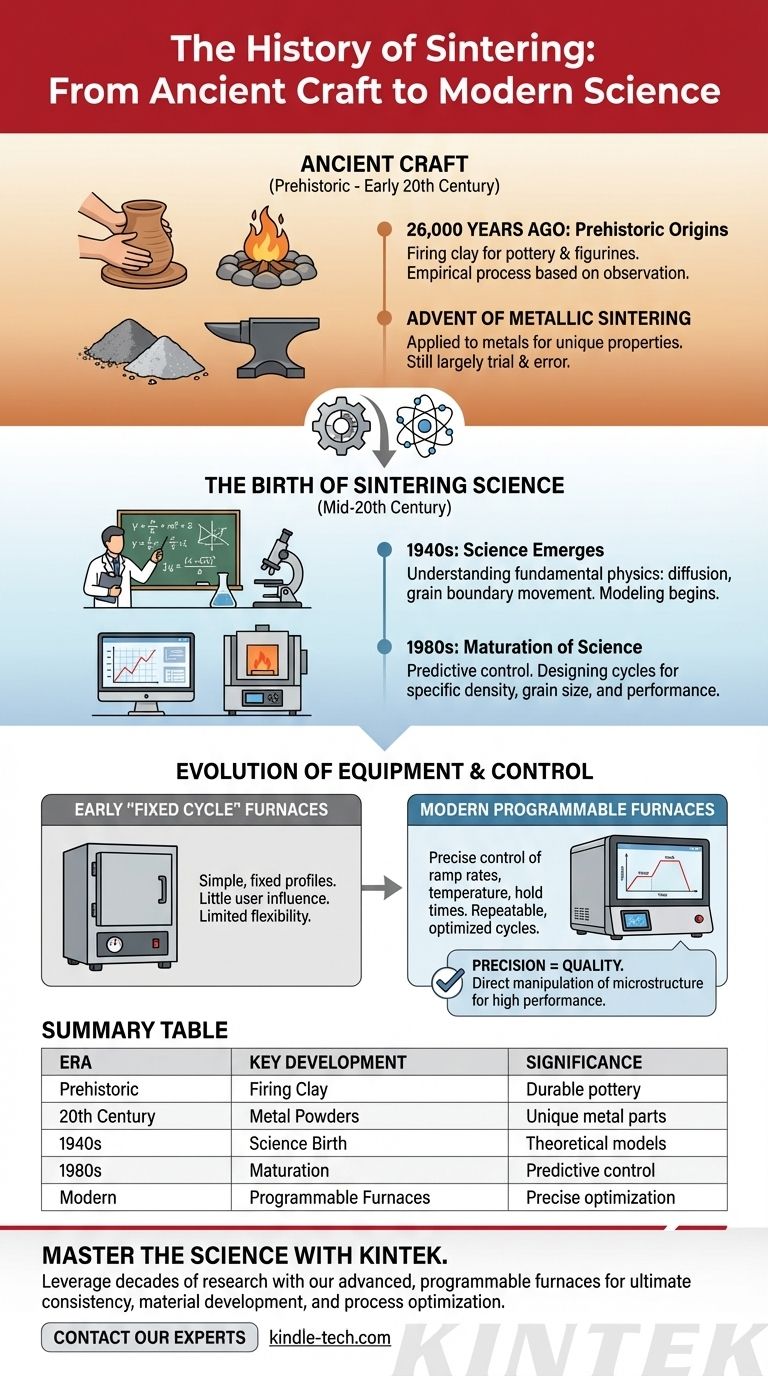
The practice of sintering is ancient, with its roots in ceramics dating back an incredible 26,000 years. This long history represents a slow journey from an empirical craft to a precise, controllable science. While early artisans fired clay based on observation, the true scientific understanding of sintering only began to emerge in the 1940s, paving the way for the advanced industrial applications we use today.
Sintering's history is best understood as a two-part evolution. It began as a prehistoric craft for basic materials and was later transformed into a precise, scientific manufacturing process, with its modern power unlocked by a deep understanding of physics and the development of highly controllable equipment.

From Ancient Craft to Industrial Technique
The core concept of sintering—using heat to bond particles into a solid mass without melting—is not a modern invention. Its application, however, has become vastly more sophisticated over millennia.
The Prehistoric Origins of Ceramic Sintering
The earliest known use of sintering dates back 26,000 years. This involved firing clay and earthen materials to create pottery and figurines.
