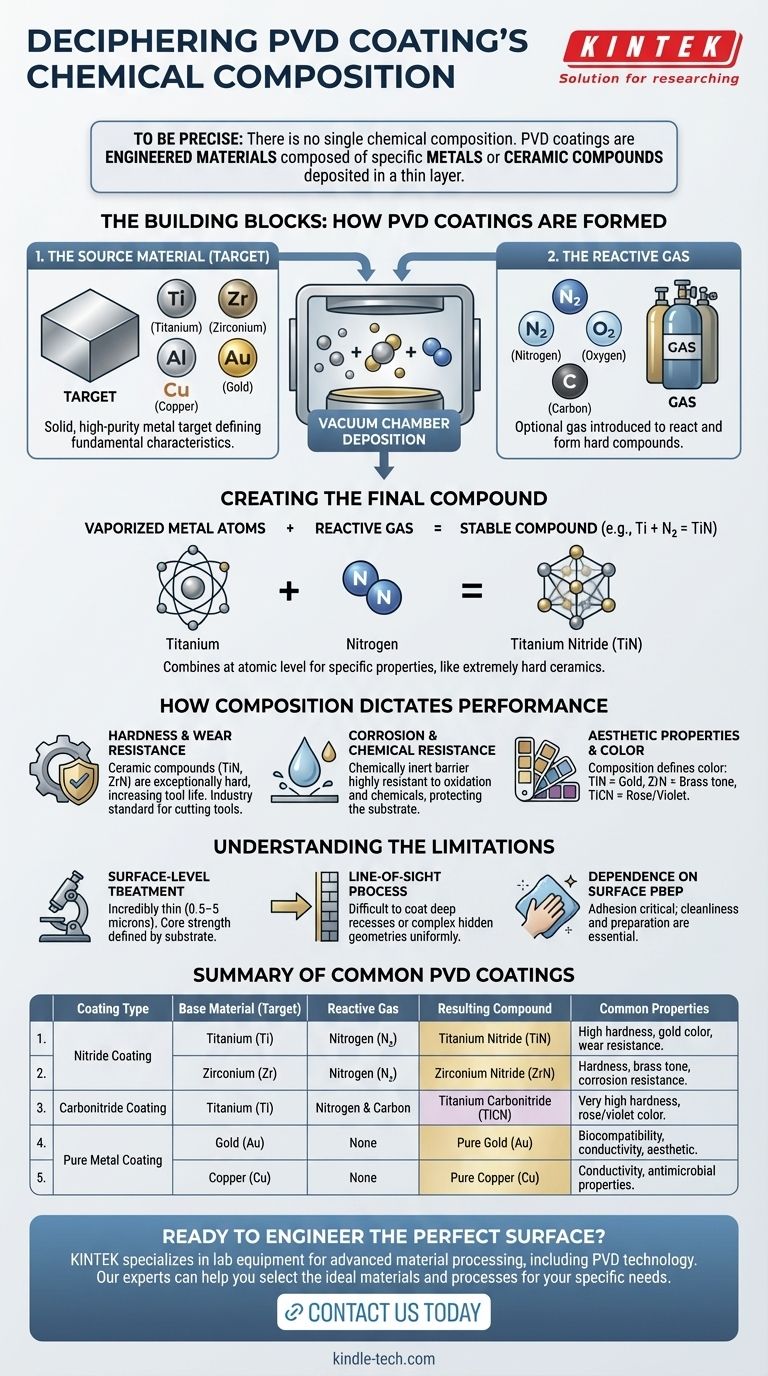
To be precise, there is no single chemical composition for a PVD coating. Instead, PVD coatings are composed of specific metals or ceramic compounds deposited in a thin layer. The most common base materials include titanium, zirconium, aluminum, copper, and stainless steel, which are often combined with reactive gases like nitrogen to form highly durable compounds such as Titanium Nitride (TiN).
The critical takeaway is that a PVD coating's chemical composition is determined by two factors: the solid source material (the "target") vaporized in the vacuum chamber, and the optional reactive gas introduced during the process. This combination allows for the creation of either pure metal films or strong ceramic compounds on a substrate's surface.

The Building Blocks: How PVD Coatings Are Formed
The final composition of a PVD coating is a direct result of the materials chosen for the deposition process. This process deliberately combines elements at an atomic level to achieve specific properties.
