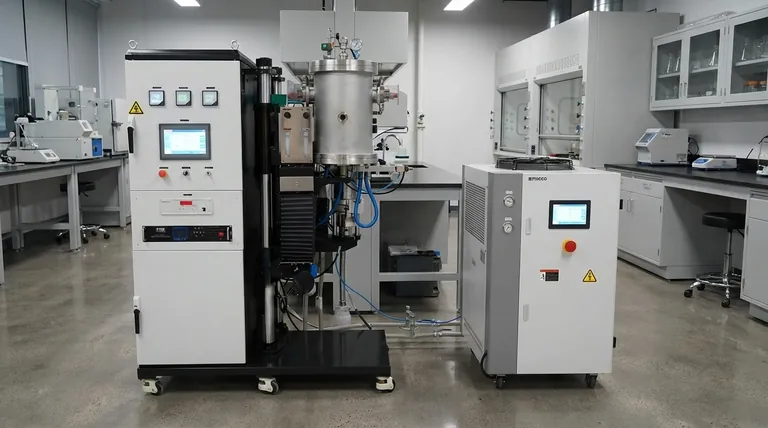
In short, temperature is the single most critical factor in the sintering process. It provides the thermal energy required for atoms to diffuse across particle boundaries, effectively welding the material together into a dense, solid mass. This process must occur at a temperature high enough to promote this atomic movement but remain below the material's melting point to avoid complete liquefaction.
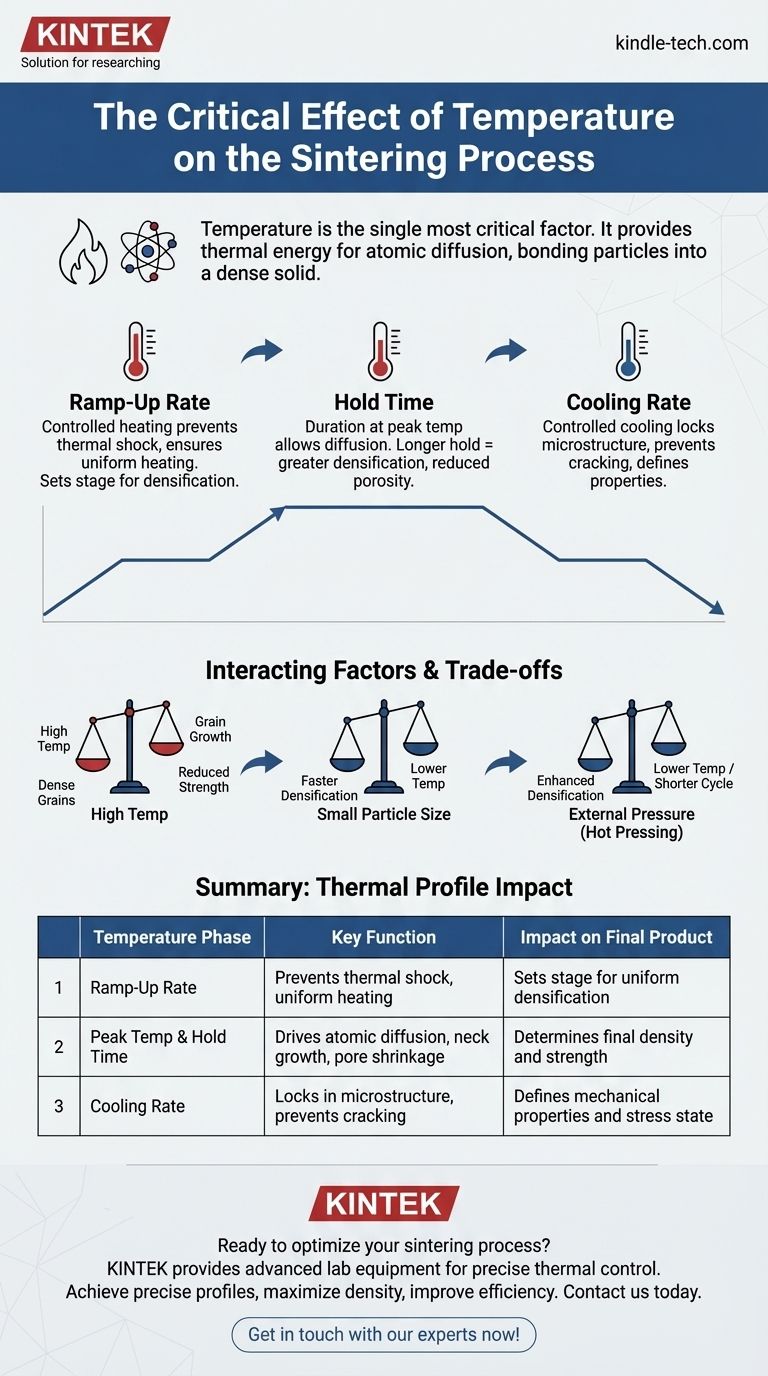
The goal is not simply to reach a high temperature, but to precisely control the entire thermal profile—the heating rate, hold time, and cooling rate. This complete temperature journey dictates the final density, microstructure, and ultimate performance of the sintered part.

