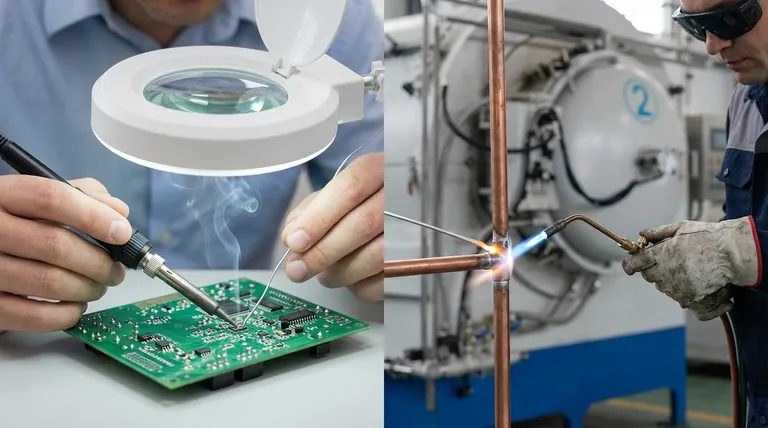
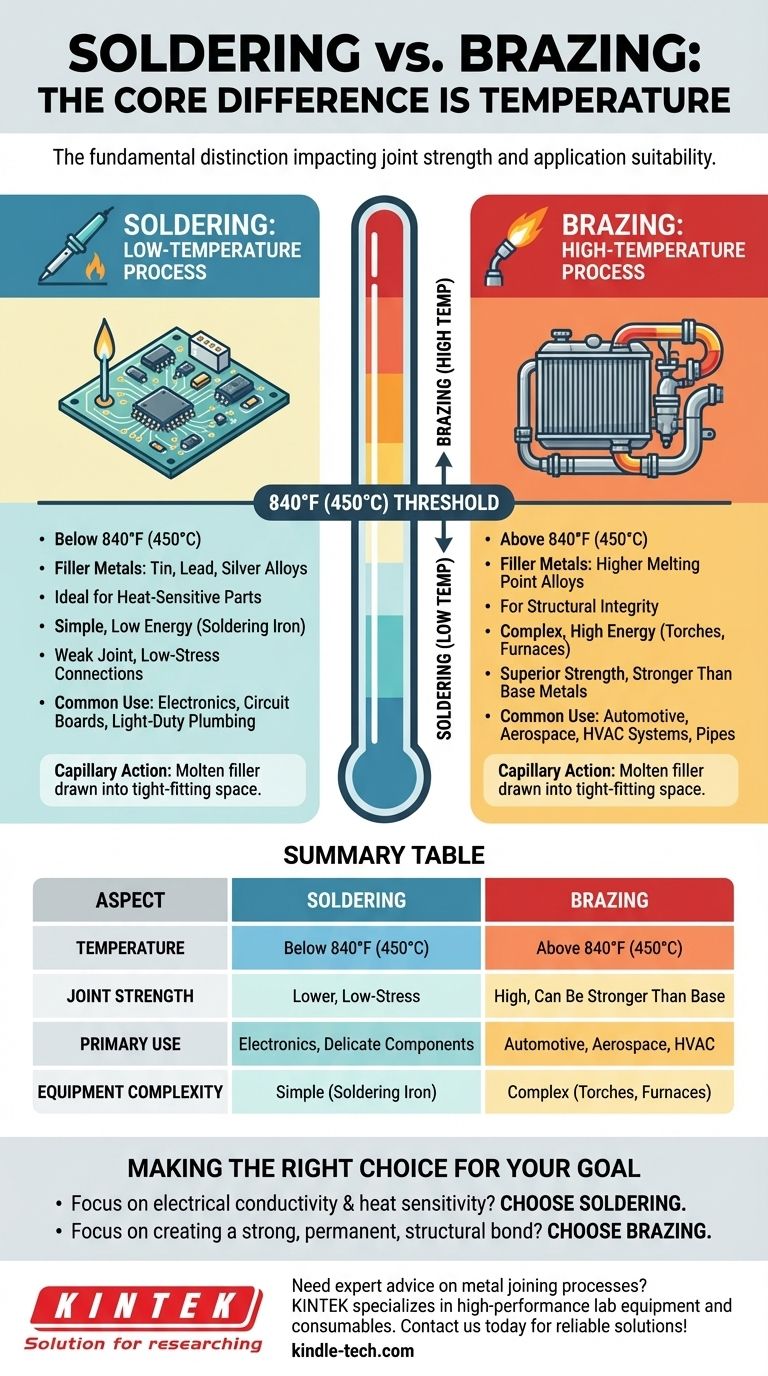
At its core, the difference between soldering and brazing comes down to a single variable: temperature. Soldering is a low-temperature joining process occurring below 840°F (450°C), while brazing is a high-temperature process that takes place above this threshold. This fundamental distinction directly impacts the strength of the resulting joint and dictates which process is suitable for a given application.
