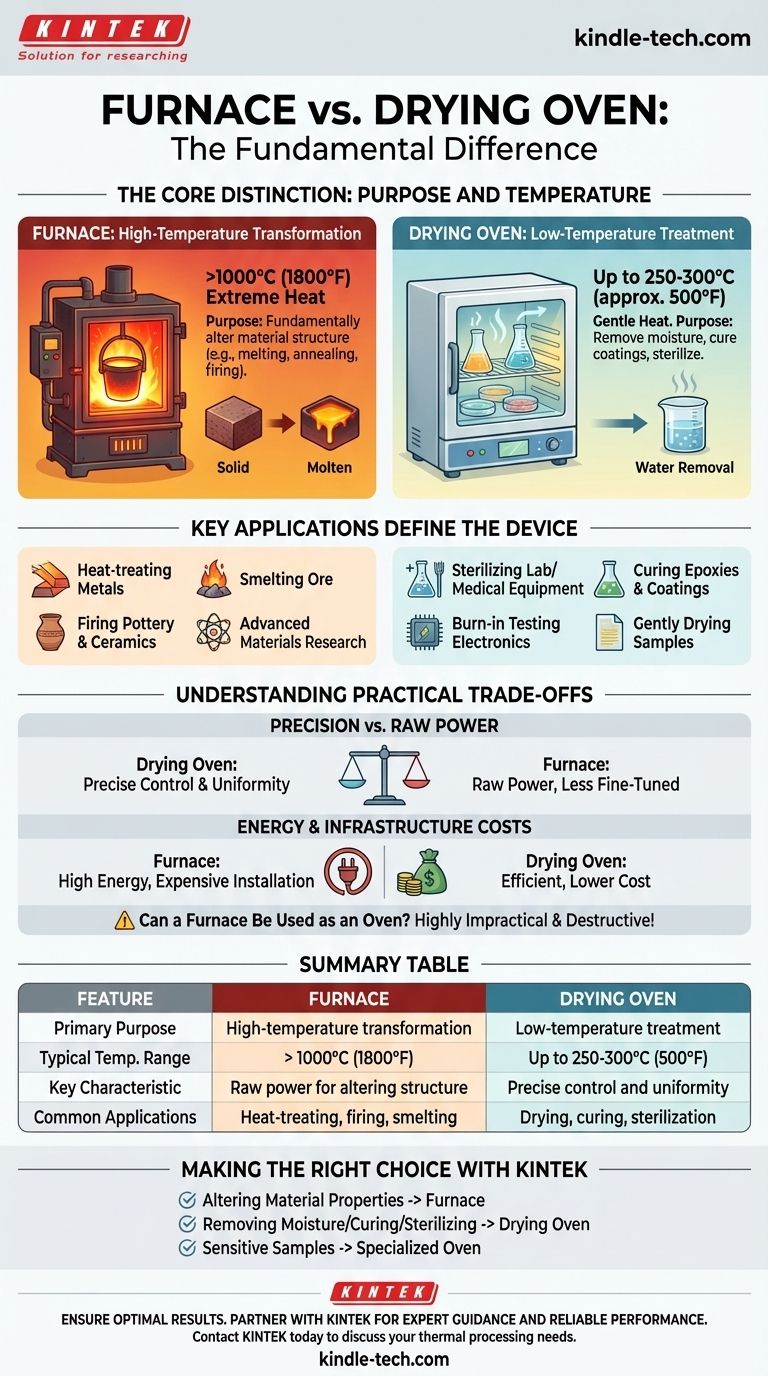
The fundamental difference between a furnace and a drying oven lies in their maximum operating temperature and their intended purpose. A furnace is designed for high-temperature applications that fundamentally alter a material's properties, such as melting metal, while a drying oven uses lower temperatures primarily to remove moisture or cure coatings.
The core distinction is one of transformation versus treatment. A furnace provides the raw thermal energy to transform a material's state or metallurgical structure, whereas an oven provides controlled, gentle heat to treat a material by drying, curing, or sterilizing it.

The Core Distinction: Purpose and Temperature
The most significant factors separating these two devices are their operational temperature range and the processes they are built to perform.
Furnaces: High-Temperature Transformation
A furnace is engineered to reach and sustain extremely high temperatures, often well above 1000°C (1800°F).
