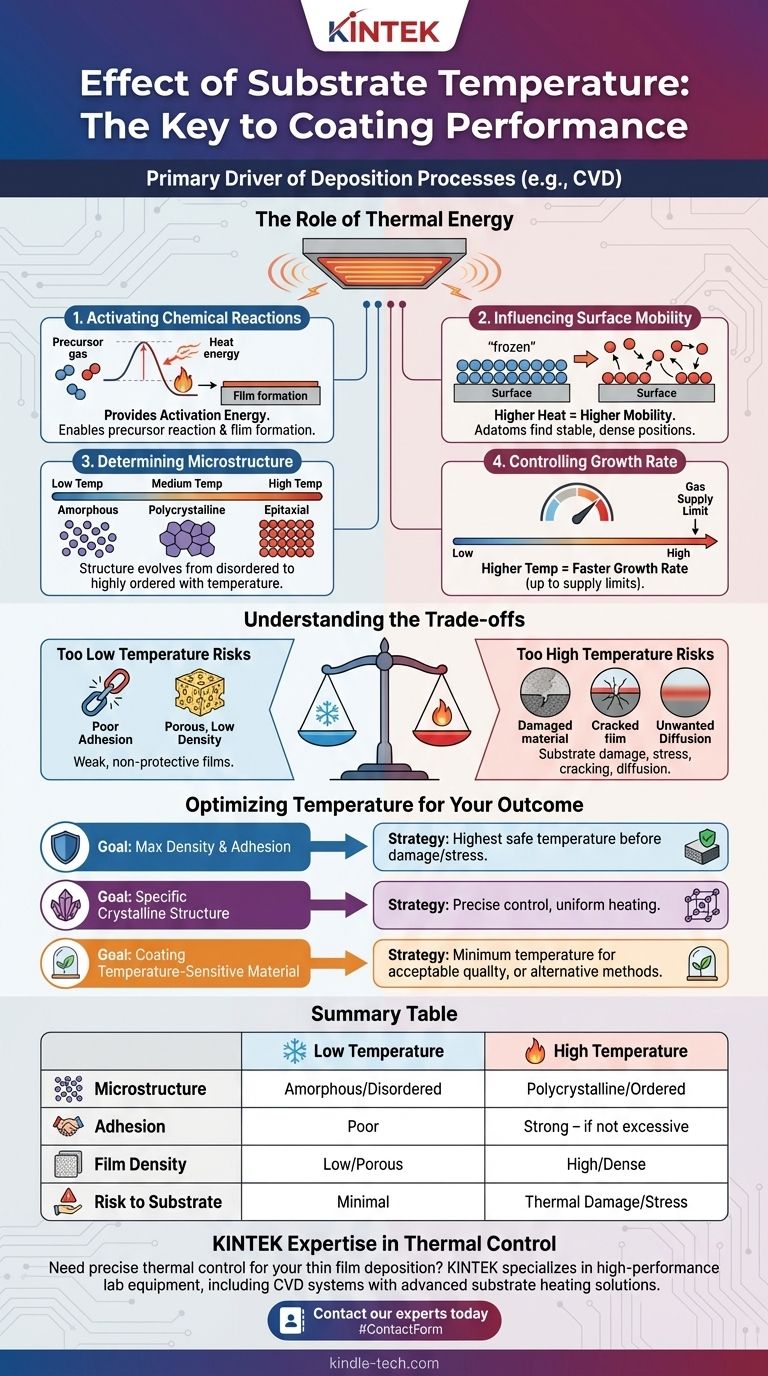
Substrate temperature is the primary driver of the coating process. In deposition techniques like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), heating the substrate provides the necessary thermal energy to initiate and sustain the chemical reactions on its surface. This energy allows gaseous precursors to break their bonds and reform as a solid, adherent thin film.
The core effect of substrate temperature is that it dictates not just if a film will form, but how it forms. It directly controls the final film's microstructure, density, adhesion, and stress, making it the most critical parameter for determining the coating's ultimate performance.
