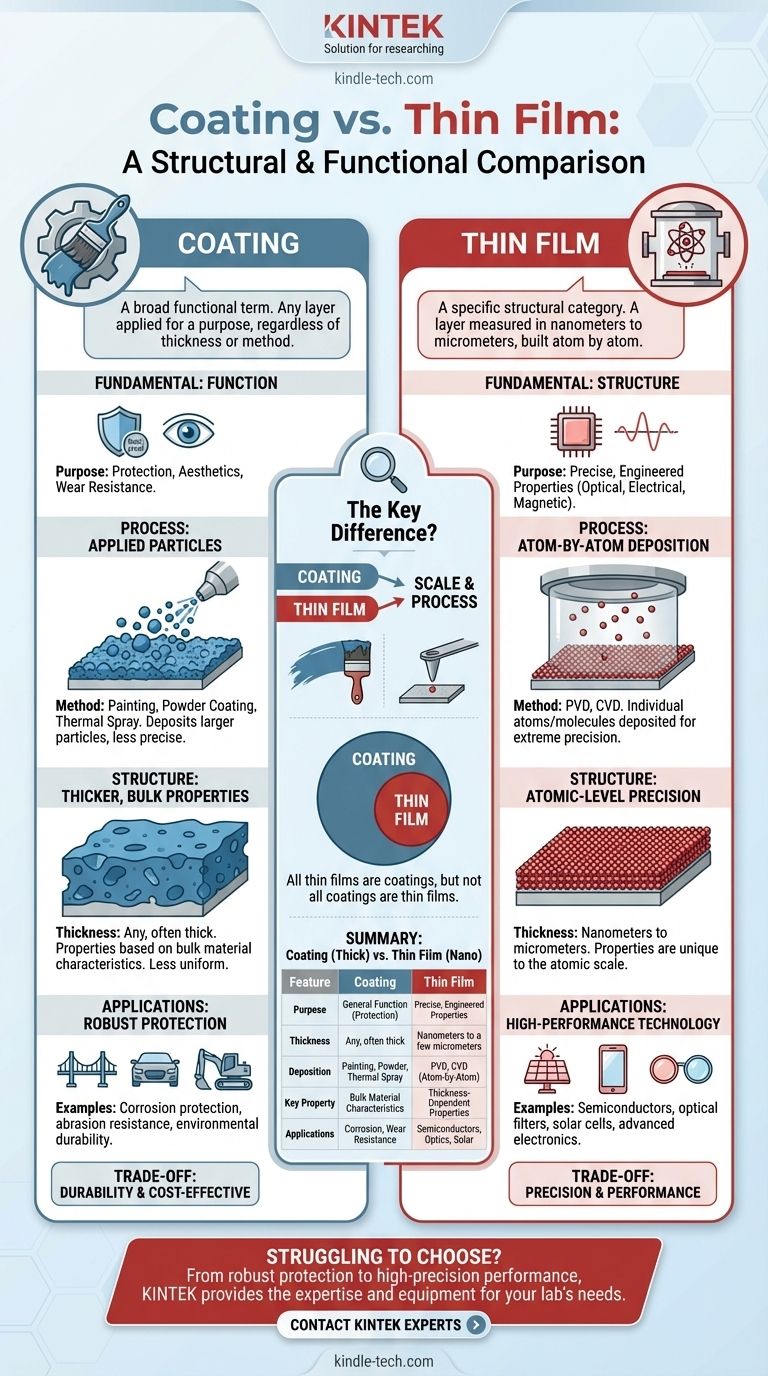
At its core, the difference between a coating and a thin film comes down to scale and process. A thin film is a highly specific type of coating defined by a thickness measured in nanometers up to a few micrometers, built by depositing individual atoms or molecules. "Coating" is a much broader functional term for any layer applied to a surface, regardless of its thickness or how it was applied.
While all thin films can be considered coatings, not all coatings are thin films. The distinction lies in whether the layer's properties are determined by its bulk material characteristics (a general coating) or by its atomic-scale thickness and structure (a thin film).
