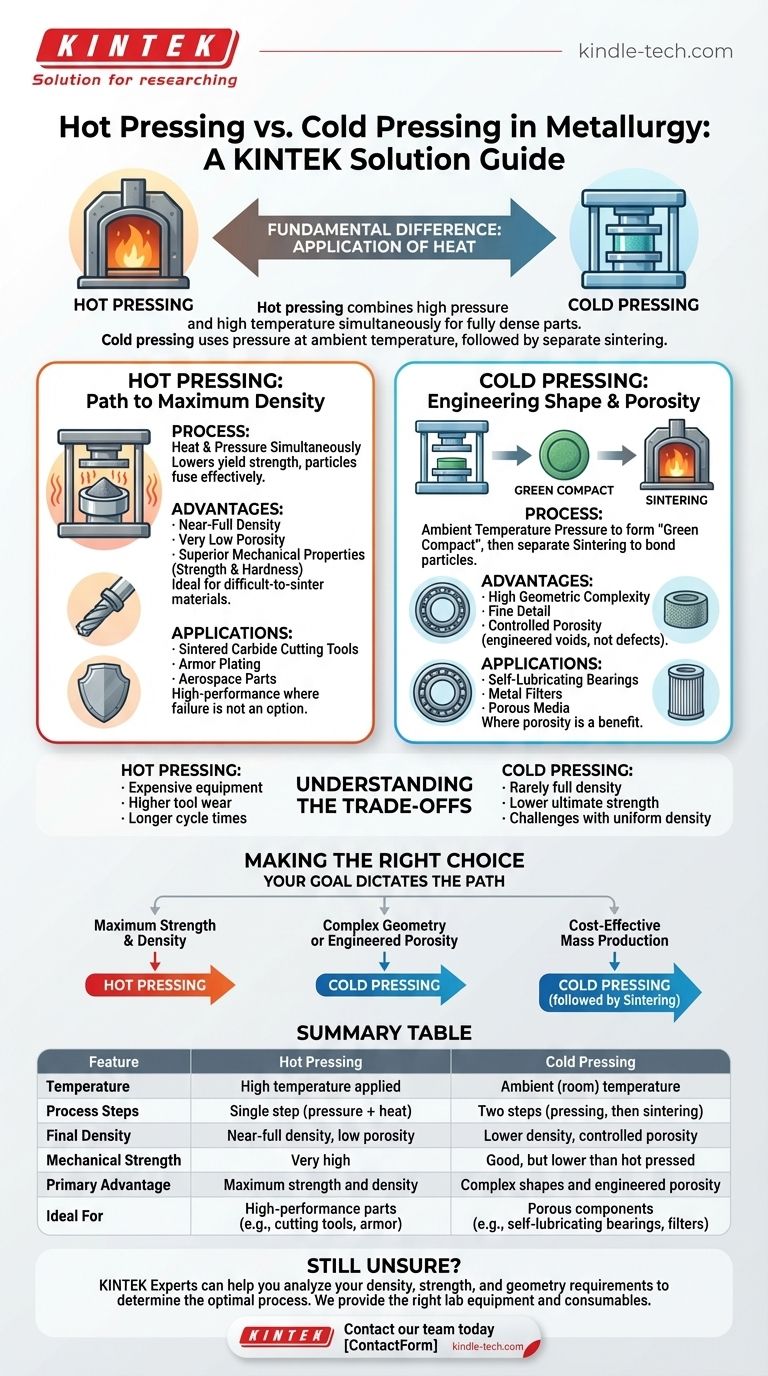
In metallurgy, the fundamental difference between hot and cold pressing lies in the application of heat. Hot pressing combines high pressure and high temperature simultaneously to create fully dense, high-strength parts in a single step. In contrast, cold pressing uses only pressure at ambient temperature to form a component, which is typically then sintered in a separate heating process to gain strength.
The choice between these techniques is not about which is superior, but about the intended function of the final part. Hot pressing is chosen for maximum density and mechanical performance, while cold pressing is chosen for intricate geometry and engineered porosity.

Deconstructing Hot Pressing: The Path to Maximum Density
Hot pressing is an advanced powder metallurgy technique designed to overcome the limitations of traditional sintering. By applying heat and pressure at the same time, it dramatically enhances the material's ability to consolidate.
