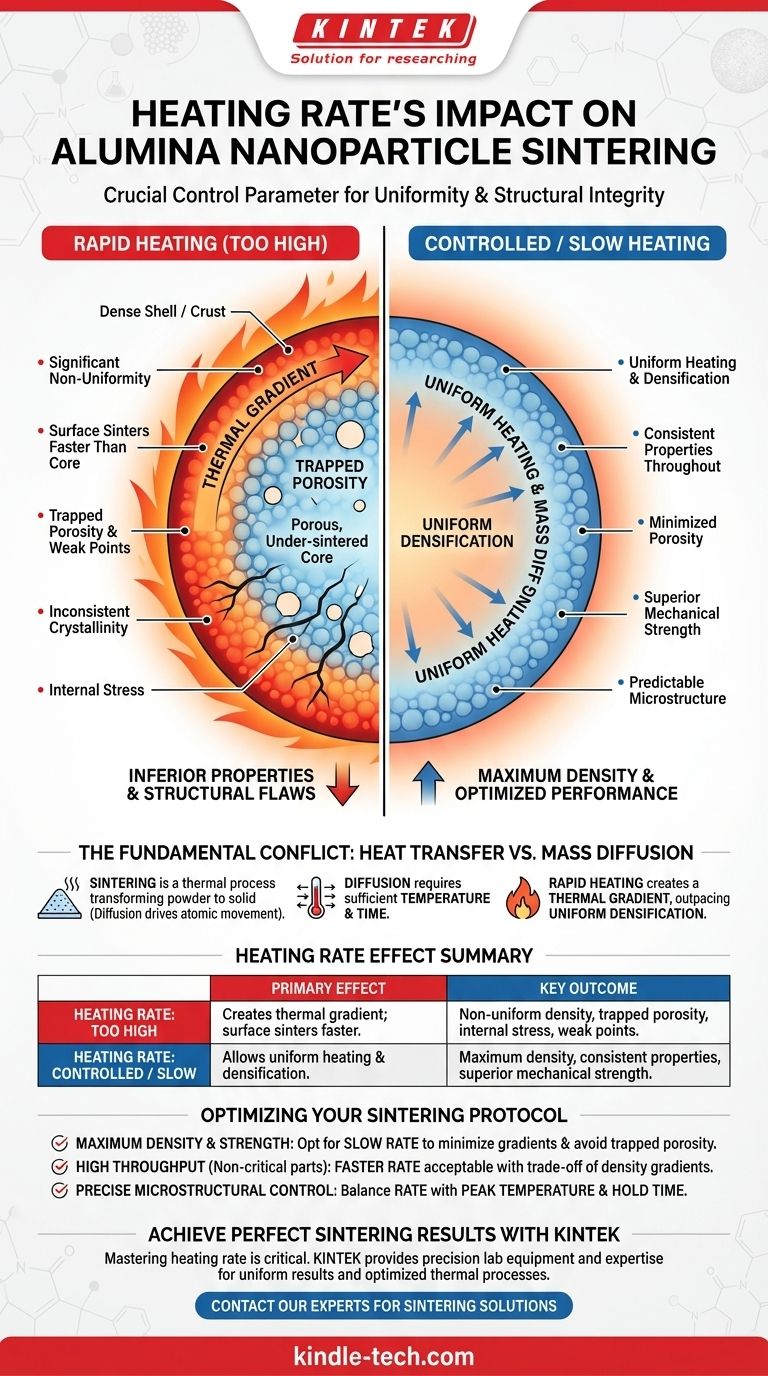
Crucially, the heating rate during the sintering of alumina nanoparticles is a primary control parameter that dictates the final uniformity and structural integrity of the component. A heating rate that is too high results in significant non-uniformity, where the exterior of the material sinters and densifies far more than the core. This creates internal stress, traps porosity, and leads to a final product with inconsistent and often inferior properties.
