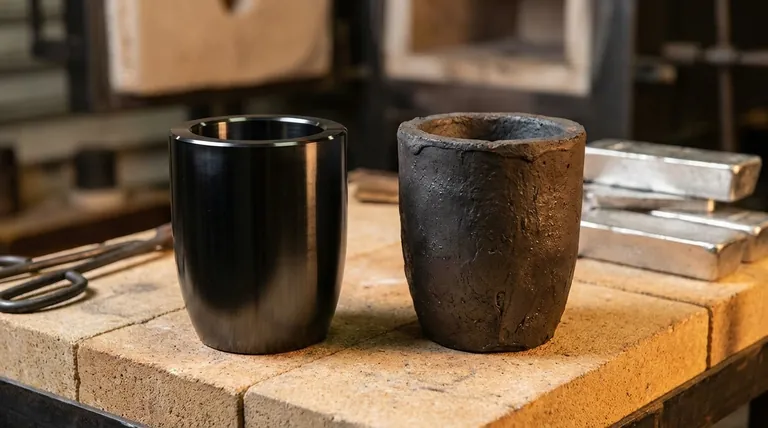
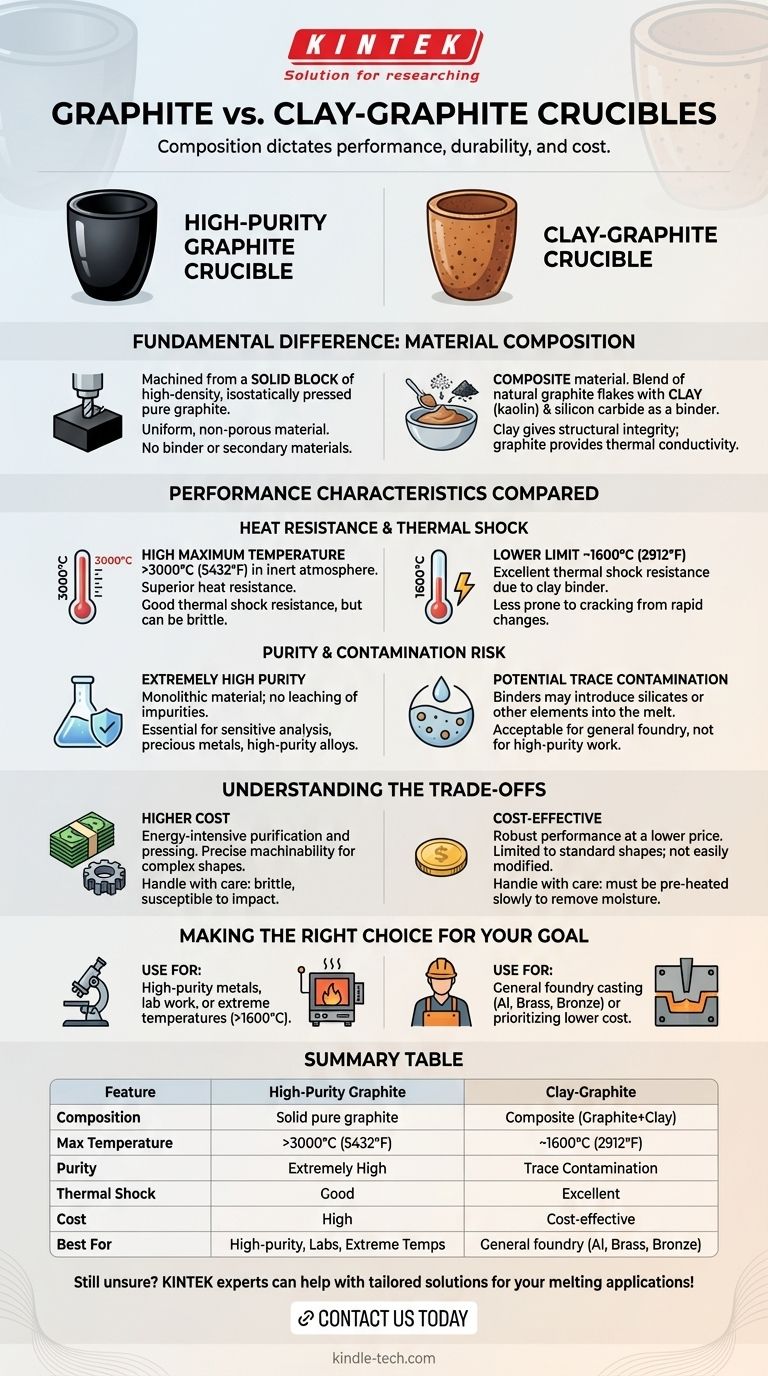
At its core, the difference between a graphite crucible and a clay crucible lies in their composition, which dictates their performance, durability, and cost. A high-purity graphite crucible is made from a solid block of pure graphite, offering superior heat resistance and purity. A clay-graphite crucible is a composite material, blending clay with graphite flakes to create a durable, cost-effective alternative for general use.