The Fundamental Role of Temperature in Atomic Diffusion
Sintering is fundamentally a process of reducing the surface energy of a collection of particles by bonding them together. Temperature is the engine that drives this transformation.
Providing the Energy for Bonding
Heat provides atoms with the kinetic energy they need to move. At sufficiently high temperatures, atoms can migrate from the bulk of a particle to the contact points, or "necks," between adjacent particles.
This movement, known as diffusion, is what causes these necks to grow, pores to shrink, and the overall part to densify and strengthen.
The Critical Temperature Window
The sintering temperature must be carefully selected. It needs to be high enough for diffusion to occur at a practical rate but must stay below the material's melting point.
In some multi-component systems, the process may cross the eutectic temperature, which is the lowest temperature at which a liquid phase can form. The introduction of this liquid can dramatically accelerate densification, a process known as liquid-phase sintering.
Temperature and Sintering Kinetics
The rate of diffusion is heavily dependent on temperature. A small increase in temperature can cause an exponential increase in the sintering rate.
This relationship means that temperature is the primary lever for controlling how quickly the densification process occurs.
Beyond Peak Temperature: The Importance of the Thermal Profile
Effective sintering is not about a single temperature point. It is about managing the entire heating and cooling cycle, as each phase has a distinct impact on the final product.
The Ramp-Up Rate
The rate at which the material is heated to the peak sintering temperature is critical. A controlled ramp-up prevents thermal shock and ensures uniform heating throughout the part.
This initial phase sets the stage for uniform particle rearrangement and the elimination of porosity during the hold time.
The Hold Time
The duration spent at the peak temperature, often called the hold or soak time, allows the diffusion process to progress toward completion.
Longer hold times generally lead to greater densification and reduced porosity. For example, increasing the hold time from 30 to 60 minutes can reduce pore size by as much as 25%.
The Cooling Rate
The rate of cooling is just as important as the heating cycle. Controlled cooling prevents the introduction of thermal stress that could crack the part.
It also locks in the final microstructure, which is essential for achieving the desired mechanical and physical properties of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Interacting Factors
Temperature does not act in isolation. Its effect is moderated by several other factors, creating a complex interplay that must be managed.
Temperature vs. Grain Growth
A primary trade-off in sintering is achieving high density without excessive grain growth. While higher temperatures accelerate densification, they also cause the individual crystals (grains) in the material to grow larger.
Overly large grains can often lead to reduced mechanical strength and toughness. The ideal process maximizes density while constraining grain size.
Interaction with Particle Size
The starting particle size has a profound impact on sintering behavior. Smaller particles have a higher surface area-to-volume ratio, which provides a greater driving force for densification.
Consequently, materials with smaller particles can often be sintered to full density at lower temperatures or in shorter times.
Interaction with Pressure
Applying external pressure during the process, known as hot pressing, can significantly enhance densification. The pressure aids in particle rearrangement and the collapse of pores.
This allows for the use of lower sintering temperatures, which is useful for preventing unwanted grain growth or thermal degradation.
Optimizing Temperature for Your Sintering Goal
The ideal temperature profile is determined entirely by the desired outcome for the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum density: You will likely need to use a temperature near the upper end of the viable range and a sufficient hold time, while carefully monitoring for excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is controlling microstructure: Pay close attention to the entire thermal profile, as the ramp-up and cooling rates are just as critical as the peak temperature for managing grain size.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Consider using finer starting powders or applying external pressure, as both can allow for the use of lower temperatures and shorter cycle times.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process comes from understanding how the entire temperature journey shapes the material's structure at an atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Phase | Key Function | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Ramp-Up Rate | Prevents thermal shock, ensures uniform heating | Sets stage for uniform densification |
| Peak Temperature & Hold Time | Drives atomic diffusion, neck growth, and pore shrinkage | Determines final density and strength |
| Cooling Rate | Locks in microstructure, prevents cracking | Defines mechanical properties and stress state |
Ready to optimize your sintering process and achieve superior material density and performance?
The precise thermal control discussed in this article is critical for success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment, including high-temperature furnaces, tailored to meet the exacting demands of sintering R&D and production.
Our solutions help you:
- Achieve precise temperature profiles with reliable heating and cooling control.
- Maximize density and control microstructure for stronger, more consistent parts.
- Improve process efficiency with equipment designed for your specific materials and goals.
Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment can enhance your sintering outcomes. Let's build the perfect thermal solution for your laboratory needs.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the factors influencing shrinkage during sintering? Control Dimensional Changes for Precision Parts
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials



