The core challenge in sintering is balancing the speed of the process against the time required for mass transport. A rapid heating rate creates a thermal gradient that outpaces the material's ability to densify uniformly, leading to a dense shell that encapsulates a porous, under-sintered core.

The Fundamental Conflict: Heat Transfer vs. Mass Diffusion
What is Sintering?
Sintering is a thermal process that transforms a powder compact into a dense, solid object. Its primary goal is to reduce or eliminate the empty space (porosity) between the initial particles by using heat to drive atomic movement.
The Role of Temperature and Time
This atomic movement, known as diffusion, is the fundamental mechanism behind densification. Diffusion is highly dependent on both temperature and time. Atoms need sufficient thermal energy to move, and they need sufficient time to travel and fill the voids between particles.
The Problem with Rapid Heating
When a part is heated very quickly, its surface temperature rises much faster than its internal core temperature. This temperature difference is known as a thermal gradient. Because sintering is temperature-dependent, this thermal gradient directly causes a densification gradient.
Consequences of a High Heating Rate
The "Crust-Core" Effect
The hotter surface begins to sinter and densify rapidly, forming a dense, relatively non-porous "crust." The cooler interior, however, has not had enough time at temperature for significant diffusion to occur.
Trapped Porosity
This dense outer shell can seal off the pathways required for gases and pores to escape from the core of the component. As a result, porosity becomes trapped within the material, severely limiting the final achievable density and creating weak points.
A Gradient in Sintering Degree
The final product exhibits a significant gradient in its properties. The sintering degree is highest at the surface and decreases towards the center. This means the component is not a uniform material but a composite of different densities.
Inconsistent Crystallinity
This thermal gradient can also affect the final crystal structure. The material along the rapidly heated surface may exhibit different grain characteristics compared to the more insulated core, which experiences a slower effective heating rate. This further contributes to the non-uniformity of the final part.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Lure of High Throughput
The primary motivation for using a high heating rate is economic. Faster cycles mean higher throughput and lower energy consumption per part, which can be very attractive in a production environment.
The Price of Speed: Structural Flaws
This speed comes at a steep cost. The resulting internal stresses, trapped porosity, and density gradients can lead to poor mechanical performance, reduced strength, and a higher likelihood of failure under load.
The Benefit of Slow Heating
A slower, more controlled heating rate allows the entire component to reach thermal equilibrium gradually. This ensures that the core and the surface heat up and sinter at a more uniform pace, allowing for consistent diffusion and the elimination of pores throughout the entire volume.
Optimizing Your Sintering Protocol
Choosing the right heating rate is a critical decision that depends on the desired outcome for your final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and mechanical strength: Opt for a slower heating rate to minimize thermal gradients, ensure uniform densification, and avoid trapped porosity.
- If your primary focus is high throughput for non-critical components: A faster heating rate may be acceptable, but you must be prepared to accept the resulting gradients in density and structural properties.
- If your primary focus is precise microstructural control: The heating rate must be carefully balanced with the peak sintering temperature and hold time, as all three variables interact to determine final grain size and uniformity.
Ultimately, mastering the heating rate is key to transitioning from simply forming a part to engineering its precise material properties.
Summary Table:
| Heating Rate | Primary Effect on Sintering | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Too High | Creates a thermal gradient; surface sinters faster than core. | Non-uniform density, trapped porosity, internal stress, weak points. |
| Controlled / Slow | Allows uniform heating and densification throughout the part. | Maximum density, consistent properties, superior mechanical strength. |
Achieve Perfect Sintering Results for Your Alumina Nanoparticles
Mastering the heating rate is critical for producing components with the precise density, strength, and microstructure you require. The wrong rate can lead to costly flaws and inconsistent performance.
KINTEK is your partner in precision sintering. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing the tools and expertise to help you optimize your thermal processes. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up production, we can help you achieve uniform results and avoid the pitfalls of improper heating.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our experts today to find the right solution for your laboratory's sintering challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















