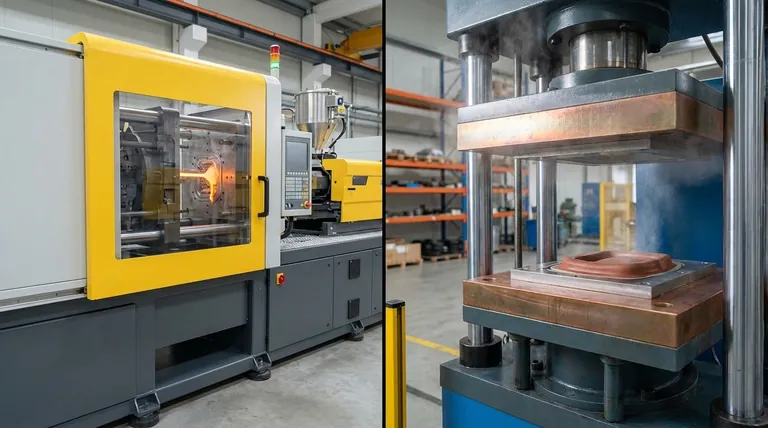
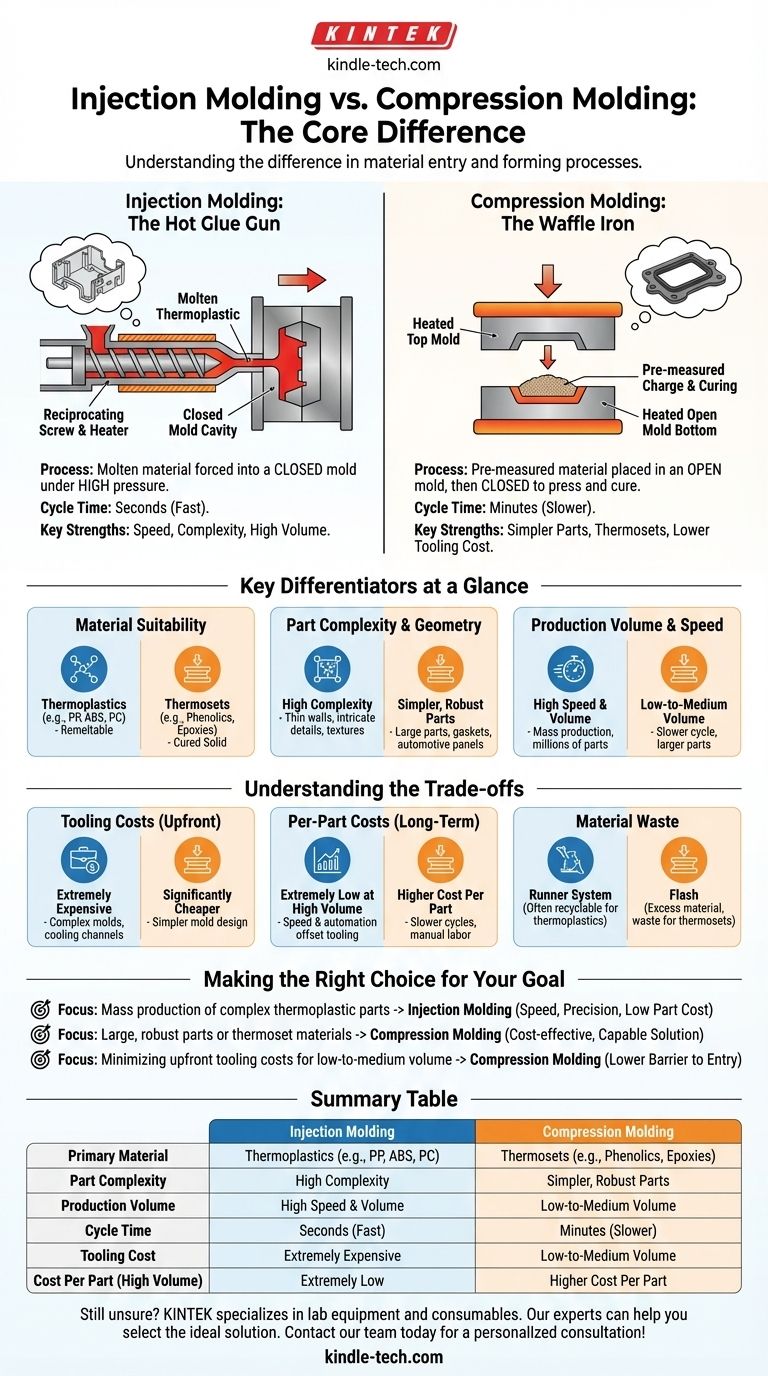
At their core, the fundamental difference between injection molding and what is commonly called "pressure molding" (more accurately, compression molding) lies in how the material enters the mold. Injection molding forces molten material into a closed mold cavity under high pressure. Compression molding places a pre-measured amount of material into an open, heated mold, which is then closed to press the material into its final shape.
The choice between these two processes is a classic engineering trade-off. Injection molding is built for speed, complexity, and high-volume production of thermoplastic parts, demanding a high initial tooling investment. Compression molding is the economical choice for simpler, larger parts, low-to-medium volumes, and is the dominant process for thermoset materials.