While both processes join metals using a filler material without melting the base parts, the choice between them is a trade-off. Soldering offers simplicity for delicate work, whereas brazing provides superior strength for structural applications.
The Defining Factor: Temperature
Both soldering and brazing rely on a metallurgical principle called capillary action, where the molten filler metal is drawn into the tight-fitting space between the base components. However, the temperature at which this happens changes everything.
Soldering: The Low-Temperature Process
Soldering uses filler metals (solder) with a melting point below 840°F (450°C). These fillers are typically alloys of tin, lead, silver, or other low-melting-point metals.
Because of the low heat required, soldering is ideal for joining delicate or heat-sensitive components, which is why it is the standard for assembling electronic circuit boards.
Brazing: The High-Temperature Process
Brazing uses filler metals with a melting point above 840°F (450°C), though still below the melting point of the base metals being joined.
The significantly higher temperatures create a much stronger metallurgical bond between the filler and the base metals. This process is used where joint strength is the primary concern.
How Temperature Impacts Strength and Application
The difference in operating temperature is not just a technical detail; it is the direct cause of the different performance characteristics and use cases for each process.
Joint Strength and Durability
A soldered joint is fundamentally weaker than a brazed joint. It is primarily used when electrical conductivity or a simple, low-stress physical connection is the goal.
A brazed joint, by contrast, is exceptionally strong. In many cases, a properly executed brazed joint can be as strong as, or even stronger than, the base metals it connects. This makes it suitable for high-stress, structural applications.
Common Use Cases
Soldering is ubiquitous in the electronics industry for attaching components to printed circuit boards (PCBs). It is also used for light-duty plumbing and sheet metal work.
Brazing is common in automotive, aerospace, and HVAC systems. It is used to join pipes, tubes, and fittings that must withstand high pressure, vibration, and temperature fluctuations, such as in radiators or refrigeration lines.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between soldering and brazing requires weighing the need for strength against the complexity and potential impact of the process itself.
The Advantage of Soldering: Simplicity
Soldering requires less energy and simpler equipment, often just a soldering iron or a small torch. The low heat minimizes the risk of thermal distortion or damage to the parent materials, especially sensitive electronic parts.
The Advantage of Brazing: Unmatched Strength
Brazing creates permanent, high-strength, and often leak-proof joints. This structural integrity is essential for mechanical systems where failure is not an option.
The Downside of Brazing: Complexity and Risk
The high temperatures of brazing require more sophisticated equipment, such as high-power torches or furnaces, and more careful control. There is a greater risk of overheating and warping the base materials if the process is not managed correctly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary requirement should be your guide.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity or joining heat-sensitive components: Choose soldering for its low-temperature application and minimal risk to the parts.
- If your primary focus is creating a strong, permanent, structural bond to withstand mechanical stress: Choose brazing, as its high-temperature process creates joints that rival the strength of the base metals.
Ultimately, selecting the right process depends on understanding that temperature is the variable that dictates strength.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Soldering | Brazing |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Below 840°F (450°C) | Above 840°F (450°C) |
| Joint Strength | Lower, for low-stress connections | High, can be stronger than base metals |
| Primary Use | Electronics, delicate components | Automotive, aerospace, HVAC systems |
| Equipment Complexity | Simple (soldering iron) | Complex (torches, furnaces) |
Need expert advice on metal joining processes for your laboratory or production needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific applications. Whether you're working with delicate electronic components or require robust brazing solutions for structural integrity, our team can help you select the right tools and materials to achieve precise, reliable results.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your metal joining processes and improve your operational efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Tungsten Crucible and Molybdenum Crucible for High Temperature Applications
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Boron Nitride (BN) Crucible for Phosphorous Powder Sintered
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project













