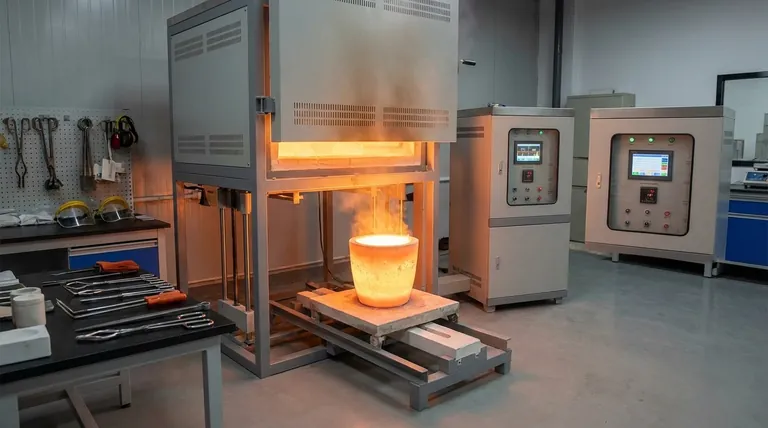
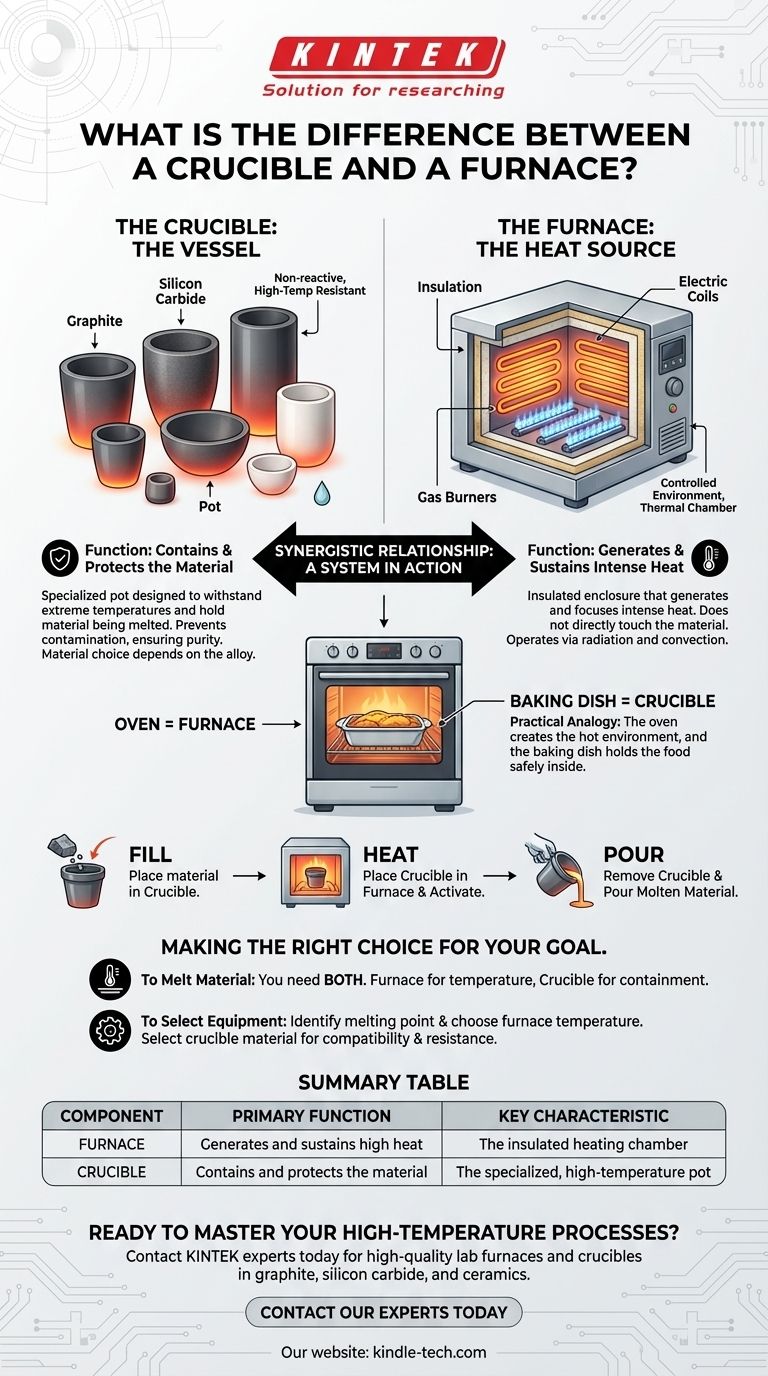
In essence, a crucible is a container, while a furnace is the heating chamber. The crucible is a specialized pot designed to withstand extreme temperatures and hold material that is being melted. The furnace is the insulated enclosure that generates the intense heat required for that melting process.
