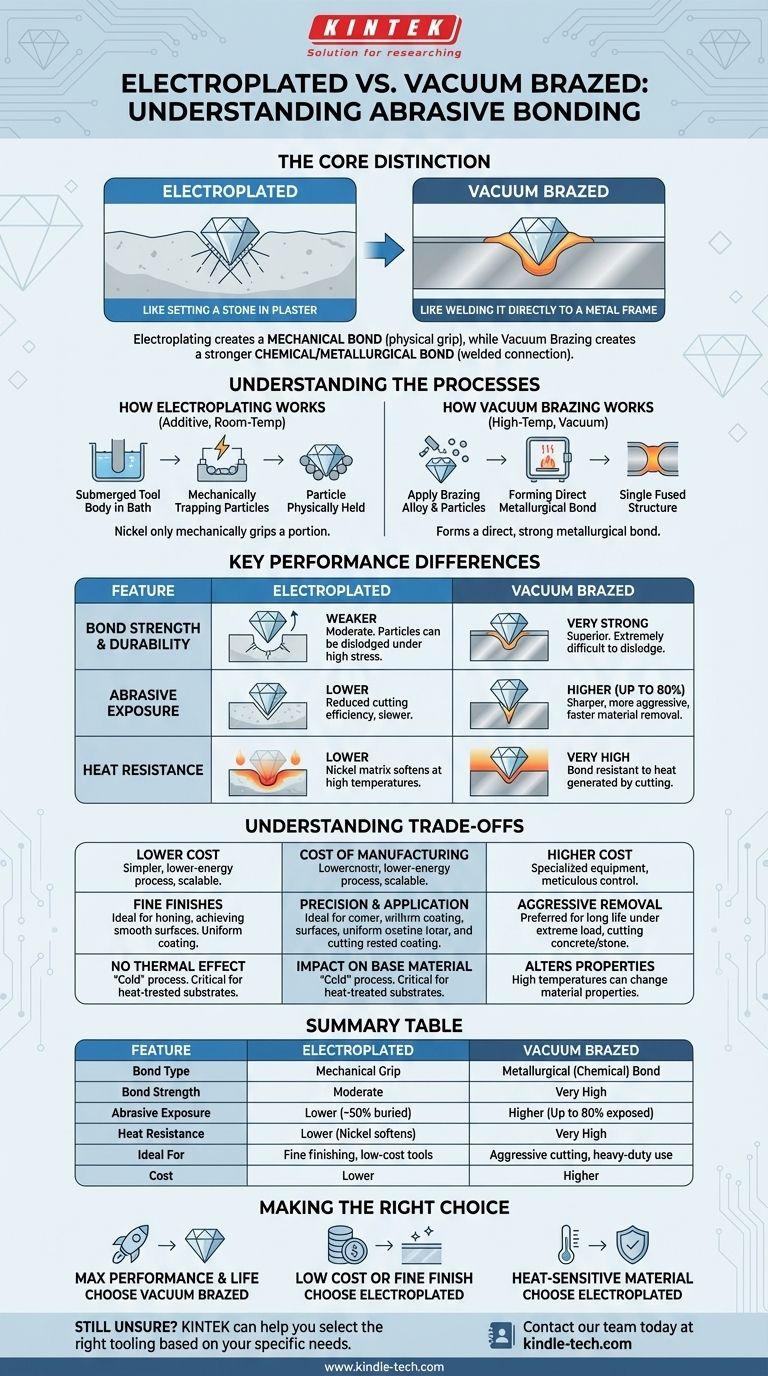
At a fundamental level, the difference between an electroplated and a vacuum brazed product lies in how an abrasive particle (like a diamond) is attached to a base material. Electroplating creates a mechanical bond, where a layer of metal is grown around the particle to physically hold it in place. Vacuum brazing creates a much stronger chemical and metallurgical bond, essentially welding the particle to the surface with a specialized alloy in a high-temperature, controlled environment.
The core distinction to understand is this: Electroplating is like setting a stone in plaster, while vacuum brazing is like welding it directly to a metal frame. This difference in bonding directly impacts the tool's durability, performance, and cost.

Understanding the Core Processes
To grasp the implications, it's essential to visualize how each method works. They are fundamentally different in their approach to adhesion.
