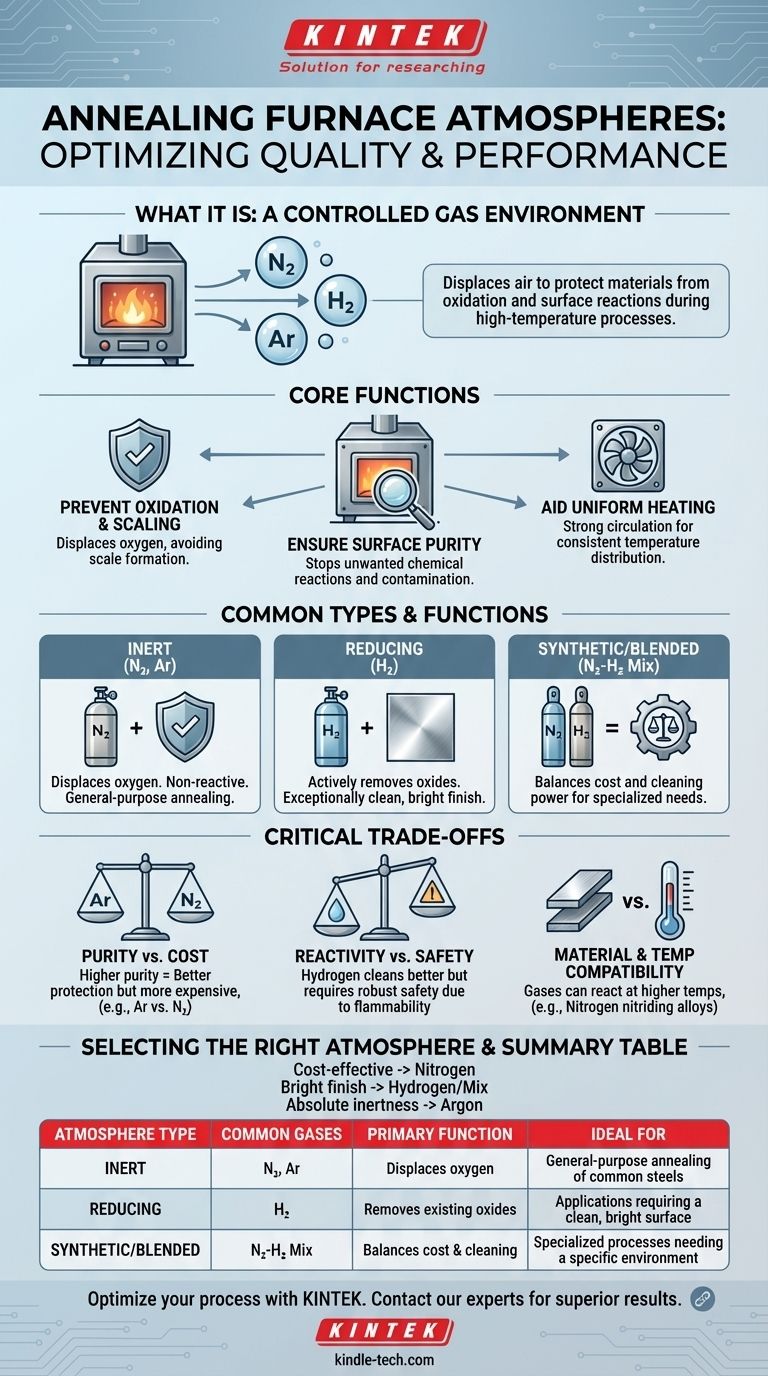
The atmosphere in an annealing furnace is a carefully controlled gas or mixture of gases intentionally introduced into the heating chamber. This atmosphere displaces ambient air to protect the material from oxidation and other unwanted surface reactions during the high-temperature process. The specific gas used—such as nitrogen, hydrogen, or argon—is selected based on the material being treated and the desired final properties.
The primary purpose of an annealing furnace atmosphere isn't just to fill a space; it's an active, engineered component of the process designed to control the surface chemistry of the material, preventing defects and ensuring the final product meets its metallurgical specifications.

The Core Function of a Furnace Atmosphere
A controlled atmosphere is fundamental to the success of the annealing process. It serves several critical purposes that directly impact the quality of the finished product.
Preventing Oxidation and Scaling
At the high temperatures required for annealing, most metals will readily react with oxygen in the air. This reaction, known as oxidation, creates a layer of scale on the material's surface, which is often undesirable and must be removed. A protective atmosphere displaces the oxygen, preventing this from happening.
