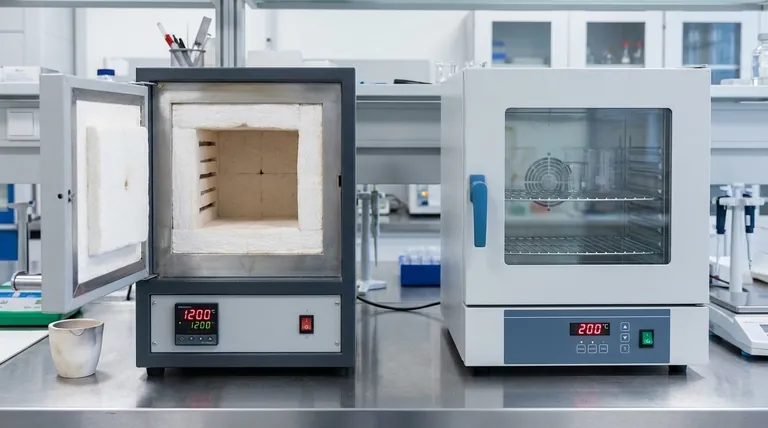
The fundamental difference between a muffle furnace and an oven lies in their maximum temperature and method of heating. A muffle furnace is a specialized piece of laboratory equipment designed for high-temperature applications (typically 900°C to 1400°C) that uses an insulated inner chamber—the "muffle"—to protect samples from direct contact with the heating elements. An oven operates at much lower temperatures (up to 450°C) and typically heats its chamber directly via convection or radiation.
While both are heated enclosures, the core distinction is purpose. An oven is for lower-temperature processes like drying and sterilizing, whereas a muffle furnace is for high-temperature material transformation where sample purity is critical.

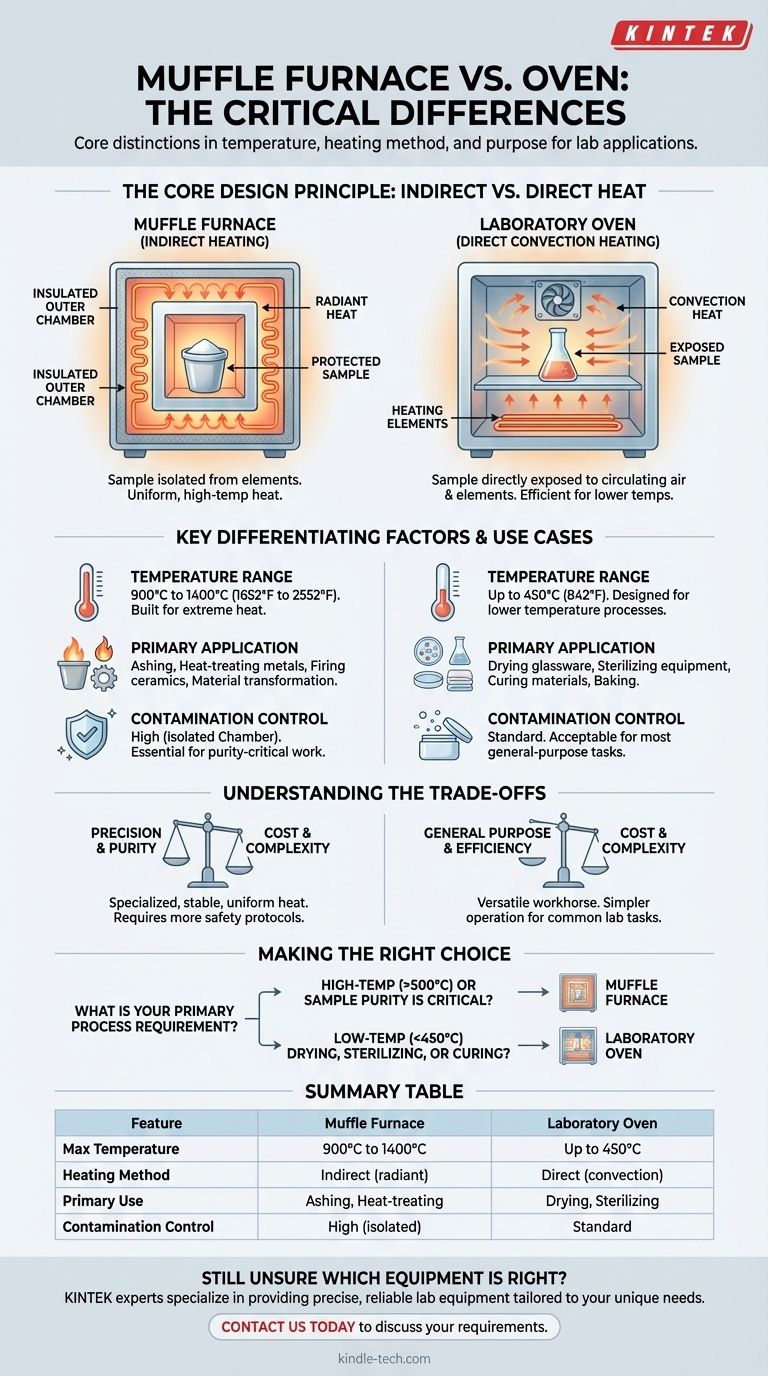
The Core Design Principle: Indirect vs. Direct Heat
The primary engineering difference that dictates the use case for each device is how heat is delivered to the sample. This design choice impacts everything from temperature range to application.
