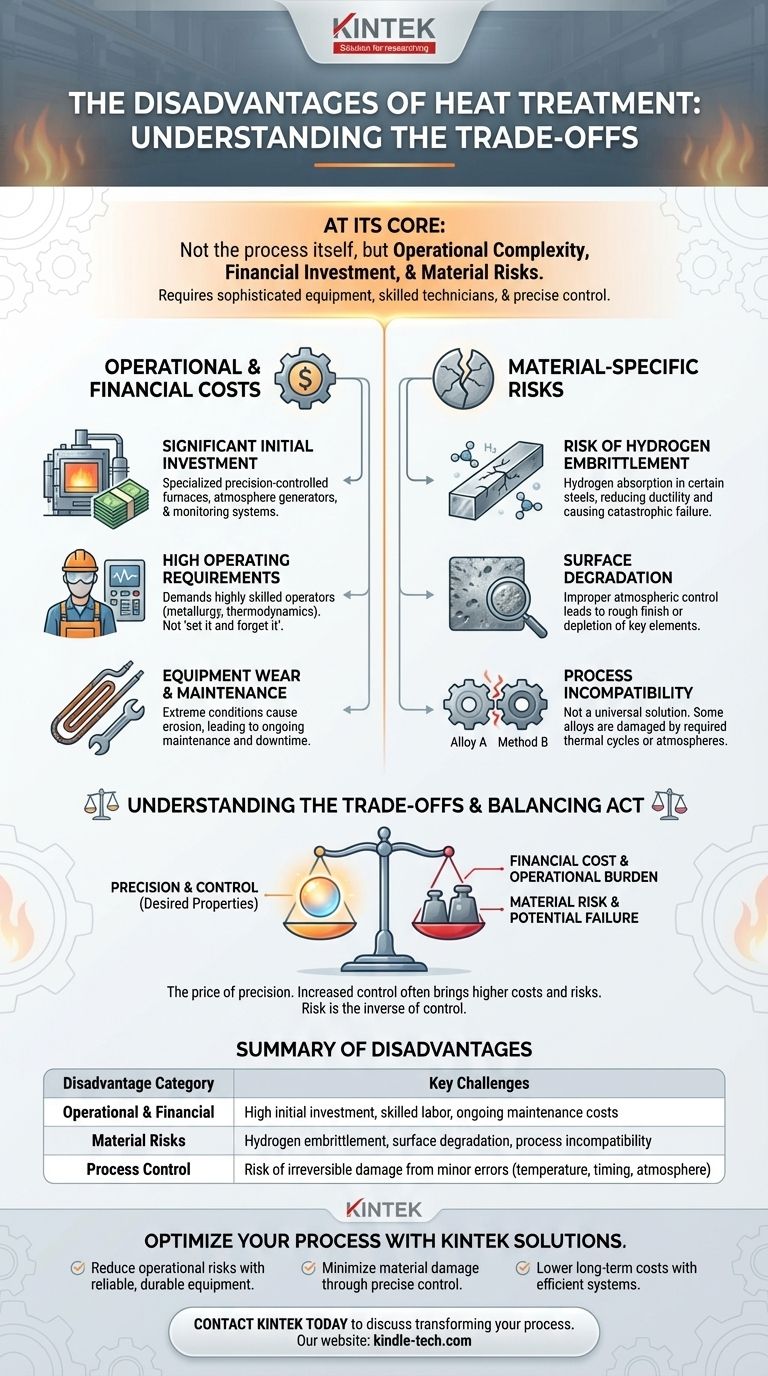
At its core, the primary disadvantages of heat treatment are not in the process itself, but in the operational complexity, financial investment, and material risks involved. Executing it correctly requires sophisticated equipment, highly skilled technicians, and precise control, as failure to do so can lead to irreversible damage to the workpiece, such as embrittlement or surface degradation.
While heat treatment offers unparalleled control over a material's final properties, its disadvantages are the costs and risks associated with achieving that control. The main challenge lies in managing the process with enough precision to gain the benefits without introducing new, unintended flaws.

The Operational and Financial Costs
The most immediate disadvantages of implementing a heat treatment process are the significant resources required to do it properly.
