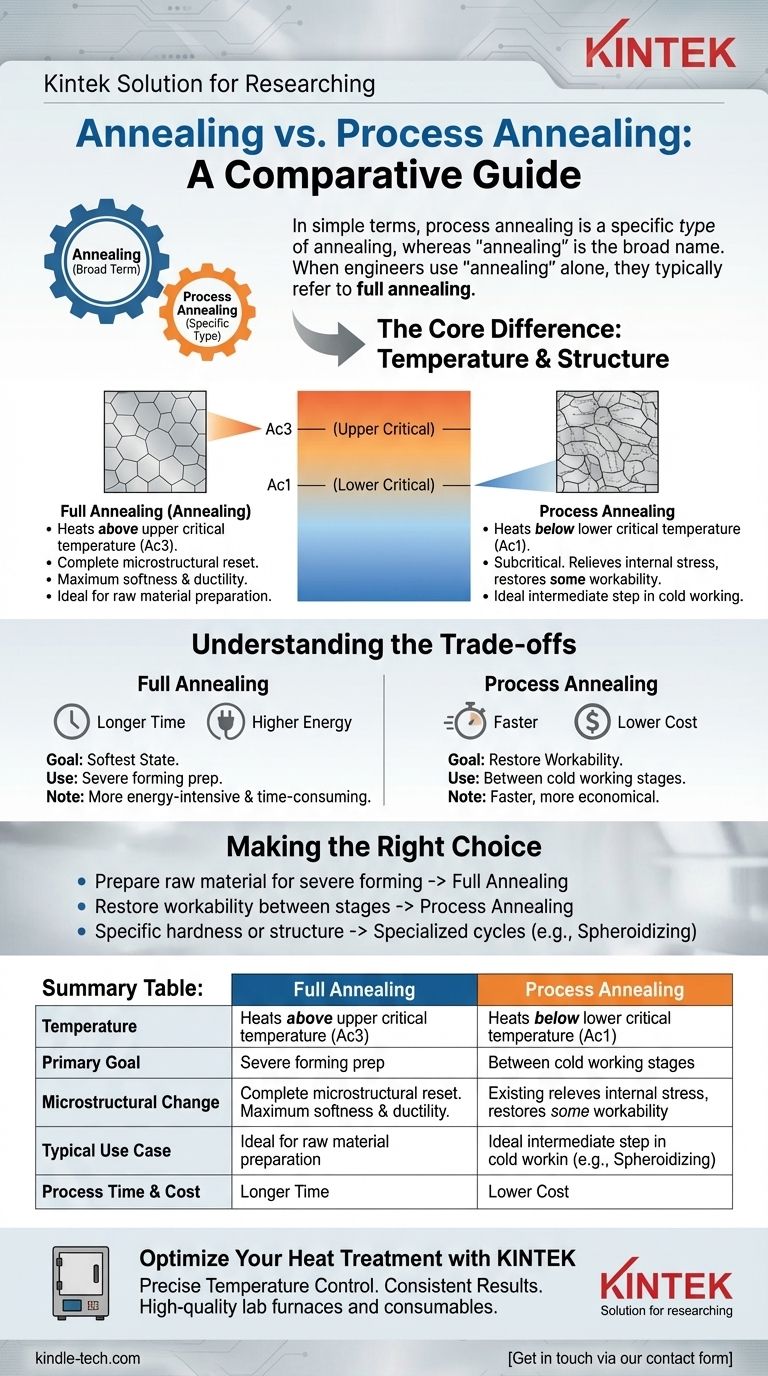
In simple terms, process annealing is a specific type of annealing, whereas "annealing" is the broad name for a family of heat treatment processes. When engineers use the term "annealing" without any other qualifier, they are typically referring to full annealing, which involves higher temperatures and creates a more profound change in the metal's structure than process annealing does.
The core difference comes down to the target temperature relative to the metal's critical transformation points. Full annealing heats the metal above its critical temperature to completely reset its internal structure, while process annealing heats it below that point just enough to relieve stress and restore some workability.

The Fundamental Principle: What is Annealing?
The Goal: Relieving Stress and Increasing Ductility
Annealing is a heat treatment process that alters the microstructure of a material. Its primary purpose is to increase ductility (the ability to be stretched or drawn) and reduce hardness.
This makes the material easier to work with, improving its formability and machinability for subsequent manufacturing steps.