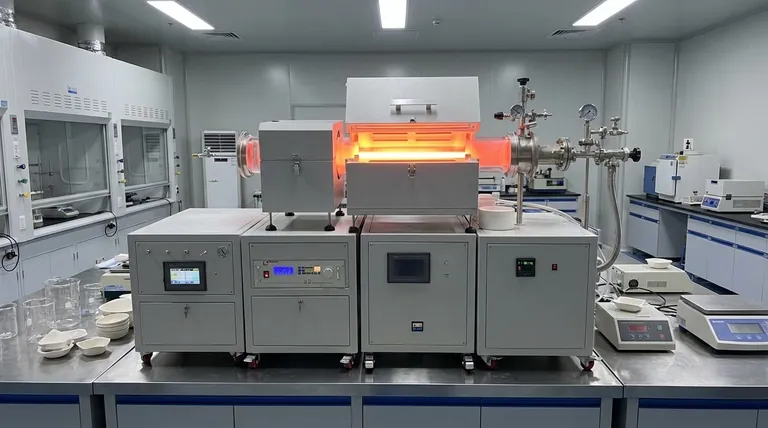

The Role of Thermal Energy in Deposition
Understanding why temperature is so influential requires looking at what happens at the atomic level on the substrate's surface. The heat you apply is doing several critical jobs simultaneously.
Activating Chemical Reactions
For a coating to form from precursor gases, a chemical reaction must occur. Substrate temperature provides the activation energy—the minimum energy required to start this reaction.
Without sufficient heat, the precursor gases will not react effectively on the surface, and little to no film will be deposited.
Influencing Surface Mobility
Once atoms from the gas phase deposit onto the surface, they are called "adatoms." Temperature gives these adatoms the energy to move around on the surface before locking into place.
Higher mobility allows adatoms to find the most stable, low-energy positions, resulting in a denser, more ordered, and less porous film. Low temperatures freeze adatoms where they land, leading to a more disordered and porous structure.
Determining Film Microstructure
The final structure of the film is a direct consequence of temperature. The level of thermal energy dictates how the atoms arrange themselves.
At low temperatures, adatoms have little mobility, resulting in a disordered or amorphous structure. As temperature increases, films become polycrystalline, with distinct grains. At very high temperatures, it's possible to achieve highly-ordered epitaxial or single-crystal growth on a suitable substrate.
Controlling Growth Rate
Generally, a higher substrate temperature increases the rate of chemical reactions, leading to a faster deposition or growth rate.
However, this relationship is not infinite. At a certain point, the growth rate may become limited by how fast the reactive gases can be supplied to the surface, not by the temperature itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing temperature is a balancing act. Pushing the temperature too far in either direction can compromise the quality and integrity of your final product.
The Risk of Too Low a Temperature
Operating at an insufficient temperature leads to coatings with poor functional properties.
The primary issues are poor adhesion to the substrate and a porous, low-density structure. These films are often mechanically weak and offer inadequate protection.
The Risk of Too High a Temperature
Excessive heat introduces a different set of problems that can be just as detrimental.
High temperatures can damage the substrate material itself, especially polymers or certain metal alloys. It can also create high internal stresses in the growing film, which can lead to cracking or delamination upon cooling due to differences in thermal expansion.
Furthermore, extreme heat can cause unwanted diffusion between the film and substrate, creating a blurred interface and potentially altering the properties of both materials.
Optimizing Temperature for Your Desired Outcome
The "correct" substrate temperature is entirely dependent on the desired properties of the final coating and the limitations of the substrate material.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and adhesion: You should use the highest temperature possible that does not cause thermal damage to the substrate or introduce excessive internal stress.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific crystalline structure: Temperature is your most precise control knob, and achieving uniform, stable heating across the entire substrate is paramount.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material: You must identify the minimum temperature that provides acceptable film quality or consider alternative deposition methods that operate at lower temperatures.
Ultimately, controlling substrate temperature is the key to engineering a film with the precise physical and chemical properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Effect | Low Temperature | High Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Microstructure | Amorphous, disordered | Polycrystalline, ordered |
| Adhesion | Poor | Strong (if not excessive) |
| Film Density | Low, porous | High, dense |
| Risk to Substrate | Minimal | Thermal damage, stress |
Need precise thermal control for your thin film deposition? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including CVD systems with advanced substrate heating solutions. Whether you're working with temperature-sensitive materials or aiming for epitaxial growth, our expertise ensures you achieve the perfect film properties. Contact our experts today to optimize your coating process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs



















