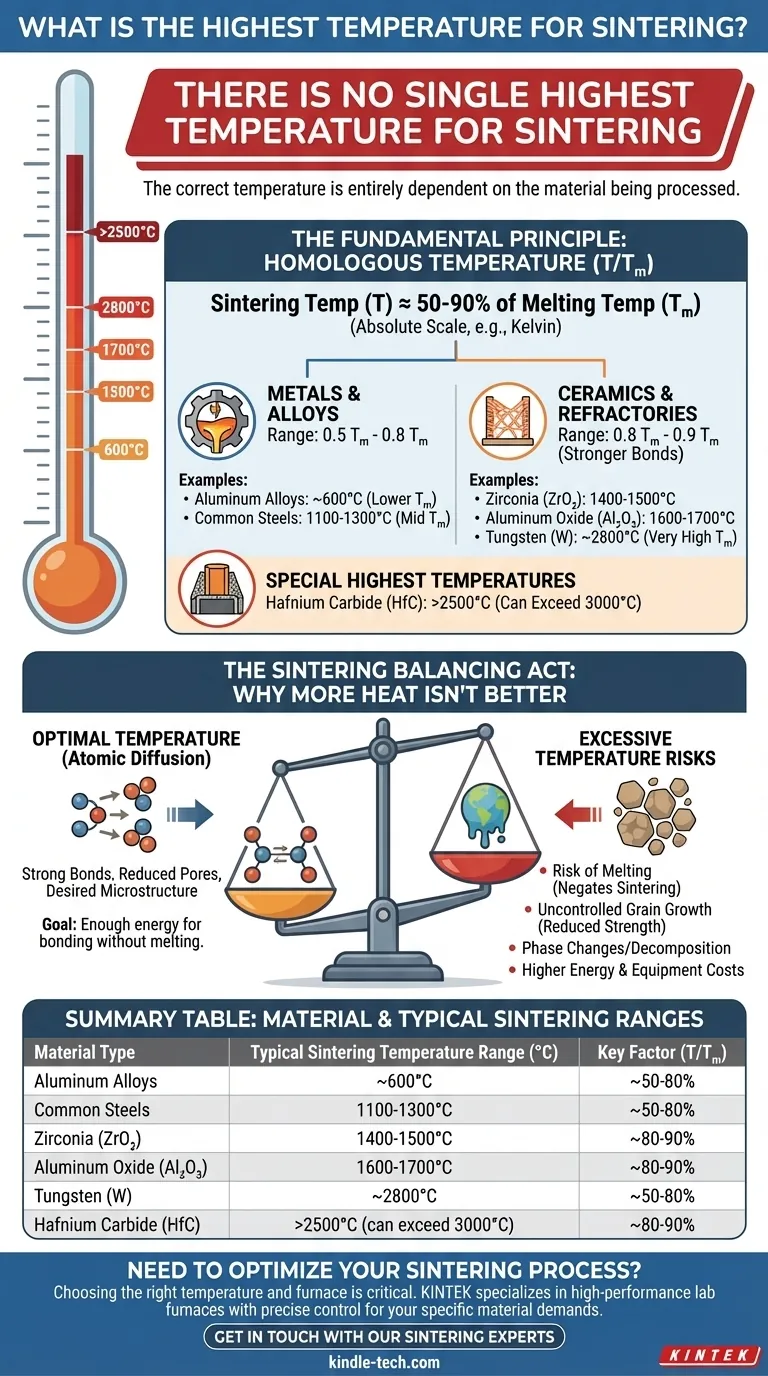
There is no single highest temperature for sintering, as the correct temperature is entirely dependent on the material being processed. Sintering is a process of atomic diffusion that occurs below the material's melting point, so the "highest" viable sintering temperature for a refractory metal like Tungsten (around 2800°C) will be drastically different from that of an aluminum alloy (around 600°C).
The critical takeaway is that sintering temperature is not an absolute value but a relative one, typically falling between 50% and 90% of the material's absolute melting temperature. The goal is to provide enough thermal energy to enable atoms to bond across particle boundaries without causing the material to melt or its microstructure to degrade.

The Fundamental Principle of Sintering Temperature
To understand why there's no universal temperature, you must first grasp the core mechanism of sintering. The process does not rely on melting but on solid-state diffusion.
Activating Atomic Diffusion
Heat provides the kinetic energy that allows atoms on the surfaces of powder particles to move. This movement, or diffusion, enables atoms to migrate across the boundaries between particles, forming strong metallic or ceramic bonds and gradually eliminating the pores between them.
