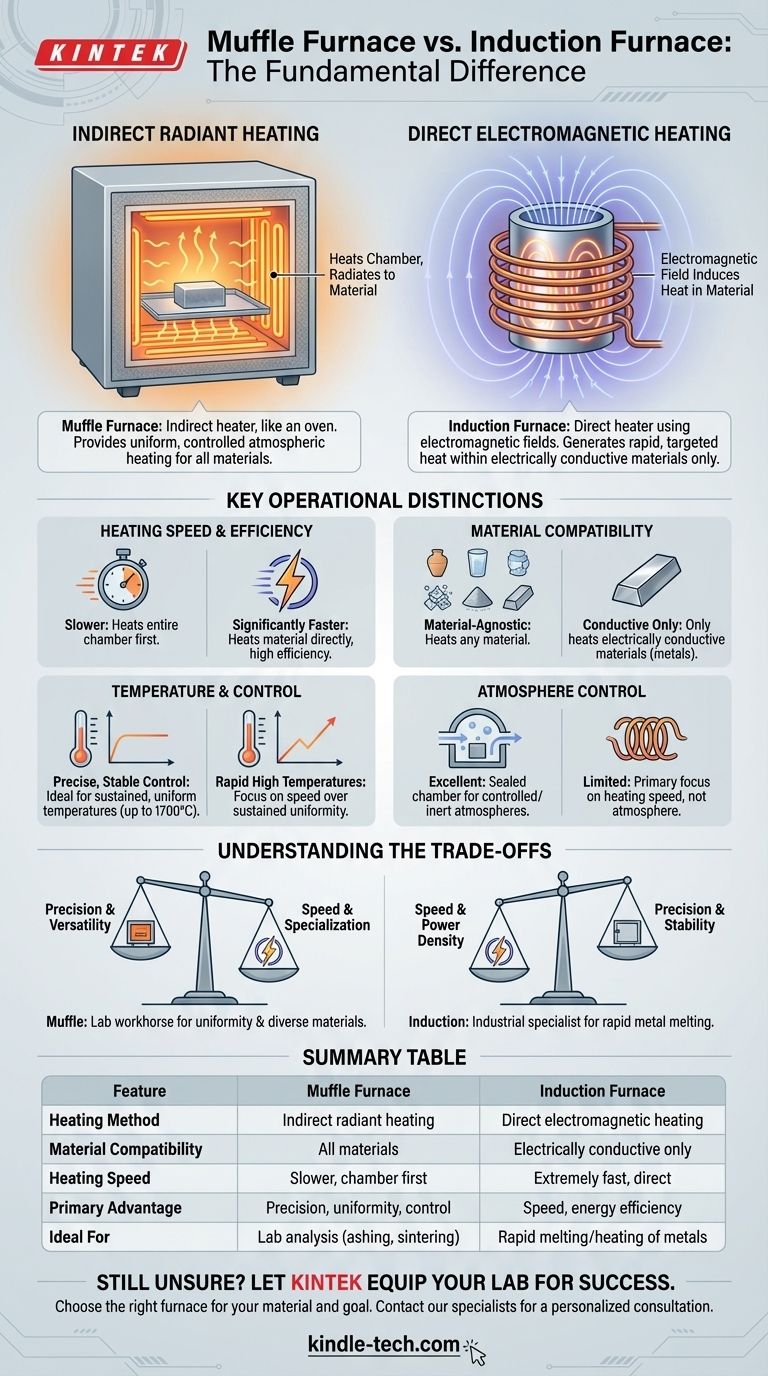
The fundamental difference between a muffle furnace and an induction furnace lies in their heating method. A muffle furnace is an indirect heater; it heats an insulated chamber, which then radiates heat onto the material inside, much like a conventional oven. In contrast, an induction furnace is a direct heater that uses an electromagnetic field to generate heat within the material itself.
At its core, the choice is between two distinct principles. Muffle furnaces provide slow, uniform, and controlled atmospheric heating for a wide variety of materials. Induction furnaces deliver extremely rapid, targeted heating exclusively for electrically conductive materials.
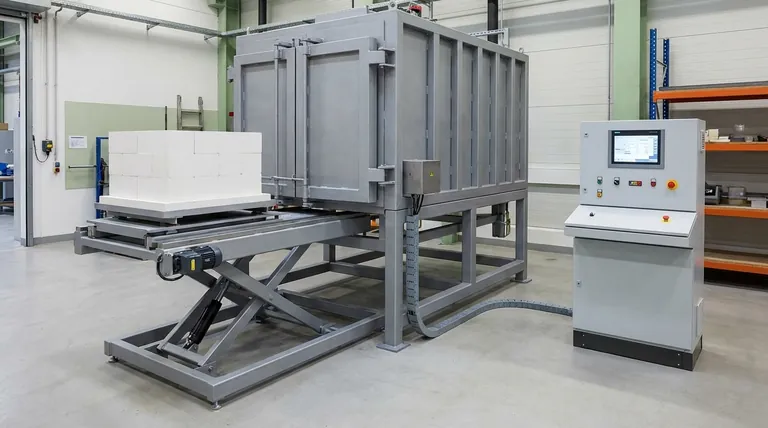

The Fundamental Difference: How Heat is Generated
To select the right tool, you must first understand how each one works. Their heating mechanisms are completely different, which dictates their respective strengths and applications.