The "Why": Recrystallization
The process involves three stages: heating the metal to a specific target temperature, holding it there for a period, and then slowly cooling it.
This controlled cycle allows the internal crystal structure, which may have been stressed or deformed by previous work, to repair itself and reform in a more orderly, low-stress state.
The Critical Difference: Temperature Defines the Process
The key distinction between different types of annealing lies in the peak temperature used during the heating stage. This temperature is always determined relative to a material's lower (Ac1) and upper (Ac3) critical temperatures, which mark the points where its internal crystal structure begins to transform.
"Annealing" as Full Annealing
When not otherwise specified, "annealing" implies full annealing. This is a high-temperature process that heats the steel to above its upper critical temperature (Ac3).
Heating above this point completely transforms the crystalline grain structure into a new, uniform state. The slow cooling that follows produces a material with maximum softness and ductility.
Process Annealing: The Subcritical Approach
Process annealing is a form of subcritical annealing. This means the material is heated to a temperature below the lower critical temperature (Ac1).
Because it never crosses that critical transformation threshold, process annealing does not fully change the grain structure. Instead, it simply relieves the internal stresses built up during cold working, restoring a significant amount of ductility without making the material fully soft.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between full annealing and process annealing is a practical decision based on manufacturing needs, cost, and time.
When to Use Full Annealing
Full annealing is used when the goal is to achieve the softest possible state. It is often performed on raw material before any significant forming operations begin.
However, because it requires higher temperatures and often longer cooling cycles, it is more energy-intensive and time-consuming than process annealing.
The Role of Process Annealing
Process annealing is most valuable as an intermediate step in a multi-stage manufacturing process, such as wire drawing or sheet metal rolling.
After a certain amount of cold work, the material becomes hard and brittle (a state known as work-hardening). Process annealing quickly restores enough ductility to allow for further work without risking fracture. It is faster and more economical than a full anneal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment is essential for manufacturing efficiency and final product quality. Your decision should be guided by the material's current state and the next step in its journey.
- If your primary focus is to prepare a raw material for severe forming: Full annealing will provide the maximum softness and ductility required.
- If your primary focus is to restore workability between cold working stages: Process annealing is the faster, more cost-effective choice to relieve stress without a full microstructural reset.
- If your primary focus is achieving a very specific hardness or grain structure: You must look beyond these two options to more specialized cycles like spheroidizing or isothermal annealing.
Ultimately, understanding the precise relationship between temperature and crystal structure is the key to mastering your material's properties.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Full Annealing | Process Annealing |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Heated above upper critical temperature (Ac3) | Heated below lower critical temperature (Ac1) |
| Primary Goal | Achieve maximum softness and ductility | Relieve internal stress, restore workability |
| Microstructural Change | Complete grain structure transformation | No full transformation; stress relief only |
| Typical Use Case | Initial preparation of raw material for severe forming | Intermediate step during multi-stage cold working |
| Process Time & Cost | Longer cycle, higher energy consumption | Faster, more economical |
Optimize Your Heat Treatment Processes with KINTEK
Choosing the right annealing process is critical for your material's performance and your manufacturing efficiency. Whether you require the full softness achieved by full annealing or the rapid stress relief of process annealing, having the right laboratory equipment is essential for precise temperature control and consistent results.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and consumables designed to meet the exacting demands of heat treatment applications. Our equipment ensures the accuracy and repeatability you need to master your material's properties.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs, and let our experts help you select the perfect solution for your laboratory. Get in touch via our contact form to learn more.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a sintering furnace for powder metallurgy? Transform Powder into High-Strength Parts
- Why does evaporation need vacuum pressure? Gain Precise Control for Your Lab Processes
- What is full brazing process? Achieve Strong, Permanent Metal Joints with Precision
- What role do dynamic vacuum heat treatment furnaces play in enhancing Inconel 718? Unlock Superior Alloy Performance
- What is the function of a high-temperature heat treatment furnace in graphite and copper composite pre-treatment?
- What is an overheated brazed joint indicated by? Signs of a Failed Brazing Process
- Why is a vacuum drying oven required for epoxy curing agents? Prevent Bubbles & Ensure Chemical Purity
- What role do electric vacuum laboratory furnaces play in LBE corrosion tests? Ensure Precision Reactor Simulations



















