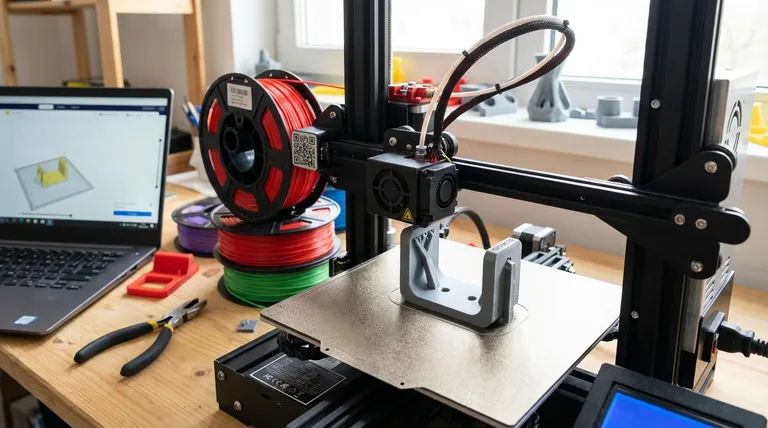
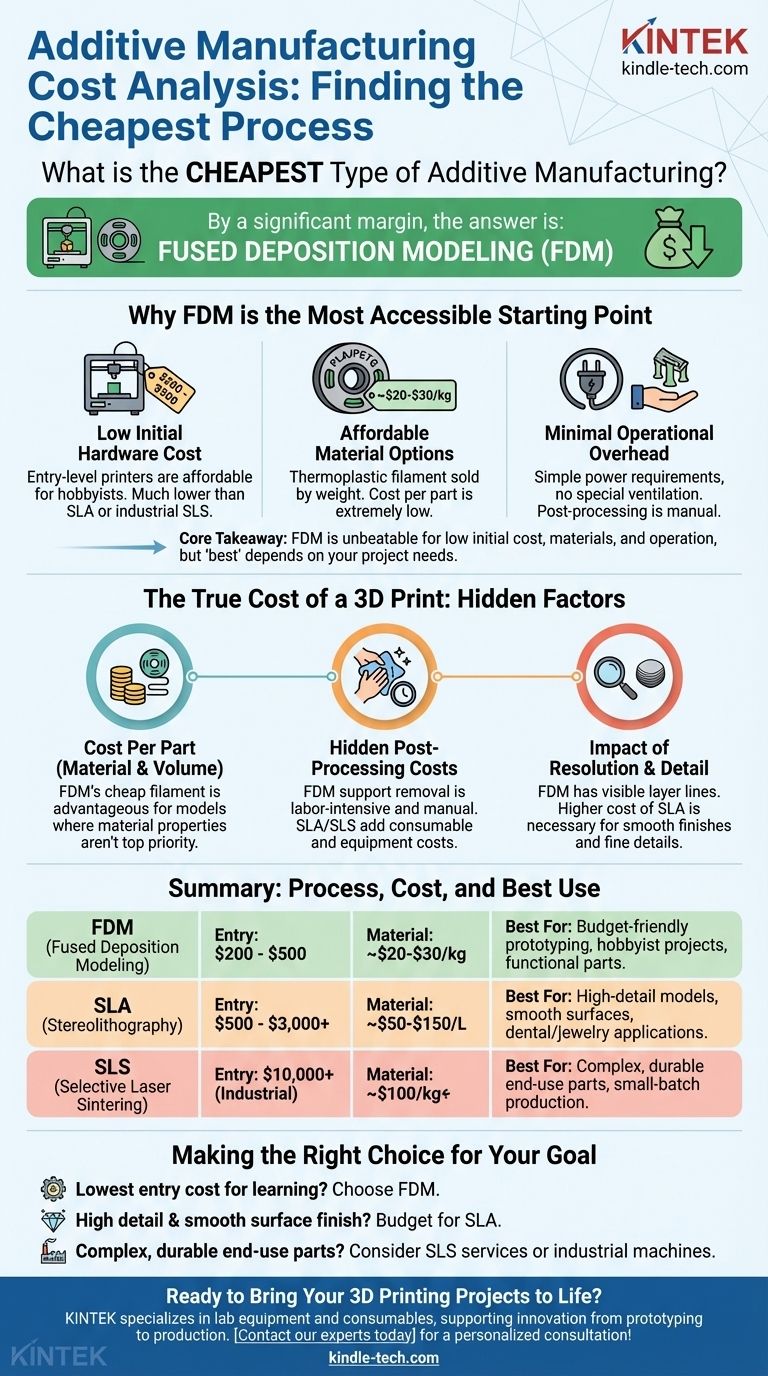
By a significant margin, the cheapest type of additive manufacturing process is Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF). This technology dominates the consumer and prosumer markets due to its exceptionally low hardware entry point, inexpensive raw materials, and straightforward operation. For anyone looking to start with 3D printing on a budget, FDM is the definitive answer.
The core takeaway is that while FDM is the cheapest process in terms of initial investment, materials, and operation, the "best" choice always depends on your project's specific needs for detail, strength, and material properties. Understanding the trade-offs between cost and capability is the key to making a sound decision.

Why FDM is the Most Accessible Starting Point
Fused Deposition Modeling's cost-effectiveness is not based on a single factor, but on its entire ecosystem. From the printer to the filament, every aspect is optimized for accessibility and low cost.