Muffle Furnace: Indirect Radiant Heating
A muffle furnace is essentially a high-temperature oven. It contains heating components, such as electric wires or specialized rods, that heat the walls of an insulated chamber (the "muffle").
This heated chamber then radiates thermal energy uniformly onto the sample placed inside. Because it heats the entire space, it provides excellent temperature stability and control over the sample's environment.
Induction Furnace: Direct Electromagnetic Heating
An induction furnace operates without any conventional heating elements. Instead, it uses a powerful alternating current passed through a coil to create a strong electromagnetic field.
When an electrically conductive material (like a metal) is placed inside this field, the field induces powerful electrical currents—called eddy currents—within the material. The material's own electrical resistance causes these currents to generate intense, rapid heat from the inside out.
Key Operational Distinctions
The differences in heating mechanisms lead to significant contrasts in performance, material compatibility, and ideal use cases.
Heating Speed and Efficiency
Induction furnaces are significantly faster. By heating the material directly, they waste very little energy warming the surrounding air or chamber walls. This makes them highly efficient for tasks like melting metals.
Muffle furnaces are slower. They must first bring the entire insulated chamber up to the target temperature before the sample can be fully heated. This ramp-up time is inherent to their design.
Material Compatibility
This is a critical dividing line. An induction furnace can only heat electrically conductive materials. It is useless for heating ceramics, glass, or other insulators.
A muffle furnace is material-agnostic. Since it relies on radiant heat, it can effectively heat any material, whether it's conductive, non-conductive, a powder, or a solid.
Temperature Range and Control
Muffle furnaces are designed for precise temperature control over long periods. Their maximum temperature is determined by the heating elements used:
- Electric heating wires: Up to 1200°C
- Silicon-carbon rods: Up to 1400°C
- Silicon molybdenum rods: Up to 1700°C
Induction furnaces can achieve extremely high temperatures very quickly, but their primary advantage is speed rather than sustained, uniform stability across a large chamber.
Atmosphere Control
Because a muffle furnace is a sealed, enclosed chamber, it is perfectly suited for processes that require a specific, controlled, or inert atmosphere. This is crucial for preventing oxidation or contamination during heat treatment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is universally superior; they are specialized tools with distinct advantages and limitations.
Precision vs. Speed
A muffle furnace offers superior temperature uniformity and precision. It is the standard for laboratory work like gravimetric analysis, sintering, or quantitative analysis where exact, stable temperatures are non-negotiable.
An induction furnace prioritizes speed and power density. It excels in industrial settings where the goal is to melt or forge large quantities of metal as quickly as possible.
Versatility vs. Specialization
The muffle furnace is a versatile workhorse. Its ability to heat any material makes it a fixture in research, development, and quality control labs across many industries.
The induction furnace is a focused specialist. Its application is almost entirely centered on the metallurgy and processing of conductive metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be based entirely on your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is precise, uniform heating of various materials (conductive or not): A muffle furnace is the correct choice for its control, stability, and versatility.
- If your primary focus is rapidly melting or heating electrically conductive metals: An induction furnace offers unmatched speed and efficiency by heating the material directly.
- If you are performing controlled laboratory analysis like annealing, ashing, or sintering: A muffle furnace provides the necessary temperature stability and atmospheric control for reliable results.
Understanding whether you need to heat the environment or the material itself is the key to selecting the right furnace for your work.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect radiant heating (like an oven) | Direct electromagnetic heating |
| Material Compatibility | All materials (metals, ceramics, powders) | Electrically conductive materials only |
| Heating Speed | Slower, heats entire chamber first | Extremely fast, heats material directly |
| Primary Advantage | Precision, uniformity, and atmosphere control | Speed and energy efficiency for metals |
| Ideal For | Lab analysis (ashing, sintering), heat treatment | Rapid melting and heating of metals |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Application?
Choosing between a muffle furnace and an induction furnace is critical for achieving accurate and efficient results. KINTEK, your trusted partner in laboratory equipment, can help you make the right choice.
We specialize in providing high-quality lab furnaces and consumables tailored to your specific needs. Whether you require the versatile, controlled heating of a muffle furnace for research and development or the rapid, targeted power of an induction furnace for metallurgy, our experts are here to guide you.
Let KINTEK equip your lab for success. Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and find the perfect furnace solution for your materials and processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a box furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lab Furnace for Your Application
- How accurate is the muffle furnace? Achieve ±1°C Control and ±2°C Uniformity
- What is the temperature of a muffle furnace for ash determination? Key Insights for Accurate Results
- What is the burnout cycle on a furnace? Stop This Destructive Overheating Pattern Now
- What is the difference between sintering and vitrification? Key Thermal Process Distinctions



















