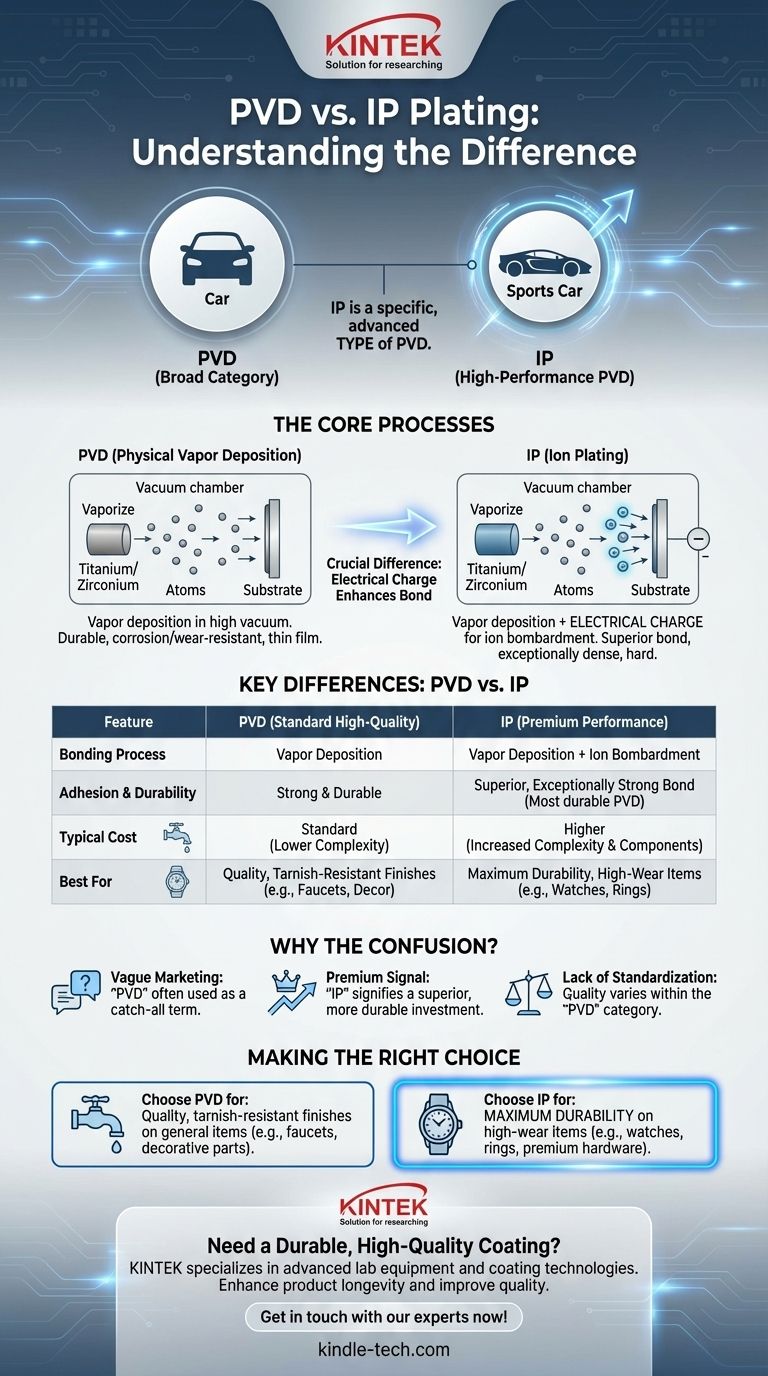
The fundamental difference is not one of opposition, but of classification. Ion Plating (IP) is a specific, more advanced type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). While both terms describe a process for creating a durable coating in a vacuum, IP uses an electrical charge to create a harder and more strongly bonded surface than some other PVD methods.
The core takeaway is that all IP plating is PVD, but not all PVD is IP. Think of PVD as the broad category of "cars," while IP is a high-performance category like "sports cars." Both are cars, but one is engineered for a higher level of performance and durability.

What is PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition)?
The Core Process
PVD is a family of coating processes that take place inside a high-vacuum chamber.