Their primary purpose is to induce a fundamental change in a material. This includes processes like smelting, casting, annealing, and firing ceramics, where the material's core structure is intentionally altered.
Drying Ovens: Low-Temperature Treatment
Drying ovens operate at significantly lower temperatures, typically ranging from slightly above ambient up to 250°C or 300°C (approx. 500°F).
The goal of an oven is not to change the base material but to remove volatile components like water or solvents. Common applications include drying laboratory glassware, curing paints, or performing moisture-content analysis.
Key Applications Define the Device
Understanding the typical use cases for each piece of equipment clarifies their distinct roles in industrial and laboratory settings.
Common Furnace Applications
Furnaces are indispensable for heavy industrial and metallurgical work.
You will find them used for heat-treating metals to change their hardness, smelting ore to extract pure metal, firing pottery and ceramics, and in advanced materials science research requiring extreme heat.
Common Drying Oven Applications
Ovens are ubiquitous in labs, manufacturing, and quality control.
Their applications include sterilizing medical or lab equipment, curing epoxies and powder coatings, burn-in testing of electronic components, and gently drying sensitive samples for analysis.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong device can lead to damaged products, inaccurate results, and significant unnecessary costs.
Precision vs. Raw Power
A drying oven is designed for precise temperature control and uniformity across its chamber, which is critical for sensitive processes.
A furnace is built for raw power. While it can hold a set point, its primary design consideration is reaching and maintaining extreme heat, not the fine-tuned control required for delicate curing or drying.
Can a Furnace Be Used as an Oven?
Attempting to use a furnace for a low-temperature drying task is highly impractical and often destructive. The immense heating power makes low-temperature control difficult, and you risk overshooting your target and ruining the sample.
Energy and Infrastructure Costs
Furnaces consume vastly more energy than ovens to achieve their high temperatures. They also require more robust construction with heavy insulation and refractory materials, making them significantly more expensive to purchase and install.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal will determine which piece of equipment is the correct and necessary tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is altering a material's physical properties (melting, annealing, firing): You absolutely require the high-temperature capabilities that only a furnace can provide.
- If your primary focus is removing moisture, curing a coating, or sterilizing components: A drying oven offers the precise temperature control, efficiency, and safety necessary for these tasks.
- If you are working with sensitive biologicals, pharmaceuticals, or electronics: A specialized laboratory or industrial oven is the only appropriate choice to prevent damage.
Ultimately, choosing the right tool begins with clearly defining whether you need to fundamentally transform your material or simply treat it.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Furnace | Drying Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | High-temperature transformation (e.g., melting, annealing) | Low-temperature treatment (e.g., drying, curing, sterilizing) |
| Typical Temp. Range | > 1000°C (1800°F) | Up to 250-300°C (approx. 500°F) |
| Key Characteristic | Raw power for altering material structure | Precise control and uniformity |
| Common Applications | Heat-treating metals, firing ceramics, smelting | Drying glassware, curing coatings, sterilization |
Ensure Optimal Results for Your Application
Choosing the right equipment is critical to your process's success, efficiency, and safety. Whether your work requires the extreme heat of a furnace for material transformation or the precise control of a drying oven for gentle treatment, KINTEK has the solution.
Why partner with KINTEK?
- Expert Guidance: Our specialists will help you select the perfect furnace or oven based on your specific temperature requirements, application, and material.
- Reliable Performance: From robust high-temperature furnaces to precisely controlled drying ovens, our equipment is built for accuracy and durability in demanding laboratory and industrial environments.
- Tailored for Your Lab: KINTEK specializes in providing the essential lab equipment and consumables that laboratories depend on for consistent, high-quality results.
Don't risk damaging samples or wasting resources with the wrong tool. Let our experts help you make the correct choice.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your thermal processing needs and find the ideal solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety, Performance, and Longevity
- What is the specific heat capacity for melting? Clarifying Latent Heat vs. Specific Heat
- How do you control a muffle furnace? Master Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- What temperature does molten steel melt? Understand the Melting Range, Not a Single Point
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a normal furnace? Ensuring Sample Purity with Indirect Heating



