Low Initial Hardware Cost
The barrier to entry for FDM is incredibly low. Capable, entry-level printers are widely available for a few hundred dollars, making it the only technology accessible at a true hobbyist price point.
In contrast, the next cheapest technology, Stereolithography (SLA), typically starts at a significantly higher price, while industrial methods like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) involve machinery costing tens of thousands of dollars or more.
Affordable Material Options
FDM printers use spools of thermoplastic filament, which are sold by weight. Standard materials like PLA (Polylactic Acid) and PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) are very inexpensive, often costing less than $25 per kilogram.
This makes the cost per part extremely low, especially for prototypes and small items. Resin for SLA printers is priced per liter and is substantially more expensive, as is the specialized polymer powder used in SLS machines.
Minimal Operational Overhead
Operating an FDM printer is relatively simple and cheap. It requires a standard power outlet and no special ventilation for most materials like PLA.
Maintenance involves replacing inexpensive parts like nozzles, and post-processing—the cleanup work done after a print finishes—is typically a manual process of snapping off support structures. This requires time but no significant recurring cost for chemicals or specialized equipment.
The True Cost of a 3D Print
While FDM is the cheapest, a professional understands that the final cost of a part is more than just the machine's price tag. To make an informed decision, you must consider the total cost of production.
Cost Per Part: Material and Volume
The primary driver of part cost is the material. FDM's use of cheap filament gives it a clear advantage for creating physical models where material properties are not the top priority.
However, for industrial applications, the higher cost of engineering-grade SLA resins or SLS powders can be justified by their superior strength, chemical resistance, or heat tolerance.
The Hidden Costs of Post-Processing
Post-processing adds cost through labor and consumables. While FDM's support removal is "free" in terms of materials, it is labor-intensive and leaves blemishes on the part's surface.
SLA requires washing parts in a solvent (like isopropyl alcohol) and curing them with UV light, adding consumable and equipment costs. SLS requires extensive de-powdering, and the unused powder must be carefully managed, adding operational complexity.
The Impact of Resolution and Detail
FDM produces parts with visible layer lines and has limitations on the fine details it can resolve. It is a trade-off for its speed and low cost.
If your project demands a perfectly smooth surface finish or intricate details, such as for jewelry patterns or dental models, the higher cost of an SLA printer becomes a necessary investment to achieve the required quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When "Cheapest" Isn't "Best"
Choosing a process is a balancing act between cost, speed, and the final part's quality and function. The cheapest option is only the right option when its limitations do not compromise your goal.
FDM: For Prototypes and General Use
FDM is the workhorse for rapid prototyping, fit checks, and creating functional parts where aesthetic perfection is not required. Its strength lies in producing decent-quality parts quickly and for an almost negligible material cost.
SLA: For High Detail and Smooth Surfaces
SLA is the clear choice when visual quality is paramount. It produces parts with an injection-molded appearance and captures fine details that are impossible on FDM printers. This justifies its higher material and operational costs for applications like miniatures, presentation models, and patterns for casting.
SLS: For Complex and Durable Parts
SLS excels at producing strong, functional nylon parts with complex internal geometries. Because parts are supported by the unfused powder around them, it does not require dedicated support structures. This makes it ideal for small-batch manufacturing of end-use parts, where its high initial cost is offset by its unique capabilities and part strength.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the right process, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible entry cost for learning or hobbyist use: Choose an FDM printer. It is the undisputed entry point into the world of additive manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is creating high-detail models with a smooth surface finish: Budget for an SLA printer and its associated post-processing equipment.
- If your primary focus is producing batches of complex, durable end-use parts: FDM can be a starting point with engineering filaments, but a professional SLS service or machine is the superior long-term solution.
Ultimately, aligning your budget with your project's technical requirements will ensure you invest in the right capability from the start.
Summary Table:
| Additive Manufacturing Process | Typical Entry-Level Hardware Cost | Common Material Cost | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) | $200 - $500 | ~$20-$30/kg (PLA/PETG) | Budget-friendly prototyping, hobbyist projects, functional parts |
| SLA (Stereolithography) | $500 - $3,000+ | ~$50-$150/L (Resin) | High-detail models, smooth surfaces, dental/jewelry applications |
| SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) | $10,000+ (industrial) | ~$100/kg+ (Nylon Powder) | Complex, durable end-use parts, small-batch production |
Ready to Bring Your 3D Printing Projects to Life?
Whether you're a research lab prototyping new equipment, an educational institution teaching design principles, or an R&D team creating custom components, having the right tools is crucial.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering solutions that support innovation across various fields. From prototyping to production, we help laboratories and research facilities achieve their goals with reliable, precise equipment.
Let's discuss how we can support your additive manufacturing needs. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Vacuum Cold Mounting Machine for Sample Preparation
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a warm isostatic press? Achieve Optimal Densification for Your Materials
- What are the advantages and limitations of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve Ultimate Material Integrity
- What are some of the attractive properties of hot isostatic pressed products? Achieve Perfect Density and Superior Performance
- What is the temperature of hot isostatic pressing? Achieve Full Density for Critical Components
- What is the HIP material process? Achieve Near-Perfect Density and Reliability



