How Electroplating Works
Electroplating is an additive, room-temperature process. A base material (the tool body) is submerged in a chemical bath, typically containing nickel salts.
An electric current is applied, causing the nickel to deposit onto the tool's surface. Abrasive particles are introduced and become physically trapped as the nickel layer builds up around them, holding them in place.
Crucially, the nickel only mechanically grips a portion of the abrasive particle. There is no chemical bond between the particle and the nickel matrix.
How Vacuum Brazing Works
Vacuum brazing is a high-temperature joining process performed inside a vacuum furnace, which prevents oxidation and ensures a pure, strong bond.
First, a brazing filler alloy is applied to the tool body along with the abrasive particles. The entire assembly is then heated in the vacuum furnace.
The alloy melts, flowing around the base of each abrasive particle through capillary action. It forms a direct, metallurgical bond between the particle and the tool body, creating a single, fused structure upon cooling.
Key Performance Differences
The distinction between a mechanical grip and a metallurgical weld has significant consequences for how a tool performs in the real world.
Bond Strength and Durability
Vacuum brazing provides a vastly superior bond. The chemical connection is incredibly strong, making it extremely difficult to dislodge an abrasive particle during heavy use.
Electroplated bonds are much weaker. Under high stress or impact, abrasive particles can be pulled out from the softer nickel matrix, leading to premature tool failure. This is often referred to as "pull-out."
Abrasive Exposure and Cutting Efficiency
Vacuum brazing allows for a much higher exposure of the abrasive particle—often up to 80% of the crystal is exposed. This creates a sharper, more aggressive cutting tool that removes material faster.
In electroplating, a significant portion of the particle (often 50% or more) must be buried within the nickel layer to secure it. This reduces the effective cutting height, resulting in a less aggressive and slower-cutting tool.
Heat Resistance
The brazing process occurs at very high temperatures, so the resulting bond is extremely resistant to heat generated during aggressive cutting or grinding.
The nickel matrix in electroplated tools can soften at high temperatures. This weakening of the bond is a common cause of particle loss and tool failure in demanding applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither process is universally superior; the choice depends entirely on the application's demands and budget constraints.
Cost of Manufacturing
Electroplating is significantly less expensive. It is a simpler, lower-energy process that can be done at a larger scale with less complex equipment.
Vacuum brazing requires specialized, expensive vacuum furnaces and more meticulous process control, making it a higher-cost manufacturing method.
Precision and Application Focus
Electroplating excels in applications requiring very fine abrasive grits for honing or achieving a smooth surface finish. The process allows for a very dense and uniform coating of fine particles.
Vacuum brazing is the preferred method for tools designed for aggressive material removal, long life, and performance under extreme load, such as in cutting concrete, stone, or exotic alloys.
Impact on the Base Material
Because electroplating is a "cold" process, it has no thermal effect on the base material. This is critical when working with substrates that have been heat-treated or tempered.
The high temperatures required for vacuum brazing can alter the properties of the base material. This must be accounted for in the engineering and material selection phase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, your decision should be guided by the performance you require and the budget you have.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and long tool life: Vacuum brazing is the clear choice for its superior bond strength, heat resistance, and aggressive cutting action.
- If your primary focus is low initial cost or fine surface finishing: Electroplating offers a perfectly suitable solution at a much more accessible price point.
- If you are working with a heat-sensitive base material: Electroplating is the safer option, as it avoids the high temperatures that could compromise the material's integrity.
Choosing the right manufacturing method is about aligning the tool's capabilities with the demands of the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electroplated | Vacuum Brazed |
|---|---|---|
| Bond Type | Mechanical Grip | Metallurgical (Chemical) Bond |
| Bond Strength | Moderate | Very High |
| Abrasive Exposure | Lower (~50% buried) | Higher (Up to 80% exposed) |
| Heat Resistance | Lower (Nickel softens) | Very High |
| Ideal For | Fine finishing, low-cost tools | Aggressive cutting, heavy-duty use |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Still Unsure Which Method is Best for Your Application?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, serving a wide range of laboratory and industrial needs. Our experts can help you select the right tooling based on your specific material, performance requirements, and budget.
Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover how the right bonding technology can enhance your tool's efficiency, durability, and overall performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- What is oxidation in brazing? How to prevent it for strong, durable joints
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds



















