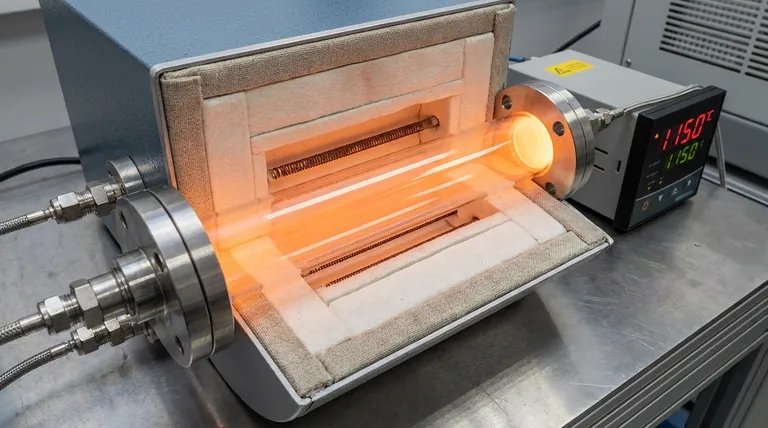
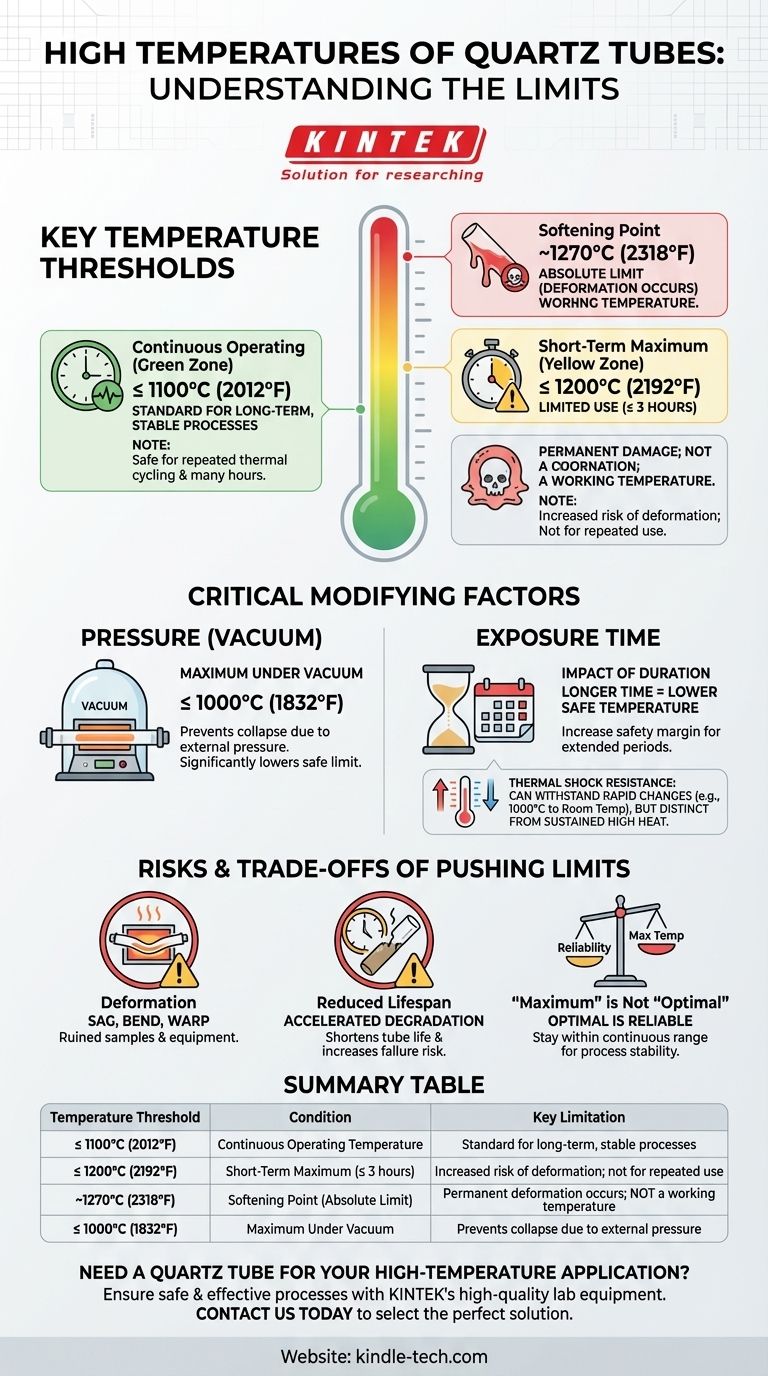
For most applications, the maximum continuous operating temperature of a transparent quartz tube is approximately 1100°C (2012°F). While it can be pushed to higher temperatures for short periods, factors like pressure and duration are critical to prevent permanent damage or failure.
