At its core, a press machine is designed to generate a significant compressive force to shape, bend, crush, or assemble materials. A hydraulic press, a common and powerful variant, achieves this by using a confined fluid to multiply a small initial effort into an immense output force. This is accomplished by leveraging a fundamental principle of fluid dynamics.
The primary function of a hydraulic press is not just to create force, but to achieve force multiplication. It masterfully exploits Pascal's Law, where a small force applied to a small area generates a pressure that, when distributed across a larger area, results in a proportionally larger output force.
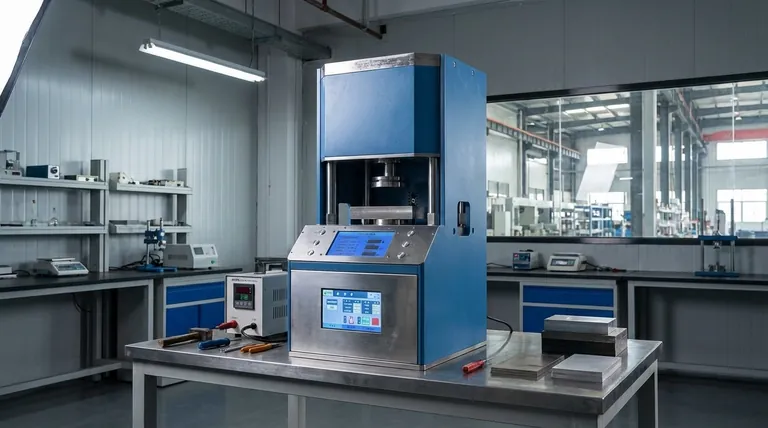

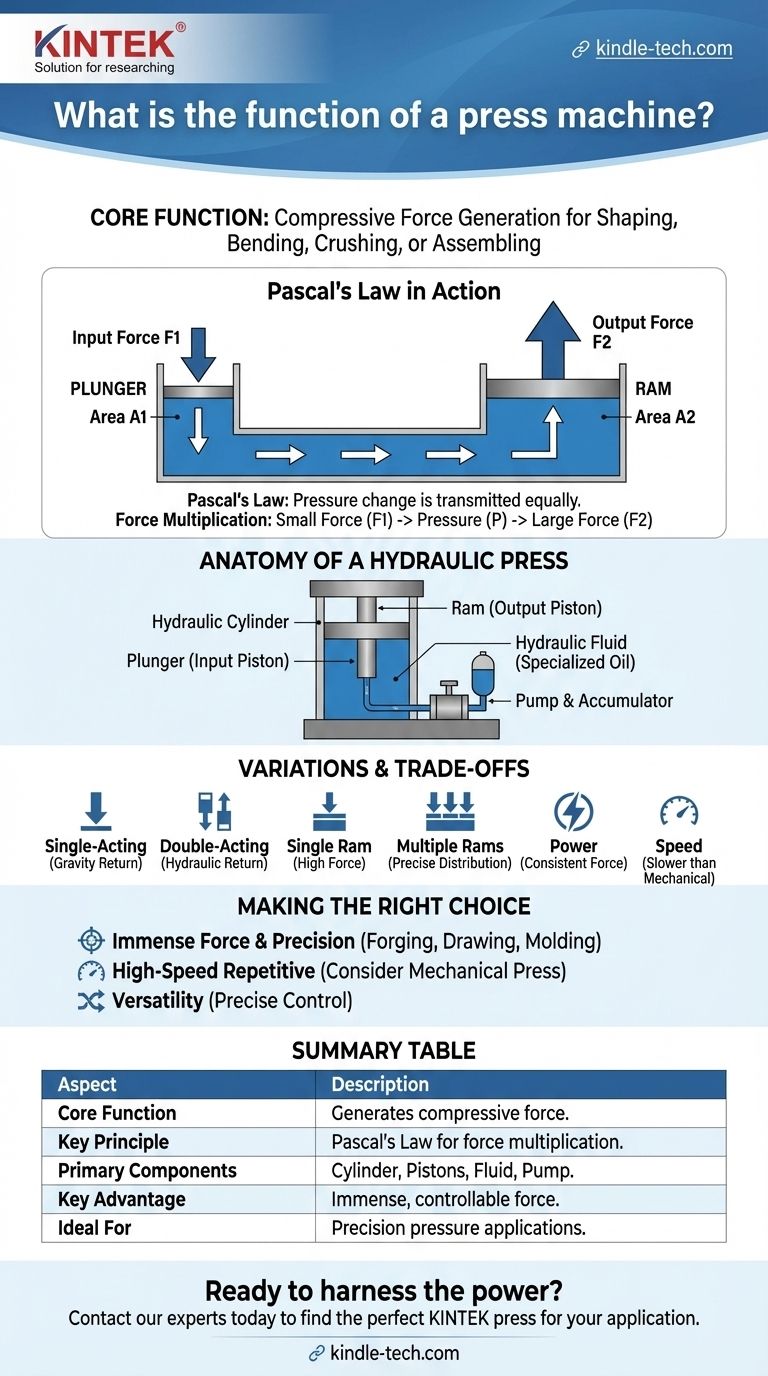
The Core Principle: Pascal's Law in Action
To truly understand a hydraulic press, you must first understand the physics that makes it possible. The entire operation hinges on a single, elegant principle discovered in the 17th century.