The Fundamental Process Difference
To truly understand which process suits your needs, you must first visualize how each one works. Their mechanics dictate their strengths and weaknesses.
How Injection Molding Works: The Hot Glue Gun
Think of injection molding as a highly sophisticated, automated hot glue gun.
A granular plastic raw material (thermoplastic) is melted in a heated barrel. A reciprocating screw then injects this molten plastic under extreme pressure into a precisely machined, closed metal mold.
The plastic fills every detail of the mold's internal cavity. After a brief cooling period, the mold opens and the finished part is ejected. This cycle is extremely fast, often taking only seconds.
How Compression Molding Works: The Waffle Iron
Compression molding is best analogized to a waffle iron.
A pre-measured amount of molding material, called a "charge," is placed into the bottom half of a heated, open mold. This charge can be in powder, putty-like, or pre-formed shape.
The top half of the mold then closes, applying immense pressure. This forces the material to spread and fill the mold cavity, with the heat and pressure curing it into a solid state. This process is ideal for thermoset materials, which undergo an irreversible chemical change when heated.
A Note on Terminology: "Pressure Molding"
The term "pressure molding" is ambiguous in manufacturing. However, when contrasted with injection molding, it almost always refers to compression molding. Both processes use pressure, but "injection" specifies how the material is delivered, while "compression" specifies how the final shape is formed.
Key Differentiators at a Glance
The mechanical differences lead to significant distinctions in material choice, part design, and production economics.
Material Suitability: Thermoplastics vs. Thermosets
Injection molding is the dominant process for thermoplastics—polymers like Polypropylene (PP), ABS, and Polycarbonate (PC) that can be repeatedly melted and solidified.
Compression molding is the primary method for thermosets—materials like phenolics, epoxies, and silicones that cure into a permanent solid state and cannot be remelted. It can also be used for some thermoplastics, but it is less common.
Part Complexity and Geometry
Injection molding excels at producing parts with high complexity. This includes thin walls, intricate ribs, fine textures, and complex features like screw bosses and snap-fits. The high injection pressure ensures the material fills every tiny detail.
Compression molding is best for simpler, often larger, and more robust parts. It's excellent for gaskets, seals, electrical switchgear, and automotive panels. It struggles with the very fine, intricate details that injection molding handles with ease.
Production Volume and Speed
Injection molding is a high-speed, high-volume process. With cycle times measured in seconds, it is built for mass production, where millions of identical parts can be made efficiently.
Compression molding is a slower, low-to-medium volume process. Cycle times are significantly longer, often measured in minutes, due to the time needed for loading the charge and for the thermoset material to cure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a process is about balancing upfront costs with long-term goals and design constraints.
Tooling Costs: The Upfront Investment
Injection molds are extremely expensive. They are complex tools engineered to withstand immense pressures and require intricate cooling channels and ejection systems. A single mold can cost tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Compression molds are significantly cheaper. Because they don't have to manage the flow of molten plastic through runners and gates, they are far simpler to design and machine, resulting in a much lower upfront investment.
Per-Part Costs: The Long-Term Economics
At high volumes, injection molding delivers an extremely low cost per part. The speed of the process and the high degree of automation overcome the initial tooling cost.
Compression molding has a higher cost per part. This is due to the slower cycle times and the often higher degree of manual labor required to load the mold and finish the part.
Material Waste
Injection molding generates waste through the runner system (the channels that deliver plastic to the part cavity), although this can often be reground and reused with thermoplastics.
Compression molding can produce "flash," which is excess material squeezed out at the mold's parting line. For thermosets, this flash is waste and cannot be recycled back into the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements will point clearly to one process over the other.
- If your primary focus is mass production of complex thermoplastic parts: Injection molding is the definitive choice for its speed, precision, and low per-part cost at scale.
- If your primary focus is producing large, robust parts or working with thermoset materials: Compression molding provides a more cost-effective and capable solution.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront tooling costs for low-to-medium volume runs: Compression molding's lower mold cost offers a significantly lower barrier to entry.
Understanding these core differences empowers you to select the manufacturing process that aligns perfectly with your project's technical and financial goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Injection Molding | Compression Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Material | Thermoplastics (PP, ABS, PC) | Thermosets (Phenolics, Epoxies) |
| Part Complexity | High (thin walls, intricate details) | Low to Moderate (simpler, larger parts) |
| Production Volume | High (mass production) | Low to Medium |
| Cycle Time | Seconds | Minutes |
| Tooling Cost | High | Low |
| Cost Per Part (High Volume) | Low | Higher |
Still unsure which molding process is right for your project? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal solution for your material, design, and production goals. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
People Also Ask
- What are the three 3 differences between compression molding and injection molding? Choose the Right Process for Your Project
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber molding? Injection, Compression, or Transfer Molding?
- What are the parameters to be considered for selecting the thin wall molding machine? Key Specs for High-Speed Production
- What is short capacity of injection Moulding machine? Optimize Your Shot Size for Flawless Parts
- What is a positive of injection moulding? Achieve High-Volume Production with Unmatched Efficiency



