Significant Initial Investment
Heat treatment, particularly controlled atmosphere methods, requires specialized and expensive equipment. This includes precision-controlled furnaces, atmosphere generators, and monitoring systems that represent a substantial capital investment.
High Operating Requirements
The process is not "set it and forget it." It demands highly skilled operators who understand metallurgy, thermodynamics, and the specific requirements of the materials being treated. Errors in timing, temperature, or atmospheric composition can ruin a batch of components.
Equipment Wear and Maintenance
The extreme conditions involved in heat treatment take a toll on the equipment itself. For example, the gases used in controlled atmospheres can cause erosion of electric heating elements, leading to ongoing maintenance costs and potential downtime.
The Material-Specific Risks
Beyond the operational costs, heat treatment introduces direct risks to the material being treated. These are not guaranteed outcomes but potential failures if the process is mismatched to the material or poorly controlled.
Risk of Hydrogen Embrittlement
Certain types of steel, when heat-treated in an atmosphere with high hydrogen content, can absorb the hydrogen. This leads to hydrogen embrittlement, a condition that severely reduces the material's ductility and can cause catastrophic failure under load.
Surface Degradation
Improper atmospheric control can negatively affect the surface of the workpiece. This can manifest as a rough, non-bright finish or, more seriously, the depletion of key metallic elements like chromium or carbon from the surface layer, compromising its hardness and corrosion resistance.
Process Incompatibility
Heat treatment is not a universal solution. Some materials cannot be treated effectively with certain methods. For instance, some alloys may not respond to a controlled atmosphere or may be damaged by the required thermal cycles, making it an unsuitable process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The disadvantages of heat treatment are best understood as the price of precision. The more specific the desired outcome, the more complex and costly the process becomes.
The Cost of a Controlled Atmosphere
Many of the most cited disadvantages—complex gas handling, equipment erosion, high investment—are specific to controlled atmosphere heat treatment. This method is used to achieve pristine surfaces and prevent oxidation, but it comes with a much higher operational burden than simpler methods like open-air furnace treating or induction hardening.
Risk Is the Inverse of Control
The biggest "disadvantage" is the potential for error. A slight deviation in the cooling rate can lead to cracking. An incorrect atmosphere can decarburize the surface of a steel part, rendering it useless. These risks highlight that the value of heat treatment is directly tied to the quality of its execution.
Balancing Benefit Against Detriment
The decision to heat-treat is a classic engineering trade-off. The process can introduce incredible strength, relieve internal stresses, and create wear-resistant surfaces. These benefits must be weighed against the financial cost, the need for expertise, and the risk of material damage if the process is not managed perfectly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To decide if heat treatment is appropriate, you must weigh its demands against your project's goals.
- If your primary focus is achieving mission-critical material properties at scale: The high investment in equipment and skilled personnel is a necessary and justifiable business expense.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive or low-volume production: The operational complexity and initial investment may be prohibitive, making outsourcing to a specialized heat-treatment facility a more viable option.
- If you are working with specialized or sensitive alloys: The risk of material damage like embrittlement is high, demanding expert metallurgical consultation and rigorously precise process control from the start.
Ultimately, the decision hinges on whether the required material improvements justify the significant investment in process control and expertise.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage Category | Key Challenges |
|---|---|
| Operational & Financial | High initial investment in equipment, skilled labor requirements, ongoing maintenance costs |
| Material Risks | Hydrogen embrittlement, surface degradation, process incompatibility with certain alloys |
| Process Control | Risk of irreversible damage from minor errors in temperature, timing, or atmosphere |
Optimize your heat treatment process with KINTEK solutions.
Heat treatment doesn't have to be a disadvantage for your lab. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed to mitigate the very challenges outlined above. Our precision-controlled furnaces and expert support help you:
- Reduce operational risks with reliable, durable equipment
- Minimize material damage through precise temperature and atmosphere control
- Lower long-term costs with efficient, easy-to-maintain systems
Whether you're scaling up production or working with sensitive alloys, we provide the tools and expertise to make heat treatment a strategic advantage rather than a liability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our lab equipment solutions can transform your heat treatment process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