What is Pascal's Law?
Pascal's Law states that a pressure change at any point in a confined, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally throughout the fluid.
Think of squeezing a sealed water bottle. The pressure you apply with your hand isn't just felt where your fingers are; it's distributed evenly to every interior surface of the bottle.
The Two-Piston System
A hydraulic press uses this principle with two interconnected cylinders, each with a piston, but of different sizes.
A small piston, often called the plunger, is where the initial, smaller force is applied. A much larger piston, called the ram, is where the massive output force is generated.
How Force is Multiplied
Because the two pistons exist in the same sealed hydraulic system, the pressure on the small plunger is the same as the pressure on the large ram.
Since Pressure = Force / Area, a small force on the small plunger's area creates the same pressure that acts on the large ram's area. To maintain that equal pressure, the force exerted by the large ram must be proportionally greater.
This mechanical advantage is what allows a press to turn a modest input from a pump into a force capable of shaping solid steel.
Anatomy of a Hydraulic Press
While the principle is simple, a functional press relies on several key components working in concert to deliver controlled power.
The Hydraulic Cylinder and Pistons
This is the heart of the machine. The cylinders contain the fluid, and the plunger (input piston) and ram (output piston) move within them to transfer and multiply the force.
The Hydraulic Fluid
The medium used to transfer the pressure is an incompressible fluid, most commonly a specialized oil. Its inability to be easily compressed is critical for the efficient transmission of pressure throughout the system.
The Pump and Accumulator
A pump provides the initial flow of hydraulic fluid, creating the pressure needed to move the plunger.
In many systems, a hydraulic accumulator acts like a rechargeable battery. It stores high-pressure fluid from the pump and can release it quickly when a strong, rapid thrust is required.
Understanding the Variations and Trade-offs
Not all hydraulic presses are identical. Their design is tailored to specific tasks, which introduces important trade-offs between control, speed, and complexity.
Single-Acting vs. Double-Acting
A single-acting cylinder uses hydraulic pressure to push the ram in one direction (usually down). The return stroke relies on gravity or springs.
A double-acting cylinder uses hydraulic power for both the extension and retraction strokes, offering greater control but at a higher complexity.
Single Ram vs. Multiple Rams
While a single large ram can deliver immense force, some presses use multiple smaller rams. This configuration allows for more precise control over the distribution of force across the workpiece.
Power vs. Speed
The defining characteristic of a hydraulic press is its ability to deliver a consistent, controllable force throughout its stroke. However, they are generally not as fast as mechanical presses, which excel at high-speed stamping operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the function of a press allows you to select the right tool for the job. The hydraulic press is a master of controlled, powerful force.
- If your primary focus is immense force and precision: A hydraulic press is the ideal choice for applications like forging, deep drawing, and molding, where consistent pressure is paramount.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repetitive production: You should evaluate if the cycle time of a hydraulic press meets your needs, as a mechanical press may be better suited for simple stamping.
- If your primary focus is versatility: The ability to precisely control force, speed, and stroke length makes the hydraulic press one of the most adaptable forming tools available.
By understanding the principle of force multiplication, you can effectively leverage the immense power and control a press machine offers.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Generates compressive force to shape, bend, crush, or assemble materials. |
| Key Principle | Pascal's Law: Force multiplication via hydraulic fluid pressure. |
| Primary Components | Hydraulic cylinder, pistons (plunger & ram), hydraulic fluid, pump. |
| Key Advantage | Delivers immense, controllable force throughout the stroke. |
| Ideal For | Forging, deep drawing, molding, and applications requiring precise pressure control. |
Ready to harness the power of a hydraulic press in your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including robust press machines designed for precision and durability. Whether you're in materials testing, sample preparation, or R&D, our solutions deliver the controlled force you need. Contact our experts today to find the perfect press for your specific application and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- How much force can a hydraulic press exert? Understanding its immense power and design limits.
- How does a vacuum furnace environment influence sintered Ruthenium powder? Achieve High Purity and Theoretical Density
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What is the role of a laboratory-grade heated hydraulic press in MEA fabrication? Optimize Fuel Cell Performance



