A solid source material (like titanium or zirconium) is vaporized into a plasma of atoms or molecules. This vapor then travels across the chamber and deposits onto the object being coated, forming a thin, tightly bonded film.
Key Characteristics
PVD coatings are known for being extremely durable, corrosion-resistant, and wear-resistant. The process is also more environmentally friendly than traditional electroplating.
Because the film is so thin—often just a few microns—it doesn't alter the underlying surface texture, allowing for both matte and polished finishes.
What is IP (Ion Plating)?
A Refinement of the PVD Process
Ion Plating begins just like any other PVD process: a source material is vaporized in a vacuum.
The crucial difference lies in the next step. IP introduces a secondary electrical process to enhance the coating's bond.
The Key Differentiator: An Electrical Charge
During the IP process, the object being coated (the substrate) is given a negative electrical charge.
This charge strongly attracts the positively charged ions of the vaporized metal. They accelerate towards the substrate at high speed, embedding themselves into the surface with significant force.
The Result: A Superior Bond
This high-energy bombardment creates an exceptionally dense, hard, and highly adherent coating. The process forms a graded interface layer between the coating and the substrate, meaning there isn't a sharp, distinct boundary. This lack of a clear boundary is what gives the coating its superior adhesion.
Understanding the Practical Differences
Durability and Adhesion
This is the most significant difference. While all PVD coatings are strong, IP is generally considered the most durable form of PVD. The enhanced atomic bond makes it more resistant to scratches, abrasion, and wear, which is critical for high-contact items.
Cost and Complexity
The added electrical components and process control make Ion Plating more complex and typically more expensive than more basic PVD methods like sputtering. This cost is often justified by the dramatic increase in longevity.
Appearance and Finish
Visually, an IP coating and another PVD coating can look identical when new. Both can produce a wide range of colors (gold, rose gold, black, etc.) with high fidelity. The difference becomes apparent over time with use and wear.
Why the Confusion in the Market?
Vague Marketing Language
Many brands use "PVD" as a general catch-all term for a quality coating. It's an easy-to-understand term that signals a step up from older methods.
Signifying a Premium Product
Companies that use the more advanced Ion Plating process will often specify "IP" or "Ion Plated" to differentiate their products. They are signaling that they have invested in a superior, more durable version of the PVD technology.
Lack of Standardization
Because "PVD" describes a category of processes, the quality can vary. A product simply marked as "PVD coated" might use a less robust method. Seeing "IP coated" provides more specific assurance about the durability of the finish.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is maximum durability for high-wear items (like watches, rings, or premium hardware): Look for products specifically marketed as IP (Ion Plated), as this signifies the strongest possible bond.
- If your primary focus is a quality, tarnish-resistant finish for general items (like faucets or decorative parts): A PVD coating is an excellent mark of quality and will offer a significant performance upgrade over traditional plating.
- If you are evaluating marketing claims: Treat "PVD" as the baseline for high-quality modern coatings and "IP" as the premium tier within that category.
Ultimately, understanding this distinction allows you to more accurately judge the quality and long-term value of a coated product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | IP (Ion Plating) |
|---|---|---|
| Relationship | Broad category of vacuum coating processes | A specific, advanced type of PVD |
| Bonding Process | Vapor deposition | Vapor deposition + electrical charge for ion bombardment |
| Adhesion & Durability | Strong and durable | Superior, exceptionally strong bond |
| Typical Cost | Standard for high-quality coatings | Higher, due to increased complexity |
| Best For | Quality, tarnish-resistant finishes (e.g., faucets) | Maximum durability for high-wear items (e.g., watches, rings) |
Need a Durable, High-Quality Coating for Your Products?
Understanding the nuances between PVD and IP plating is crucial for selecting the right finish to meet your performance and durability requirements. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including coating technologies, to help you achieve superior results.
We can help you:
- Select the ideal coating process for your specific application and material.
- Enhance product longevity with durable, wear-resistant finishes.
- Improve quality and performance using advanced, environmentally friendly technologies.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise in lab equipment and consumables can support your coating needs and bring lasting value to your products.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Tungsten Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD



















