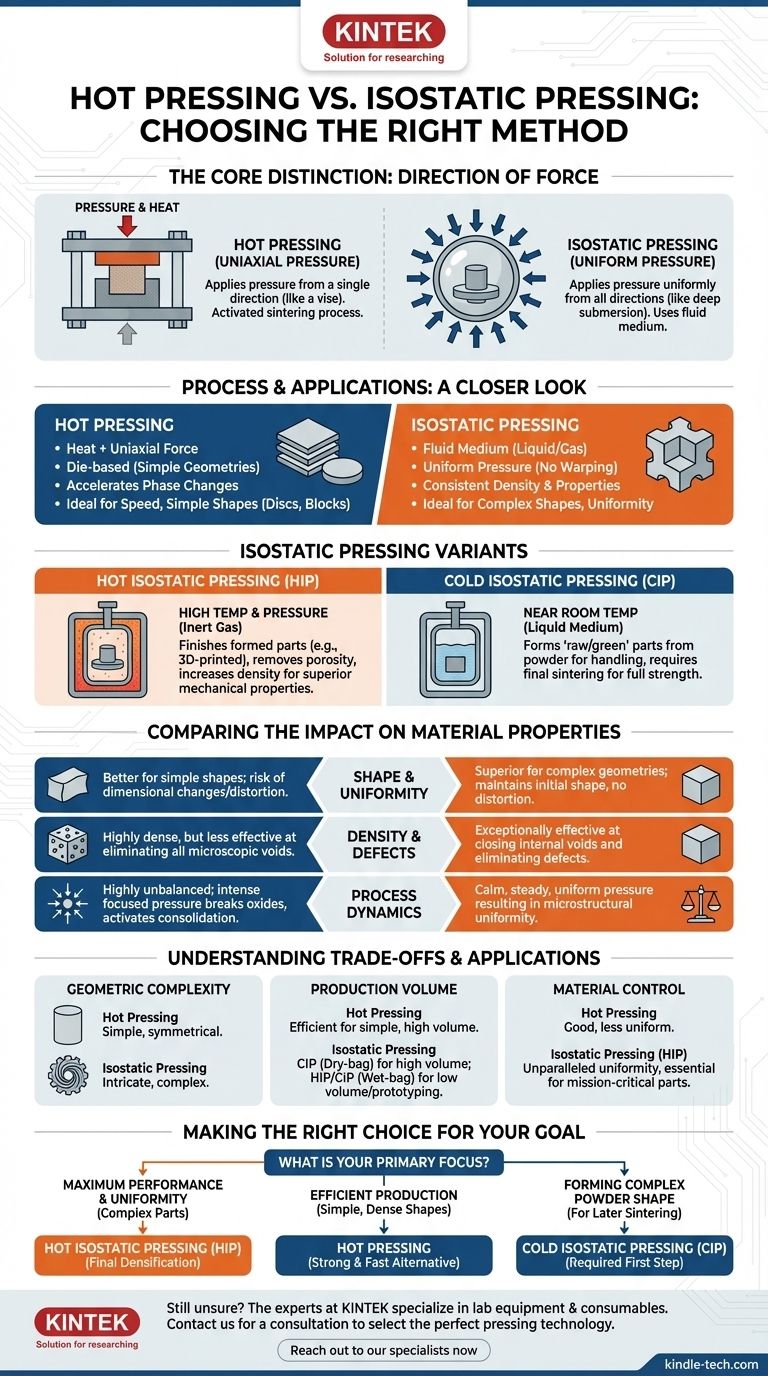
The fundamental difference between hot pressing and isostatic pressing lies in the direction of the applied force. Hot pressing applies pressure from a single direction (uniaxially), much like a vise. In contrast, isostatic pressing applies uniform pressure from all directions simultaneously, as if the object were submerged deep in the ocean.
The choice between these methods is a choice between targeted, directional force and uniform, all-encompassing force. Hot pressing is ideal for simpler geometries where speed is a factor, while isostatic pressing excels at creating highly uniform components with complex shapes.

The Core Distinction: How Pressure is Applied
Understanding how force is delivered to the material is the key to differentiating these two powerful manufacturing processes. The method of pressure application directly influences the final properties and geometry of the component.
Hot Pressing: Uniaxial Pressure
Hot pressing combines heat and one-directional pressure at the same time, typically using a die. Think of it as a highly controlled, heated stamping process.
This simultaneous application of heat and force makes it an "activated sintering process." It significantly accelerates phase changes and the formation of alloys within the powder mixture.
Isostatic Pressing: Uniform Pressure
Isostatic pressing uses a fluid—either a liquid or a gas—to transmit pressure evenly over the entire surface of the part. This ensures there are no directional forces that could warp or distort the component.
This method is defined by its uniformity, resulting in consistent density and mechanical properties throughout the material.