The Metallic Foundation (The Target)
The process begins with a solid, high-purity source material known as a target. This target contains the primary metal that will form the basis of the coating.
Common target materials include titanium (Ti), zirconium (Zr), aluminum (Al), copper (Cu), and even precious metals like gold (Au). The choice of target material is the first and most important decision in defining the coating's fundamental characteristics.
The Reactive Element (The Gas)
To create coatings with superior hardness and wear resistance, a reactive gas is often introduced into the vacuum chamber. This gas reacts with the vaporized metal atoms before they settle on the substrate.
The most common reactive gas is nitrogen (N₂), which forms nitrides. Other gases can be used to form oxides or carbides, resulting in a wide range of possible ceramic compounds.
Creating the Final Compound
The magic of PVD happens when the vaporized metal atoms from the target combine with the reactive gas. This forms a new, stable compound that deposits onto the component's surface, one molecule at a time.
For example, a titanium target vaporized in the presence of nitrogen gas does not create a titanium coating; it creates an extremely hard ceramic coating of Titanium Nitride (TiN).
How Composition Dictates Performance
The specific chemical makeup of the coating directly determines its functional and aesthetic properties. Understanding this link is key to selecting the right finish for an application.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
Ceramic compounds like nitrides and carbides are exceptionally hard and durable. This is why coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) are industry standards for cutting tools and high-wear components, dramatically increasing their service life.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
PVD coatings create a chemically inert barrier on the surface of the substrate. This molecularly bonded layer is highly resistant to oxidation, corrosion, and attack from most chemicals, protecting the underlying material.
Aesthetic Properties and Color
The final composition also dictates the coating's color and finish. Titanium Nitride (TiN) produces a characteristic gold color, while other compounds like Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) can create a brass tone, and Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) can range from rose to violet.
Understanding the Limitations
While powerful, PVD is a surface treatment with specific requirements and limitations. Recognizing these trade-offs is essential for successful implementation.
It's a Surface-Level Treatment
PVD coatings are incredibly thin, typically ranging from 0.5 to 5 microns. While the coating is extremely hard, the core strength and properties of the part are still defined by the underlying substrate material.
A Line-of-Sight Process
The PVD process deposits material in a line-of-sight from the source. This means that deep recesses, internal channels, or complex hidden geometries are very difficult to coat uniformly without specialized fixtures and part rotation.
Dependence on Surface Preparation
The quality and adhesion of a PVD coating are critically dependent on the cleanliness and preparation of the substrate. Any surface contamination, from oils to microscopic dust, will compromise the final result.
Matching the Coating to Your Goal
Your choice of PVD composition should be driven entirely by the primary goal for your component.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and tool life: You should specify a ceramic-based coating, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN) or a similar nitride or carbonitride.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance or a specific color: Your choice will be based on a stable compound known for its inertness and aesthetic, such as those based on zirconium or chrome.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility or conductivity: You should specify a pure metallic coating, such as pure titanium or gold, which are frequently used in medical and aerospace electronics.
Ultimately, understanding that PVD coatings are engineered materials, not just simple layers of metal, is the key to unlocking their full potential.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Base Material (Target) | Reactive Gas | Resulting Compound | Common Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitride Coating | Titanium (Ti) | Nitrogen (N₂) | Titanium Nitride (TiN) | High hardness, gold color, wear resistance |
| Nitride Coating | Zirconium (Zr) | Nitrogen (N₂) | Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) | Hardness, brass tone, corrosion resistance |
| Carbonitride Coating | Titanium (Ti) | Nitrogen & Carbon | Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) | Very high hardness, rose/violet color |
| Pure Metal Coating | Gold (Au) | None | Pure Gold (Au) | Biocompatibility, conductivity, aesthetic |
| Pure Metal Coating | Copper (Cu) | None | Pure Copper (Cu) | Conductivity, antimicrobial properties |
Ready to engineer the perfect surface for your components? The right PVD coating composition is critical for achieving hardness, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, or a specific aesthetic. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material processing, including PVD technology. Our experts can help you select the ideal materials and processes to meet your specific laboratory or production needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your project's performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications



















