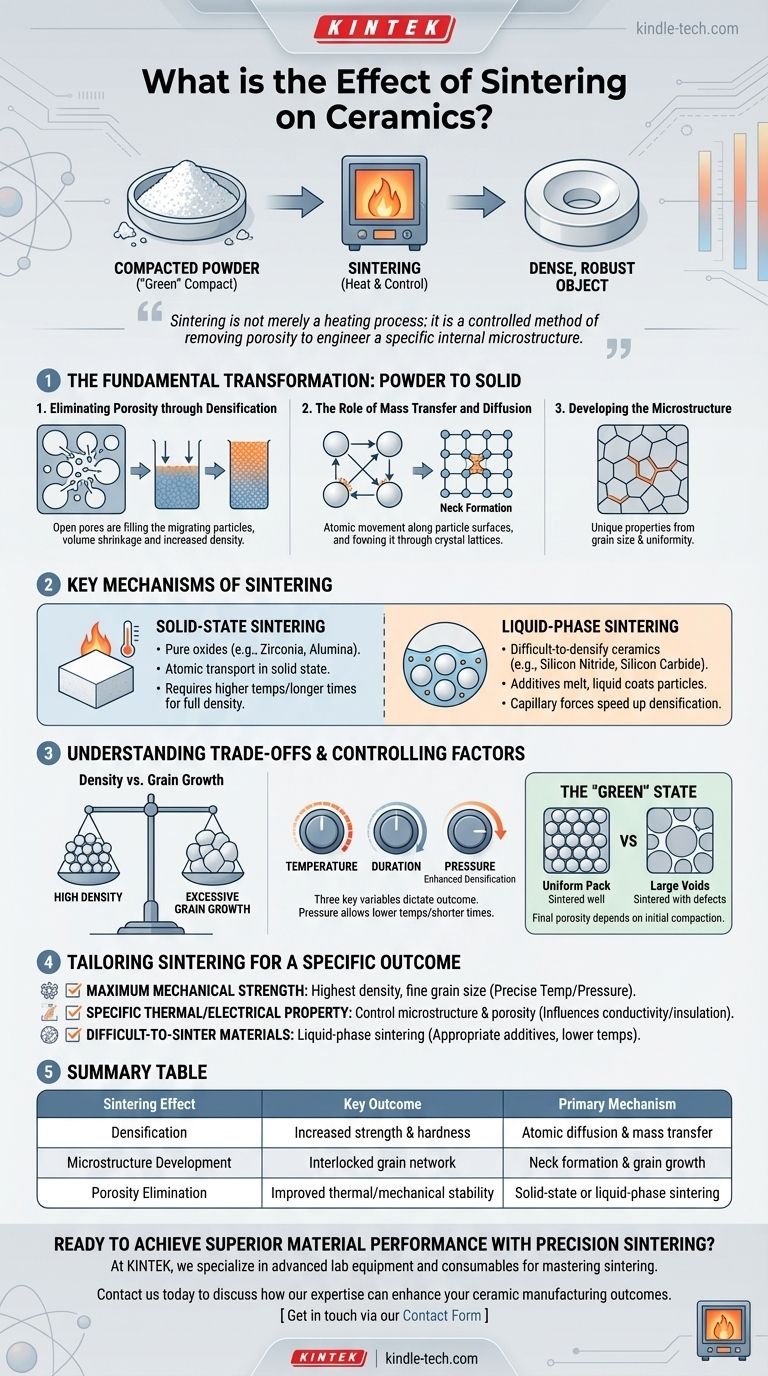
At its core, the primary effect of sintering is the transformation of a compacted ceramic powder into a dense, solid, and mechanically robust object. This high-temperature process fundamentally enhances a ceramic's properties—such as strength, hardness, and thermal stability—by bonding individual particles together and significantly reducing the empty space between them.
Sintering is not merely a heating process; it is a controlled method of removing porosity to engineer a specific internal microstructure. The mastery of sintering is the critical step that dictates the final performance and reliability of any advanced ceramic component.

The Fundamental Transformation: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is the most important stage in ceramic manufacturing. It takes a fragile "green" compact, which is essentially pressed powder, and converts it into a durable, functional material through carefully controlled heat.