The fundamental distinction is one of function: a furnace generates the heat, and a crucible contains the material being heated within that furnace. One cannot typically function without the other in a metallurgical or laboratory setting.

Deconstructing the Furnace: The Heat Source
A furnace's sole purpose is to create and sustain a high-temperature environment in a controlled way. It is the engine of the heating operation.
The Primary Function: A Thermal Chamber
The furnace is an insulated structure equipped with a heating element (electric resistance, induction coils, or gas burners). Its job is to generate heat and focus it within its chamber.
The furnace itself does not directly touch the material being melted. Instead, it heats the space and any objects placed inside it.
How a Furnace Operates
The heating element, such as an electric coil, generates immense heat. This thermal energy is transferred to the crucible placed inside the furnace, often through radiation and convection.
The furnace's control system allows the operator to regulate the temperature precisely, ensuring the material inside the crucible melts efficiently without being damaged.
Understanding the Crucible: The Vessel
The crucible is the component that comes into direct, physical contact with the substance you are melting. Its design and material are critical for a successful and clean process.
The Primary Function: Containment and Purity
A crucible acts as a protective, non-reactive pot. Its first job is to safely contain the liquid metal or other substance at temperatures that would destroy a standard container.
Its second job is to prevent contamination. The crucible material is carefully chosen so it does not react with the molten substance, ensuring the final product remains pure.
The Importance of Material Choice
Crucibles are made from specialized refractory materials like graphite, silicon carbide, or various ceramics.
The choice of crucible material depends entirely on the alloy or substance being melted. A material suitable for melting aluminum may be entirely wrong for melting steel, as it could react with the melt or fail under the higher temperature.
The Synergistic Relationship: A System in Action
Thinking of a furnace and a crucible as separate, unrelated items is a common mistake. They are two essential parts of a single system that work in concert.
A Practical Analogy: The Oven and the Baking Dish
The clearest way to understand the relationship is to think of a kitchen oven.
The furnace is the oven—it creates the controlled, hot environment. The crucible is the baking dish—it holds the material (the "food") safely inside the oven so it can be heated properly.
The Process Step-by-Step
A typical melting process involves placing the solid material into a crucible. The crucible is then placed inside the furnace.
The furnace is activated, heating the crucible. The crucible absorbs this heat and transfers it directly to the material inside, causing it to melt. Once molten, the crucible is removed from the furnace to pour the liquid.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is to melt a material: You need both. A furnace to generate the required temperature and a crucible to safely contain your material within that furnace.
- If your primary focus is to select equipment: First, identify the melting point of your substance to determine the required furnace temperature. Then, choose a crucible made of a material that can both withstand that temperature and remain non-reactive with your specific substance.
Understanding this functional partnership between the heat source and the container is the foundation for mastering any high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace | Generates and sustains high heat | The insulated heating chamber |
| Crucible | Contains and protects the material | The specialized, high-temperature pot |
Ready to Master Your High-Temperature Processes?
Understanding the partnership between a furnace and a crucible is the first step. Choosing the right equipment for your specific material and application is the next. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab furnaces and a wide range of crucibles made from materials like graphite, silicon carbide, and ceramics to ensure purity, efficiency, and safety in your laboratory.
Contact our experts today to discuss your needs and we'll help you build the perfect heating system for your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of muffle furnaces? Essential Tools for High-Temperature Processes
- What is the effect of calcination temperature on the properties of nanoparticles? Master the Trade-Off for Optimal Performance
- What are the safety precautions for using a muffle furnace? Essential Tips for Safe Operation
- How long is the calcination process? Optimize Your Process Time for Maximum Efficiency
- Is a muffle furnace used for ash determination? Discover Its Critical Role in Accurate Analysis



