This was an entirely empirical process. Early humans knew that heating clay in a fire would make it hard and durable, but they had no knowledge of the underlying atomic diffusion or particle necking that was occurring.
The Advent of Metallic Sintering
The application of sintering to metals is a much more recent development in its long history. Engineers and metallurgists realized the same principles used for ceramics could be applied to metal powders.
This opened the door to creating metal parts with unique properties, often for applications where melting and casting were impractical or produced inferior results.
Modern Materials: Cemented Carbides
Relatively modern materials like cemented carbides represent a pinnacle of sintering application. These materials combine a hard ceramic phase (like tungsten carbide) with a tough metallic binder (like cobalt).
Creating these advanced composites is only possible through the precise control offered by modern sintering science, demonstrating how far the technique has come from its prehistoric origins.
The Birth of Sintering Science
For most of its history, sintering was a "black box" process driven by trial and error. The 20th century marked a critical turning point where craft became science.
The Turning Point: The 1940s
The scientific study of sintering began in earnest in the 1940s. Researchers started to investigate the fundamental physics behind the process.
Instead of just observing results, they began to model the mechanisms of mass transport, atomic diffusion, and grain boundary movement. This work laid the theoretical foundation for controlling the final properties of a sintered part.
Maturation of the Science: The 1980s
By the mid-1980s, the science of sintering had matured significantly. The theoretical models developed decades earlier were refined, allowing for predictive control over the process.
This maturation meant engineers could design a sintering cycle—including temperature, time, and atmosphere—to achieve a specific density, grain size, and mechanical performance. The process was no longer a guess, but an engineered solution.
The Evolution of Equipment and Control
The journey from craft to science is mirrored perfectly in the evolution of the sintering furnace. The equipment directly reflects the level of understanding and control available at the time.
The "Fixed Cycle" Era: Early Furnaces
Early industrial sintering furnaces were simple and rigid. They typically offered a single, fixed heating profile or, at best, a few pre-programmed cycles.
The user had little to no ability to influence the process. The trade-off was simplicity at the cost of flexibility, optimization, and the ability to work with a wide range of materials.
The Dawn of Programmability: Modern Furnaces
Modern sintering furnaces are highly sophisticated, programmable instruments. Users can precisely define every stage of the process.
This includes setting specific ramp rates (how fast to heat up), the final temperature, the hold time (soak time), and the cooling rates. Advanced furnaces can also store dozens of unique profiles, ensuring absolute repeatability for specific production runs.
The Impact of Control on Quality
This leap in equipment control is the practical application of the matured science. Precise control over the thermal profile allows for direct manipulation of the part's final microstructure. This is the key to achieving high density, preventing unwanted grain growth, and maximizing the mechanical properties of the final component.
How This History Informs Your Process
Understanding this evolution from an ancient art to a modern science is critical for leveraging the technology effectively today. It explains why process control is paramount.
- If your primary focus is consistency and high performance: Leverage the full programmability of modern furnaces, applying the scientific principles of diffusion and grain growth to design cycles that optimize your part's final microstructure.
- If your primary focus is developing new materials: Recognize that sintering is a mature science, which means predictive models can guide your experiments, saving significant time compared to the purely empirical methods of the past.
- If your primary focus is basic component fabrication: Acknowledge that even simple applications benefit immensely from the repeatability that modern equipment provides—a direct result of the historical demand for more process control.
By appreciating this journey, you are better equipped to master the process and control your outcomes with scientific precision.
Summary Table:
| Era | Key Development | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Prehistoric | Firing of clay (26,000 years ago) | Empirical craft; created durable pottery |
| 20th Century | Application to metal powders | Enabled creation of unique metal parts |
| 1940s | Birth of sintering science | Theoretical models for diffusion and grain growth |
| 1980s | Maturation of science | Predictive control over density and properties |
| Modern | Programmable furnaces | Precise control over thermal profiles for optimization |
Master the science of sintering with KINTEK.
Our advanced, programmable sintering furnaces put decades of scientific research and development at your fingertips. Whether your focus is achieving ultimate consistency in production, developing new materials, or optimizing your current process, KINTEK's lab equipment delivers the precise control you need to replicate results and achieve superior material properties.
Ready to control your outcomes with scientific precision? Contact our sintering experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and air oven? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
- How do you control a muffle furnace? Master Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- What are the conditions for a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety, Performance, and Longevity
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and a normal furnace? Ensuring Sample Purity with Indirect Heating
- What are the different types of laboratory furnaces? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Application



