Eliminating Porosity through Densification
The main objective of sintering is densification. This is the process of reducing or eliminating the pores (empty spaces) that exist between the raw powder particles.
As the material is heated, atoms migrate to fill these voids, causing the entire component to shrink and become more dense. This is directly responsible for the dramatic increase in strength and hardness.
The Role of Mass Transfer and Diffusion
Densification occurs through diffusion and mass transfer. At temperatures below the material's melting point, atoms on the surfaces of the ceramic particles become mobile.
These atoms move along the particle surfaces and through the crystal lattice to the points of contact, forming "necks" that grow and eventually pull the particles together, closing the pores.
Developing the Microstructure
The result of this atomic movement is the formation of a polycrystalline microstructure. This internal network of interlocked grains and grain boundaries is what gives the final ceramic its unique set of properties.
The size and uniformity of these grains are critical and are directly influenced by the sintering parameters.
Key Mechanisms of Sintering
Not all ceramics are sintered in the same way. The mechanism used depends on the material's chemistry and the desired final properties.
Solid-State Sintering
This is the most common method, used for pure oxide ceramics like zirconia and alumina. In this process, atomic transport happens entirely in the solid state.
Because diffusion through a solid is relatively slow, this method often requires higher temperatures and longer processing times to achieve full density.
Liquid-Phase Sintering
For ceramics that are very difficult to densify, such as silicon nitride and silicon carbide, a liquid phase is introduced.
Small amounts of additives are mixed with the ceramic powder. At the sintering temperature, these additives melt and form a liquid that coats the ceramic particles. This liquid uses capillary forces to pull the particles together and dramatically speeds up densification.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Controlling Factors
Achieving the perfect ceramic component is a balancing act. The parameters of the sintering process must be carefully controlled to avoid common pitfalls.
The Balance Between Density and Grain Growth
The primary trade-off in sintering is between achieving high density and preventing excessive grain growth.
While longer times and higher temperatures promote densification, they can also cause the microscopic grains to grow too large. Overly large grains can create internal stress points and make the final ceramic more brittle, negating the benefits of high density.
The Impact of Sintering Parameters
The outcome is dictated by three key variables: temperature, duration, and pressure. Higher temperatures and longer times increase the rate of diffusion but also increase the risk of unwanted grain growth.
The Influence of Pressure
Applying external pressure during heating can significantly enhance densification. This allows for the use of lower temperatures and shorter times, which helps to limit grain growth and can produce materials with superior mechanical properties.
The Importance of the "Green" State
The final porosity of a sintered part is heavily dependent on the initial porosity of the unsintered, or "green," compact. A uniformly packed powder with minimal voids will sinter more effectively and result in a more reliable final product.
Tailoring Sintering for a Specific Outcome
The choice of sintering parameters and mechanisms depends entirely on the desired properties of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical strength: Aim for the highest possible density with a fine, uniform grain size, which often requires precise temperature control and may benefit from applied pressure.
- If your primary focus is a specific thermal or electrical property: Control the microstructure and final porosity to meet those requirements, as these factors heavily influence conductivity and insulation.
- If your primary focus is processing difficult-to-sinter materials: Utilize liquid-phase sintering by selecting appropriate additives to enable densification at more manageable and cost-effective temperatures.
Ultimately, controlling the sintering process is how you transform a simple powder into a high-performance engineered ceramic.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Effect | Key Outcome | Primary Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Densification | Increased strength & hardness | Atomic diffusion & mass transfer |
| Microstructure Development | Interlocked grain network | Neck formation & grain growth |
| Porosity Elimination | Improved thermal/mechanical stability | Solid-state or liquid-phase sintering |
Ready to achieve superior material performance with precision sintering?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary to master the sintering process. Whether you are developing high-strength zirconia components or engineering complex silicon carbide parts, our solutions help you control temperature, pressure, and atmosphere for optimal densification and microstructure.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your ceramic manufacturing outcomes. Let's transform your ceramic powders into reliable, high-performance materials together.
Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