The physical softening point of quartz is near 1270°C, but this is not a safe operating temperature. For reliable and repeatable results, you must operate well below this limit, treating 1100°C as the standard for continuous use and 1200°C as a strict short-term maximum.

Understanding the Key Temperature Thresholds
To use a quartz tube safely, it's essential to understand the difference between its continuous, short-term, and absolute physical limits.
The Continuous Operating Temperature (≤ 1100°C)
This is the most important number for general use. For processes that require heating for many hours or repeated thermal cycling, staying at or below 1100°C ensures the tube maintains its structural integrity and longevity.
The Short-Term Maximum Temperature (≤ 1200°C)
Quartz tubes can be used at temperatures up to 1200°C, but only for very limited periods. As a rule, this exposure should not exceed three hours.
Operating at this level places significant stress on the material, bringing it closer to its softening point and increasing the risk of deformation over time.
The Softening Point (~1270°C)
This is the temperature at which the quartz begins to lose its rigidity and will deform under its own weight. It is an absolute physical limit and should never be considered a working temperature. Reaching this point will permanently damage the tube.
Critical Factors That Modify the Limit
The "maximum temperature" is not a single number. It changes based on the conditions of your specific application, primarily pressure and time.
The Impact of Pressure
The presence of a vacuum dramatically lowers the safe operating temperature. When operating a tube furnace under vacuum, the maximum temperature should be reduced to 1000°C.
The external atmospheric pressure can cause a softened tube to collapse inward, so a lower temperature limit is crucial for safety and success.
The Role of Exposure Time
As noted, time is a critical variable. A process running at 1150°C for 30 minutes is far less risky than one running at that same temperature for 5 hours.
The longer the exposure to high temperatures, the more you should lower your operating setpoint to create a wider safety margin.
The Benefit of Thermal Shock Resistance
Quartz has excellent thermal shock resistance, meaning it can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. It can be heated to 1000°C and then cooled to room temperature very quickly.
This property relates to the material's durability during heating and cooling cycles, but it is distinct from its ability to withstand a high temperature for a sustained period.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Pushing a quartz tube to its absolute limit is rarely a good strategy and involves significant trade-offs that can compromise your work.
The Primary Risk: Deformation
As a quartz tube approaches its softening point, it can begin to sag, bend, or warp. In a furnace, this can ruin the sample, damage the heating elements, and make the tube impossible to remove or reuse.
The Consequence: Reduced Lifespan
Consistently operating near the maximum temperature limit, even for short durations, will shorten the lifespan of the tube. It accelerates the degradation process and makes the material more susceptible to failure over time.
The Reality: "Maximum" is Not "Optimal"
The optimal operating temperature is one that achieves your goal reliably and repeatedly. For most, this means staying within the continuous use range (≤ 1100°C) to ensure process stability and preserve the integrity of your equipment.
How to Determine Your Safe Operating Temperature
Use the following guidelines to select the right temperature limit for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is process stability and long-term use: Do not exceed 1100°C for any process lasting more than a few hours.
- If your primary focus is a short, high-temperature experiment: You may operate up to 1200°C, but for no longer than three hours and with careful monitoring.
- If your primary focus is any process under vacuum: Your absolute maximum temperature should be 1000°C to prevent structural failure.
By respecting these material and environmental limits, you can ensure your equipment remains safe and your results are reliable.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Threshold | Condition | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| ≤ 1100°C (2012°F) | Continuous Operating Temperature | Standard for long-term, stable processes |
| ≤ 1200°C (2192°F) | Short-Term Maximum (≤ 3 hours) | Increased risk of deformation; not for repeated use |
| ~1270°C (2318°F) | Softening Point (Absolute Limit) | Permanent deformation occurs; NOT a working temperature |
| ≤ 1000°C (1832°F) | Maximum Under Vacuum | Prevents collapse due to external pressure |
Need a Quartz Tube for Your High-Temperature Application?
Ensure your lab processes are both safe and effective with the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including quartz tubes designed for reliability and performance.
Contact us today to discuss your specific temperature requirements and let our experts help you select the perfect solution for reliable, repeatable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of temperature sensors? Choose the Right Sensor for Your Application
- What specific function does a laboratory electric constant temperature drying oven serve? | Coal Gangue Acid Leaching
- What are the sources of sputtering? A Guide to the Target and Ion Source
- What is the role of a laboratory heating system in electrolyte ohmic resistance? Optimize Precise Thermal Analysis
- What is the working temperature of quartz glass? Master Its High-Temp Limits & Applications
- What role does an ultrasonic cleaner play in the pre-treatment of 4140 steel? Ensure Uniform Nitriding Activation
- What temperature does quartz tube soften? Master Safe Operating Limits for Your Lab
- What are quartz glass tubes used for? Essential for High-Temp, High-Purity Applications



