How a Muffle Furnace Works
A muffle furnace is built around the concept of indirect heating. The heating elements heat an outer chamber, which then radiates heat into a separate, isolated inner chamber (the muffle).
This design accomplishes two critical goals. First, it protects the sample from any potential contamination from the byproducts of combustion or degradation of the heating elements. Second, it allows for extremely uniform and precisely controlled high temperatures.
How a Laboratory Oven Works
A laboratory or industrial oven typically uses direct heating. The heating elements are located within the main chamber, often assisted by a fan to circulate hot air.
This method, known as convection heating, is highly efficient for lower-temperature applications like drying glassware, sterilizing equipment, or curing materials. The sample is directly exposed to the heated air and the elements.
Key Differentiating Factors
Beyond the heating method, several operational factors clearly separate these two instruments. Understanding them is key to selecting the right tool for your process.
Temperature Range
This is the most unambiguous difference. A hot air oven is designed for a temperature range from slightly above ambient up to approximately 450°C (842°F).
A muffle furnace, by contrast, is engineered for high-temperature work, with a typical operating range between 900°C and 1400°C (1652°F to 2552°F).
Primary Application & Use Case
The temperature difference directly dictates their use. Ovens are used for drying, curing, baking, and sterilizing.
Muffle furnaces are used for processes that transform materials, such as ashing (burning off organic material), heat-treating metals, firing ceramics, or conducting advanced materials science research.
Contamination Control
If your process cannot tolerate any contamination, a muffle furnace is essential. The muffle acts as a barrier, ensuring the sample is only exposed to radiant heat in a controlled atmosphere.
In an oven, the sample is directly exposed to the circulating air and the heating elements, which is perfectly acceptable for most low-temperature applications but unsuitable for sensitive analytical work.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these devices involves balancing process requirements against equipment capabilities and cost. Neither is inherently better; they are simply designed for different tasks.
Precision vs. General Purpose
Muffle furnaces are specialized instruments built for high-temperature precision and purity. Their design is focused on delivering stable, uniform heat under very specific conditions.
Ovens are general-purpose workhorses of the lab. They are versatile and suitable for a wide array of tasks that do not require extreme temperatures or the isolation of a muffle chamber.
Cost and Complexity
The materials and engineering required to safely achieve and control temperatures above 1000°C make muffle furnaces significantly more complex and expensive than laboratory ovens.
They also require more rigorous safety protocols and user training due to the extreme heat involved in their operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on the specific requirements of your process, with temperature being the primary deciding factor.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature material transformation (above 500°C): You must use a muffle furnace.
- If your primary focus is drying, sterilizing, or curing (below 450°C): A laboratory oven is the correct and more efficient tool.
- If your primary focus is protecting a sample from any contamination from the heat source: The muffle furnace's indirect heating design is non-negotiable.
Ultimately, selecting the correct instrument is a matter of matching its fundamental design and operational range to your scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Laboratory Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | 900°C to 1400°C | Up to 450°C |
| Heating Method | Indirect (radiant) | Direct (convection) |
| Primary Use | Ashing, heat-treating, material transformation | Drying, sterilizing, curing |
| Contamination Control | High (isolated chamber) | Standard |
Still unsure which equipment is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in providing precise, reliable lab equipment tailored to your unique needs. Whether you require the high-temperature purity of a muffle furnace or the versatile efficiency of a laboratory oven, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to enhance your lab's productivity and accuracy.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let us help you make the right choice. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is metal purity measured? Understand Karats, Fineness & Percentage for Gold & Silver
- What are the safety precautions for muffle furnace? A Complete Guide to Safe High-Temperature Operation
- What is the precaution of furnace? Essential Safety Steps to Protect Operators and Equipment
- How do you test a metal to determine its quality? Verify Mechanical & Chemical Properties for Your Application
- How do you use the muffle furnace? Master Safe and Precise High-Temperature Processing



















