In professional practice, the terms regeneration and reactivation are often used interchangeably to describe the high-temperature thermal process used to restore the adsorptive capacity of spent activated carbon. Both terms refer to the procedure of heating the carbon in a controlled environment to desorb and destroy the organic contaminants it has captured, allowing it to be reused.
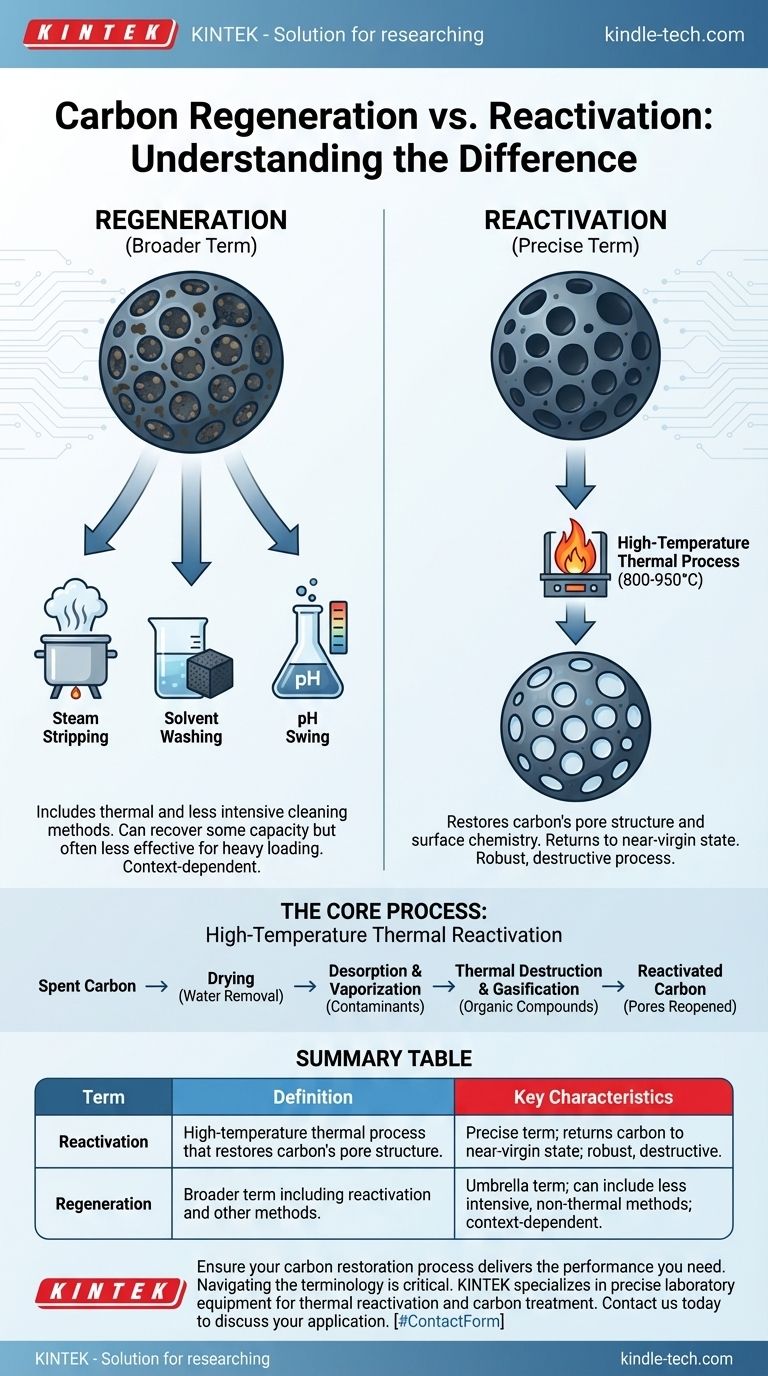
While frequently treated as synonyms, a subtle but important technical distinction exists. Reactivation is the more precise term for the high-temperature thermal process that restores carbon's pore structure, while regeneration can be a broader term that includes other, less intensive cleaning methods.

Decoding the Terminology: Interchangeable or Distinct?
Understanding the context in which these terms are used is critical. In most industrial conversations, the distinction is minor, but in technical specifications or scientific literature, the difference can be significant.
The Common Industrial Usage
In the vast majority of operational settings, you will hear "regeneration" and "reactivation" used to mean the exact same thing. They both describe the process of sending spent carbon to a high-temperature furnace (often a rotary kiln or multiple hearth furnace).
