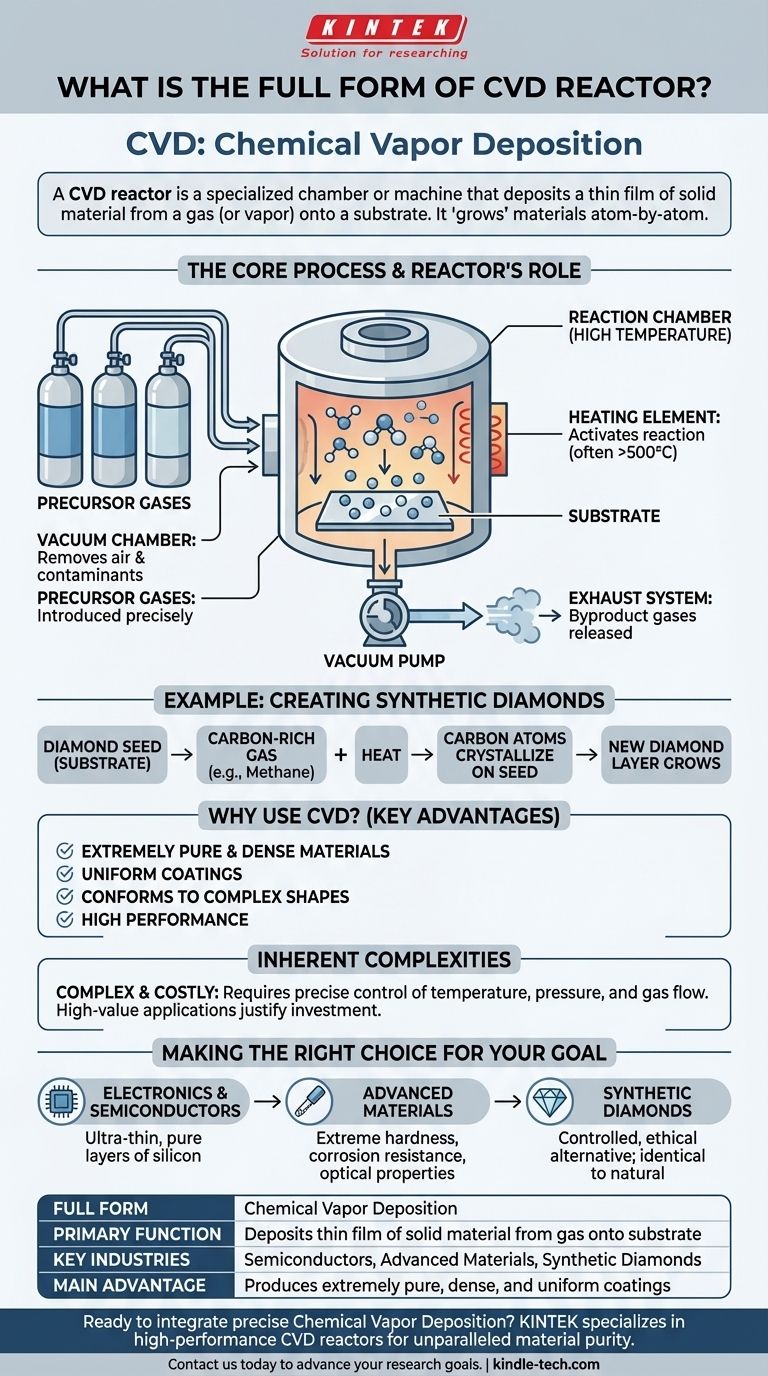
In short, CVD stands for Chemical Vapor Deposition. A CVD reactor is the specialized chamber or machine where this process takes place. It's a controlled environment designed to deposit a thin film of solid material from a gas (or vapor) onto a substrate.
The term "CVD reactor" refers to the equipment used for Chemical Vapor Deposition, a highly precise manufacturing process that "grows" solid materials atom-by-atom from a gaseous state onto a surface.