The Core Process
In a hot press, metal powder is placed in a die (often made of graphite or a superalloy) which is then heated to a high temperature, typically below the material's melting point. Simultaneously, a large compressive force is applied.
This combination of heat and pressure lowers the material's yield strength, allowing the powder particles to deform and fuse together much more effectively than with pressure or heat alone.
Key Advantages
The primary advantage of hot pressing is its ability to produce parts with very low porosity and near-full density.
This results in superior mechanical properties, such as high strength and hardness. It is particularly effective for materials that are inherently difficult to sinter, like certain ceramics and superalloys.
Typical Applications
Hot pressing is the ideal method for creating high-performance components where failure is not an option. Common examples include sintered carbide cutting tools, armor plating, and specialized aerospace parts where maximum strength-to-weight ratio is critical.
Deconstructing Cold Pressing: Engineering Shape and Porosity
Cold pressing is the more conventional and widely used powder metallurgy method. It focuses on achieving a specific shape and internal structure at room temperature before any heat is applied.
The Core Process
Metal powder is loaded into a die and compacted under high pressure. This action forms a fragile, precisely shaped part known as a "green compact."
This green compact has enough strength to be handled but requires a subsequent heating process, called sintering, to bond the particles and develop its final mechanical properties.
Key Advantages
The main strength of cold pressing is its ability to create parts with high geometric complexity and fine detail.
Crucially, it also allows for the intentional creation of a controlled network of pores within the material. This calculated porosity is not a defect but a design feature.
Typical Applications
Cold pressing is used to create components where porosity is a benefit. The classic example is a self-lubricating bearing, where the internal voids are impregnated with oil, which is released during operation. Other applications include metal filters and other porous media.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither process is a universal solution. The right choice depends on a careful balance of cost, desired properties, and production volume.
Hot Pressing: Cost and Complexity
The equipment for hot pressing is significantly more expensive and complex. The combination of extreme heat and pressure leads to higher tool wear and requires specialized, costly die materials. Cycle times are also generally longer, making it less suitable for high-volume mass production.
Cold Pressing: Density and Strength
Cold-pressed parts rarely achieve the full density of onların hot-pressed counterparts. The final product will have some residual porosity, which typically results in lower ultimate strength and hardness. Achieving uniform density in very complex or tall parts can also be a challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final goal dictates the correct manufacturing path. Use this guide to determine which process aligns with your project's primary requirement.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: Hot pressing is the definitive choice for creating a fully consolidated, high-performance component from advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is complex geometry or engineered porosity: Cold pressing excels at producing intricate shapes and parts designed to hold fluids, like self-lubricating bearings.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: Cold pressing, followed by sintering, is generally the more economical and faster method for producing large quantities of components where extreme density is not the top priority.
Ultimately, selecting the right pressing technique is about matching the process capabilities to the functional demands of the final product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Pressing | Cold Pressing |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | High temperature applied | Ambient (room) temperature |
| Process Steps | Single step (pressure + heat) | Two steps (pressing, then sintering) |
| Final Density | Near-full density, low porosity | Lower density, controlled porosity |
| Mechanical Strength | Very high | Good, but lower than hot pressed |
| Primary Advantage | Maximum strength and density | Complex shapes and engineered porosity |
| Ideal For | High-performance parts (e.g., cutting tools, armor) | Porous components (e.g., self-lubricating bearings, filters) |
Still unsure which pressing technique is right for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to support your metallurgy projects. Our experts can help you analyze your requirements for density, strength, and geometry to determine the optimal process.
Contact our team today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve superior results, whether you're developing high-performance aerospace components or intricate porous metal parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- How does increasing sintering pressure from 20 to 50 MPa affect Cr-50 wt% Si? Enhance Density and Grain Refinement
- How does Vacuum Hot Pressing densify W-Si alloys? Master Mechanical Force for High-Density Alloys
- What are the primary functions of a vacuum hot press furnace? Optimize WC/Cu-Zr-Ti Composite Consolidation
- What is the principle of spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Material Densification
- What advantages does a vacuum hot press furnace provide for LSLBO ceramic electrolytes? Achieve 94% Relative Density
- Why is carbon paper placed between the powder and the graphite mold? Protect Your LTPO Electrolytes & Tooling
- What are the different types of hot pressing? Uniaxial, HIP, and SPS Explained
- Why is it necessary to equip a Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) system with a precision optical pyrometer?



