The decision is a direct trade-off between performance and price. High-purity graphite delivers maximum heat resistance and prevents melt contamination at a premium cost, while clay-graphite provides excellent, all-around performance for most common foundry tasks at a much lower price point.

The Fundamental Difference: Material Composition
Understanding what each crucible is made of is the key to understanding how it will perform. They are not interchangeable materials; they are engineered for different purposes.
High-Purity Graphite Crucibles
These crucibles are machined from a large, solid block of high-density, isostatically pressed graphite. This process creates a uniform, non-porous material with extremely high purity.
There is no binder or secondary material. The entire object is simply graphite, giving it a characteristic glossy black appearance and a smooth finish.
Clay-Graphite Crucibles
These are composite crucibles. They are manufactured by mixing natural graphite flakes with other materials, primarily clay (like kaolin) and silicon carbide. This mixture is then formed into a crucible shape and fired.
The clay acts as a binder, giving the crucible structural integrity and resistance to physical damage. The graphite provides thermal conductivity, allowing heat to transfer efficiently to the metal inside.
Performance Characteristics Compared
The material differences lead to significant variations in how each crucible behaves under the stress of high temperatures and molten metal.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Shock
High-purity graphite has a much higher maximum service temperature, capable of withstanding over 3000°C (5432°F) in an inert atmosphere. This makes it suitable for melting materials with extremely high melting points.
Clay-graphite crucibles typically have a lower limit, often around 1600°C (2912°F). However, the clay binder gives them excellent thermal shock resistance, making them less likely to crack from rapid temperature changes, a common risk in many foundry environments.
Purity and Contamination Risk
This is a critical distinction for many users. Because high-purity graphite is a monolithic material, it will not leach impurities into the molten metal. This is essential for laboratory analysis, dental applications, or melting precious metals and high-purity alloys where contamination would ruin the final product.
Clay-graphite crucibles, by their nature, contain binders and other elements. It is possible for trace amounts of silicates or other materials from the clay to enter the melt, which is unacceptable for high-purity applications but perfectly fine for most hobbyist or general industrial casting.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a crucible is an exercise in balancing your specific needs against cost and operational realities.
The Cost Factor
High-purity graphite is significantly more expensive. The process of purifying and isostatically pressing graphite is energy-intensive and complex, which is reflected in the final price.
Clay-graphite is the workhorse of the foundry world precisely because it is cost-effective. It offers robust performance for a fraction of the cost, making it the default choice for melting common metals like aluminum, brass, and bronze.
Machinability and Shape
The reference to machinability is important. Solid graphite blocks can be machined on a lathe or mill to precise dimensions and complex shapes. This is vital for custom scientific apparatus or specialized industrial parts.
Clay-graphite crucibles are typically formed into a limited range of standard foundry shapes and sizes. They cannot be easily modified or machined after they are fired.
Durability and Handling
While more resistant to thermal shock, clay-graphite crucibles must be handled carefully. They can absorb moisture from the air, which requires a slow, careful pre-heating process on first use to drive it out and prevent cracking.
High-purity graphite crucibles do not absorb moisture in the same way, but they can be more brittle and susceptible to chipping or cracking from mechanical impact (i.e., dropping them or being too aggressive with tongs).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your crucible based on the demands of your specific task, not just on a single feature.
- If your primary focus is high-purity metals or lab work: You must use a high-purity graphite crucible to prevent contamination of your melt.
- If your primary focus is general foundry casting (aluminum, brass, copper): A clay-graphite crucible provides the best balance of performance, durability, and cost.
- If your primary focus is melting materials above 1600°C (2912°F): You will require a high-purity graphite crucible for its superior heat tolerance.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial cost: A clay-graphite crucible is the most budget-friendly and effective starting point.
Matching the tool to the task ensures a predictable, successful outcome and the best use of your resources.
Summary Table:
| Feature | High-Purity Graphite Crucible | Clay-Graphite Crucible |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Solid block of pure graphite | Composite of graphite flakes & clay binder |
| Max Temperature | >3000°C (5432°F) | ~1600°C (2912°F) |
| Purity | Extremely high, no contamination risk | Potential for trace contamination |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | High | Cost-effective |
| Best For | High-purity metals, labs, extreme temps | General foundry work (Al, Brass, Bronze) |
Still unsure which crucible is right for your specific lab needs? The experts at KINTEK can help! We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for your melting applications. Whether you require high-purity graphite for sensitive research or durable clay-graphite for general use, we have the expertise to guide you to the perfect choice. Contact us today via our contact form to discuss your requirements and ensure optimal performance for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Carbon Graphite Boat -Laboratory Tube Furnace with Cover
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- Why use an alumina crucible in a stainless steel autoclave? Ensure Purity in Liquid Lead and LBE Exposure Experiments
- Why are high-alumina crucibles selected for Cs-zeolite heat treatment? Ensure Sample Purity at 1100 °C



