The Fundamental Distinction: Function vs. Structure
The confusion between these terms arises because one describes a general purpose, while the other describes a specific physical form.
"Coating": A Broad Functional Term
A coating is any material applied to the surface of an object, known as a substrate. Its purpose is to impart a new or improved property.
This is an umbrella category. A coat of paint on a house is a coating. A layer of chrome on a car bumper is a coating. The goal is function—protection, aesthetics, or wear resistance.
"Thin Film": A Precise Structural Category
A thin film is a layer of material whose thickness ranges from fractions of a nanometer to several micrometers. It is a specific structural class of coating.
The defining characteristic is that the film's thickness is so minimal that its properties (optical, electrical, magnetic) are fundamentally different from the bulk material.
The Critical Differentiator: Process and Properties
The "how" and "why" behind their creation reveals the most important differences. It's a matter of building with atoms versus applying particles.
Deposition Method: Atoms vs. Particles
Thin films are created through processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where individual atoms or molecules are deposited onto a substrate one by one. This allows for extreme precision and purity.
Most other coatings are applied using methods like painting, powder coating, or thermal spray, which involve depositing larger particles of the material. This process is less precise at the microscopic level.
Resulting Structure and Thickness
The atomic-level deposition of thin films allows for unparalleled control over thickness, density, and uniformity. This precision is what enables their unique, engineered properties.
Thicker coatings are inherently less uniform at the micro-level. Their properties are based on the bulk characteristics of the material being applied, not the precise thickness of the layer itself.
Impact on Performance
The unique, engineered structure of thin films gives them properties that thicker coatings cannot achieve. They are used to precisely manipulate light (anti-reflection), control the flow of electricity (semiconductors), or create specific magnetic behaviors.
Thicker coatings are primarily used for robust, bulk protection against corrosion, abrasion, and environmental exposure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a thin film and a conventional thick coating is a decision driven by performance requirements and cost.
Why Choose a Thin Film? Precision and Performance
Thin films are essential for high-technology applications. Their unique optical and electrical properties are indispensable for products like solar panels, computer chips, and advanced lenses.
This precision comes at a cost. Thin film deposition requires vacuum chambers and sophisticated equipment, making it a more complex and expensive process.
When Is a Thicker Coating Better? Durability and Cost
For robust, large-scale protection, a thicker coating is almost always the correct choice. It provides a durable physical barrier against mechanical wear and corrosion.
These methods are generally faster, less expensive, and better suited for covering large or irregularly shaped objects where atomic-level precision is unnecessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Using the right term demonstrates a clear understanding of the technology and its purpose. Your choice depends on what aspect of the layer you are emphasizing.
- If your primary focus is general function: Use the term "coating." For example, "We need a protective coating to prevent rust."
- If your primary focus is the precise, sub-micron structure and its unique properties: Use the term "thin film." For example, "The device uses a multi-layer thin film to filter specific wavelengths of light."
- If your primary focus is manipulating light: Use "optical coating," with the understanding that this is almost always achieved using thin-film technology.
Ultimately, distinguishing between a coating and a thin film is about moving from a general description of purpose to a precise definition of structure and performance.

Summary Table:
| Feature | Coating | Thin Film |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | General function (protection, aesthetics) | Precise, engineered properties |
| Typical Thickness | Any thickness, often thick | Nanometers to a few micrometers |
| Deposition Method | Painting, powder coating, thermal spray | PVD, CVD (atom-by-atom deposition) |
| Key Property | Bulk material characteristics | Thickness-dependent properties |
| Common Applications | Corrosion protection, wear resistance | Semiconductors, optical filters, solar cells |
Struggling to choose the right surface solution for your lab's specific needs? Whether your project requires the robust protection of a standard coating or the high-precision performance of a thin film, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to help. We specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to achieve your desired results. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance

