Understanding the Core Process
What is Chemical Vapor Deposition?
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a technique for creating high-performance, solid materials, often as coatings or thin films. It's fundamentally a process of building from the bottom up.
The process involves introducing specific gases, known as precursors, into a reaction chamber (the reactor).
These gases are then subjected to conditions—such as high temperature—that cause them to react or decompose, depositing a specific solid material onto a target surface, called a substrate.
The Role of the Reactor
The CVD reactor is the heart of the operation. It's a highly controlled environment where all critical parameters are managed.
Key components and functions include:
- A vacuum chamber to remove unwanted air and contaminants.
- A system to introduce precise amounts of precursor gases.
- A heating element to bring the substrate and gases to the required reaction temperature, often above 500°C.
- An exhaust system to remove byproduct gases.
Think of the reactor as a high-tech oven where the "baking" process creates a new solid material on a surface instead of a cake.
A Common Example: Creating Synthetic Diamonds
The creation of synthetic diamonds is a perfect illustration of how a CVD reactor works.
First, a small slice of a diamond, known as a diamond seed, is placed inside the reactor to act as the substrate.
The chamber is then filled with a carbon-rich gas, like methane, and heated.
This high-energy environment breaks down the gas molecules, allowing pure carbon atoms to settle and crystallize on the diamond seed, effectively growing a new, larger diamond layer by layer.
Key Principles and Trade-offs
Why Use CVD?
CVD is favored for its ability to produce materials that are extremely pure, dense, and strong. The resulting films or coatings are uniform and can conform perfectly to complex shapes.
This makes it essential for applications requiring high performance, such as in semiconductors, optical components, and wear-resistant tools.
Inherent Complexities
The primary trade-off with CVD is its complexity and cost. The equipment is sophisticated, and the process requires precise control over temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates.
Any small deviation can impact the quality of the final material. This makes it a highly technical process best suited for high-value applications where performance justifies the investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the role of a CVD reactor helps you grasp why it's used in specific industries.
- If your primary focus is electronics and semiconductors: The CVD reactor is a critical tool for depositing the ultra-thin, pure layers of silicon and other materials that form the basis of microchips.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials: The reactor allows for the creation of coatings that provide extreme hardness, corrosion resistance, or specific optical properties on tools and components.
- If your primary focus is gem-quality diamonds: The CVD process in a reactor offers a controlled, ethical alternative to mining, producing diamonds that are chemically and physically identical to their natural counterparts.
Ultimately, the CVD reactor is a foundational piece of technology that enables the atomic-level construction of advanced materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Full Form | Chemical Vapor Deposition |
| Primary Function | Deposits a thin film of solid material from a gas onto a substrate. |
| Key Industries | Semiconductors, Advanced Materials, Synthetic Diamonds |
| Main Advantage | Produces extremely pure, dense, and uniform coatings. |
Ready to integrate precise Chemical Vapor Deposition into your lab's workflow?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including CVD reactors, to help you achieve unparalleled material purity and coating uniformity. Whether your focus is on semiconductor development, creating advanced material coatings, or synthetic diamond growth, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your high-value applications.
Contact us today to discuss how our CVD technology can advance your research and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the CVD growth process? A Step-by-Step Guide to Chemical Vapor Deposition
- How does a CVD system facilitate electrode materials for microbial fuel cells? Precision Nanomaterial Growth
- What is the difference between sputtering and ion beam deposition? Precision vs. Throughput for Your Thin Films
- What is the working of CVD technique? A Step-by-Step Guide to Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What are the applications of physical vapor deposition method? Unlock Superior Thin-Film Performance
- What does flexibility mean in the context of a deposition system? Optimize Your R&D Adaptability
- How are thin films manufactured? A Guide to Physical and Chemical Deposition Methods
- What is material deposition in manufacturing? Unlock Design Freedom with Additive Processes



