Ensuring Surface Purity
Beyond just preventing oxidation, the furnace atmosphere ensures the surface of the material remains clean and free from contamination. It provides a specific, controlled environment that stops other unwanted chemical reactions from occurring at high temperatures.
Aiding in Uniform Heating
The atmosphere itself acts as a medium for heat transfer. In many furnace designs, powerful convection fans stir the heated protective atmosphere, as noted with aluminum products. This strong circulation ensures that all parts of the workpiece reach the target temperature evenly and consistently.
Common Types of Annealing Atmospheres
The choice of atmosphere depends entirely on the material being processed and the specific goals of the annealing cycle. Different gases provide different levels of protection and reactivity.
Inert Atmospheres (Nitrogen, Argon)
Inert atmospheres are the most common choice for general-purpose annealing. Gases like nitrogen (N₂) and argon (Ar) are used because they are non-reactive with most metals under annealing conditions. They work by simply displacing the oxygen.
Reducing Atmospheres (Hydrogen)
A reducing atmosphere, typically containing hydrogen (H₂), goes a step further. Instead of just preventing oxidation, hydrogen actively reacts with and removes any existing oxides on the material's surface. This results in an exceptionally clean and bright surface finish.
Synthetic & Blended Atmospheres
For highly specialized processes, gases are often mixed to create a synthetic atmosphere with specific properties. For example, a blend of nitrogen and hydrogen can balance the cost-effectiveness of nitrogen with the cleaning power of hydrogen.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting an atmosphere is an engineering decision that involves balancing performance, cost, and safety. There is no single "best" option for all applications.
Gas Purity vs. Cost
Higher purity gases provide better protection. Argon, for instance, is more inert than nitrogen at very high temperatures but is also significantly more expensive. The required purity level is dictated by the sensitivity of the material being processed.
Reactivity vs. Safety
While hydrogen provides superior surface cleaning, it is also highly flammable. Furnaces designed for hydrogen atmospheres require robust safety features, including specialized pressure and flow control systems, which adds to their complexity and cost.
Material and Temperature Compatibility
The inertness of a gas can change with temperature. While nitrogen is non-reactive with most steels, it can form nitrides on the surface of certain alloys at higher temperatures. Understanding the specific interaction between the gas, the material, and the temperature is critical to avoid unintended surface modification.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Process
Your choice of atmosphere should be directly aligned with the technical requirements of your material and the desired outcome of the annealing cycle.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective oxidation prevention for common steels: A nitrogen-based atmosphere is often the most balanced and widely used choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving the brightest, cleanest possible surface finish: A hydrogen or a nitrogen-hydrogen blend is superior due to its active reducing properties.
- If your primary focus is treating highly reactive metals or applications demanding absolute inertness: A pure argon atmosphere is necessary, despite the higher operational cost.
Choosing the correct furnace atmosphere is a critical engineering decision that directly impacts the quality, performance, and cost of the final product.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Common Gases | Primary Function | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inert | Nitrogen (N₂), Argon (Ar) | Displaces oxygen to prevent oxidation | General-purpose annealing of common steels |
| Reducing | Hydrogen (H₂) | Actively removes existing oxides for a bright finish | Applications requiring a clean, bright surface |
| Synthetic/Blended | Nitrogen-Hydrogen Mix | Balances cost and cleaning power | Specialized processes needing a specific environment |
Optimize your annealing process with the right atmosphere. The choice of furnace gas is critical to achieving your desired material properties, from preventing oxidation to ensuring a bright surface finish. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for your laboratory's thermal processing needs. Contact our experts today to discuss the ideal annealing furnace atmosphere for your specific application and ensure superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is hydrogen annealing important? Achieve Bright, Stress-Free Metal Parts
- What is an inert gas and which processes is it used in? A Guide to Protective Atmospheres
- What is the controlled atmosphere brazing process? Achieve High-Volume, High-Strength Metal Joining
- What is the purpose of pre-treating coal samples? Ensure Accurate Pyrolysis with Nitrogen Drying
- What are inert atmosphere conditions? Control Chemical Reactions and Ensure Safety
- What is disassociated ammonia? A Cost-Effective Hydrogen Source for Heat Treating
- Why is a high-precision atmosphere furnace necessary for Au or Mo modified nickel anodes? Unlock Superior Stability
- What role does an atmosphere furnace play in catalyst calcination? Ensure High Performance for Denitration Catalysts



