The "Homologous Temperature" Rule
A reliable guideline for estimating the sintering temperature is the concept of homologous temperature (T/Tₘ), where T is the sintering temperature and Tₘ is the melting temperature, both expressed in an absolute scale like Kelvin.
For most metals, effective sintering occurs between 0.5 Tₘ and 0.8 Tₘ.
For ceramics, which have stronger atomic bonds and slower diffusion rates, the range is typically higher, often between 0.8 Tₘ and 0.9 Tₘ.
Sintering Temperatures for Common Materials
The vast differences in melting points lead to an equally vast range of sintering temperatures.
Metals and Alloys
Common steels are sintered around 1100-1300°C (2012-2372°F). In contrast, Tungsten, with its extremely high melting point of 3422°C, requires sintering temperatures approaching 2800°C (5072°F), pushing the limits of furnace technology.
High-Performance Ceramics
Technical ceramics demand very high temperatures to achieve full density. Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), a widely used ceramic, is typically sintered between 1600-1700°C (2912-3092°F). Zirconia (ZrO₂) is often processed in a slightly lower range of 1400-1500°C (2552-2732°F).
The Highest Temperatures: Refractory Carbides
The absolute highest sintering temperatures are reserved for ultra-high temperature ceramics (UHTCs) and refractory compounds. Materials like Hafnium Carbide (HfC), with a melting point near 3900°C, can require sintering temperatures well above 2500°C and sometimes even exceeding 3000°C using specialized techniques like spark plasma sintering.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why More Heat Isn't Better
Simply increasing the temperature is a flawed strategy that often leads to inferior results. The process is a careful balance.
The Risk of Melting
The most obvious risk is exceeding the material's solidus temperature. This causes partial or complete melting, which negates the purpose of sintering. The resulting component would be cast, not sintered, possessing a completely different and uncontrolled microstructure.
Uncontrolled Grain Growth
Even below the melting point, excessive temperature (or holding time) promotes grain growth. As small grains merge into larger ones, the material's mechanical properties, particularly strength and hardness, often decrease significantly.
Phase Changes and Decomposition
For some complex alloys or compounds, high temperatures can trigger undesirable phase transformations. In other cases, a material might decompose or react with the furnace atmosphere before it ever reaches its melting point.
Practical and Economic Costs
Higher temperatures demand more advanced and expensive furnace systems with specialized heating elements and insulation. The energy consumption and maintenance costs escalate dramatically, making the process economically unviable if not strictly necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal sintering temperature is always a function of your specific material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density: You will likely operate at the higher end of the material's recommended sintering range, but you must carefully control the time at temperature to prevent excessive grain growth.
- If your primary focus is preserving a fine microstructure for superior mechanical properties: You may use a lower temperature for a longer duration or employ pressure-assisted techniques (like Hot Isostatic Pressing) to enhance diffusion without excessive heat.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production: You must find the lowest possible temperature that still achieves the minimum required density and performance specifications for your application.
Ultimately, determining the correct sintering temperature is a precise balancing act between promoting atomic diffusion and preventing microstructural damage.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Typical Sintering Temperature Range (°C) | Key Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | ~600°C | ~50-80% of melting point (T/Tₘ) |
| Common Steels | 1100-1300°C | ~50-80% of melting point (T/Tₘ) |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | 1400-1500°C | ~80-90% of melting point (T/Tₘ) |
| Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃) | 1600-1700°C | ~80-90% of melting point (T/Tₘ) |
| Tungsten (W) | ~2800°C | ~50-80% of melting point (T/Tₘ) |
| Hafnium Carbide (HfC) | >2500°C (can exceed 3000°C) | ~80-90% of melting point (T/Tₘ) |
Need to Optimize Your Sintering Process?
Choosing the right sintering temperature is a precise balancing act between promoting atomic diffusion and preventing microstructural damage. The furnace you use is just as critical as the temperature you set.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment designed to meet the exact demands of your sintering applications, whether you're working with common steels or ultra-high temperature ceramics. Our solutions provide the precise temperature control and uniform heating necessary to achieve optimal density and microstructure for your specific materials.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise and equipment can help you achieve superior sintering results. Let's find the perfect thermal solution for your laboratory needs.
Get in Touch with Our Sintering Experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