This process effectively burns off the adsorbed organic materials, clearing the carbon's vast network of pores and restoring its ability to capture new contaminants.
"Reactivation": The Precise Technical Term
Strictly speaking, reactivation refers to the high-temperature process (typically 800-950°C or 1500-1750°F) that not only removes adsorbed compounds but also restores the carbon's original surface chemistry and porous structure.
The goal of reactivation is to return the carbon to a state as close to its virgin condition as possible. It is a robust, destructive process designed for heavily loaded carbons.
"Regeneration": A Broader Concept
Regeneration can be used as an umbrella term that includes reactivation but also covers other, less aggressive methods of cleaning activated carbon. These can include:
- Steam Stripping: Using steam to desorb volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Solvent Washing: Using a chemical solvent to wash away the adsorbed substance.
- pH Swing: Altering the pH to release the adsorbed compound.
These methods can recover some of the carbon's capacity but are generally less effective than thermal reactivation and are only suitable for specific contaminants.
The Core Process: High-Temperature Thermal Reactivation
Whether you call it regeneration or reactivation, the high-temperature thermal process is the most common and effective method for restoring spent activated carbon on an industrial scale.
How It Works
The process involves heating the spent carbon in a low-oxygen environment through several stages. First, water is driven off in a drying stage. Then, as temperatures increase, the adsorbed contaminants are desorbed and vaporized.
Finally, at the highest temperatures, these vaporized organic compounds are thermally destroyed. Any remaining carbonaceous residue is gasified with steam, which reopens the pore structure, thus "reactivating" the carbon.
The Goal: Restoring Adsorptive Capacity
The ultimate objective is to free the millions of microscopic pores that give activated carbon its immense surface area. By removing the previously adsorbed components, the carbon is once again ready to perform its function as a powerful adsorbent.
Understanding the Practical Implications
Failing to appreciate the potential difference in these terms can lead to miscommunication in technical and commercial discussions.
Why the Distinction Matters
If a vendor offers to "regenerate" your carbon using a non-thermal method, the outcome will be vastly different from thermal "reactivation." The level of cleanliness, performance of the restored carbon, and cost will not be comparable.
Using the term thermal reactivation in contracts and technical specifications eliminates ambiguity and ensures all parties understand the exact process being employed.
Inevitable Material Loss
It is crucial to understand that even the best thermal reactivation process is not 100% efficient. Typically, 5-10% of the carbon mass is lost during each cycle due to handling (attrition) and the thermal process itself (burn-off). This loss must be factored into the economic viability of reusing the carbon.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Clarity in communication prevents costly operational misunderstandings. Use the terminology that best fits your specific need and audience.
- If your primary focus is restoring carbon to near-original performance: Use the term "thermal reactivation" to be technically precise and ensure you are specifying the high-temperature, destructive process.
- If you are in a general operational discussion: Using "regeneration" is common and widely understood to mean the thermal process, but be prepared to clarify if needed.
- If you are evaluating a service provider's proposal: Always ask them to define their "regeneration" method to confirm if it is thermal reactivation or a less intensive alternative like steam stripping.
Ultimately, precise language ensures that your technical requirements are clearly understood and met.
Summary Table:
| Term | Definition | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Reactivation | High-temperature thermal process (800-950°C) that restores carbon's pore structure. | Precise term; returns carbon to near-virgin state; robust, destructive process. |
| Regeneration | Broader term that can include reactivation and other cleaning methods (e.g., steam stripping). | Umbrella term; can refer to less intensive, non-thermal methods; context-dependent. |
Ensure your carbon restoration process delivers the performance you need.
Navigating the terminology of carbon regeneration vs. reactivation is critical for achieving your desired results. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise laboratory equipment and consumables needed for effective thermal reactivation and other carbon treatment processes. Our expertise ensures your lab operates with clarity and efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and how our solutions can enhance your carbon management strategy. Let's achieve optimal performance together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the fundamental characteristics of glassy carbon? Discover its Unique Synergy of Properties
- What is an RVC glassy carbon sheet? A High-Performance Material for Demanding Applications
- What is the porosity of an RVC glassy carbon sheet? Understanding the Critical Difference Between PPI and Porosity
- What is the applicable potential range for an RVC glassy carbon sheet? Master Your Electrochemical Analysis
- What are the functions of a glassy carbon electrode in CV testing of antioxidants? Enhance Your Redox Analysis Accuracy



