A Closer Look at Isostatic Pressing Methods
"Isostatic pressing" is a category that includes two distinct processes based on the application of heat.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is performed at very high temperatures and pressures. It uses a high-pressure inert gas, such as argon, to consolidate materials.
HIP is a finishing step used to remove internal porosity and increase the density of parts that have already been formed, such as metal castings or 3D-printed components. This results in superior mechanical properties and material uniformity.
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP)
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) applies pressure at or near room temperature using a liquid medium like water or oil.
Its purpose is not to create a final, fully dense part. Instead, CIP is used to form a "raw" or "green" part from a powder. This part has enough strength to be handled and machined before it undergoes a separate, final sintering process to achieve its full strength.
Comparing the Impact on Material Properties
The difference between uniaxial and isostatic pressure has significant consequences for the final product.
Shape and Uniformity
HIP is superior for maintaining the initial shape of a component, especially for complex geometries. The uniform pressure prevents distortion.
Hot pressing, with its one-directional force, is better suited for simpler shapes like discs or blocks and can cause dimensional changes that must be accounted for.
Density and Internal Defects
Both processes produce highly dense materials. However, HIP is exceptionally effective at closing internal voids and eliminating microscopic defects.
This leads to materials with highly consistent and predictable mechanical properties, which is critical for high-performance applications like aerospace components.
Process Dynamics
The sintering process during hot pressing is described as a highly unbalanced one. The intense, focused pressure is effective at breaking down surface oxides on powder particles, activating the consolidation process.
This can be advantageous for certain materials but results in less microstructural uniformity compared to the calm, steady pressure of HIP.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Applications
Choosing between these methods requires a clear understanding of your project's goals, from geometry to production volume.
Geometric Complexity
For parts with intricate or complex shapes, isostatic pressing is the clear choice. The uniform pressure conforms perfectly to any surface, ensuring even densification without damaging delicate features. Hot pressing is limited to simpler, often symmetrical, geometries.
Production Volume
Hot pressing can be an efficient method for producing simple shapes like plates or rods. For isostatic pressing, dry-bag CIP can be automated for high-volume production of parts like spark plug insulators, while wet-bag CIP is better suited for prototyping and research.
Material Property Control
HIP provides unparalleled control over the final microstructure of a material. It minimizes segregation in alloys and delivers the most uniform mechanical properties possible, making it essential for mission-critical parts. While effective, hot pressing does not achieve the same level of uniformity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the best process depends entirely on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and uniformity for complex parts: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is the correct choice for final densification.
- If your primary focus is efficiently producing simple, dense shapes: Hot Pressing is a strong and often faster alternative.
- If your primary focus is forming a complex powder shape for later sintering: Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is the required first step.
Choosing the correct pressing method is fundamental to achieving the desired density, shape, and mechanical performance in your final component.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Pressing | Isostatic Pressing |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Direction | Uniaxial (one direction) | Uniform (all directions) |
| Ideal Geometry | Simple shapes (discs, blocks) | Complex, intricate shapes |
| Material Uniformity | Good | Superior (Highly consistent) |
| Primary Use | Efficient production of dense shapes | Eliminating internal defects, forming complex 'green' parts (CIP) |
| Best for Performance | Simpler components where speed is key | Mission-critical parts requiring maximum uniformity (HIP) |
Still Unsure Which Pressing Method is Right for Your Project?
Choosing between hot pressing and isostatic pressing is critical to achieving the desired density, shape, and performance in your final component. The experts at KINTEK are here to help you navigate these complex decisions.
We specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables for your specific materials processing needs. Whether you are developing new materials, working with complex geometries, or require maximum material uniformity for high-performance applications, we have the expertise and solutions to support your work.
Contact us today for a consultation, and let us help you select the perfect pressing technology to optimize your results.
Reach out to our technical specialists now to discuss your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Split Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure control system of hot press sintering equipment affect copper-based nano-reinforced composites?
- What are the advantages of SPS over hot-press for h-BN? Preserve Nanostructure & Reduce Heat by 200°C
- What conditions does a vacuum hot pressing furnace provide for LLZTO? Achieving 99% Density for Solid Electrolytes
- How does a vacuum hot pressing furnace facilitate the densification of SiCp/2009Al composites? Achieve Near-Zero Porosity
- What role does the hot pressing process play in the fabrication of TlBr crystals? Achieve High-Performance Densification
- How does a vacuum hot pressing furnace solve manufacturing challenges for MPCF/Al composites? Enhance Bond Integrity
- What is the role of high-strength graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing Beryllium? Enhance Densification & Precision
- What is the necessity of continuous vacuum pump operation during the hot pressing of UHMWPE/nano-HAP? Ensure High Purity.



















