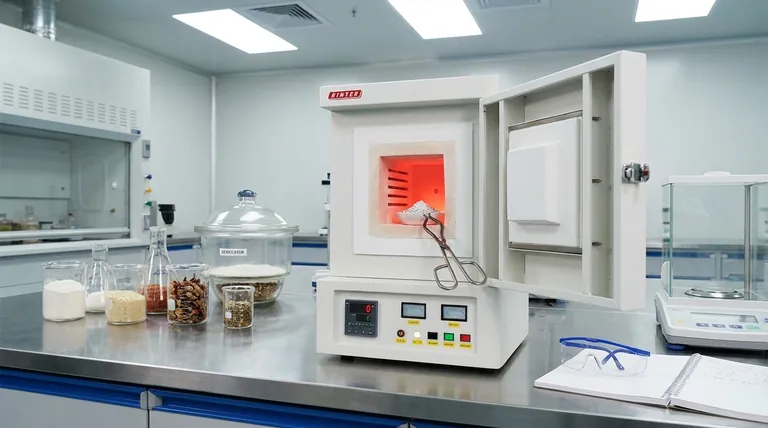
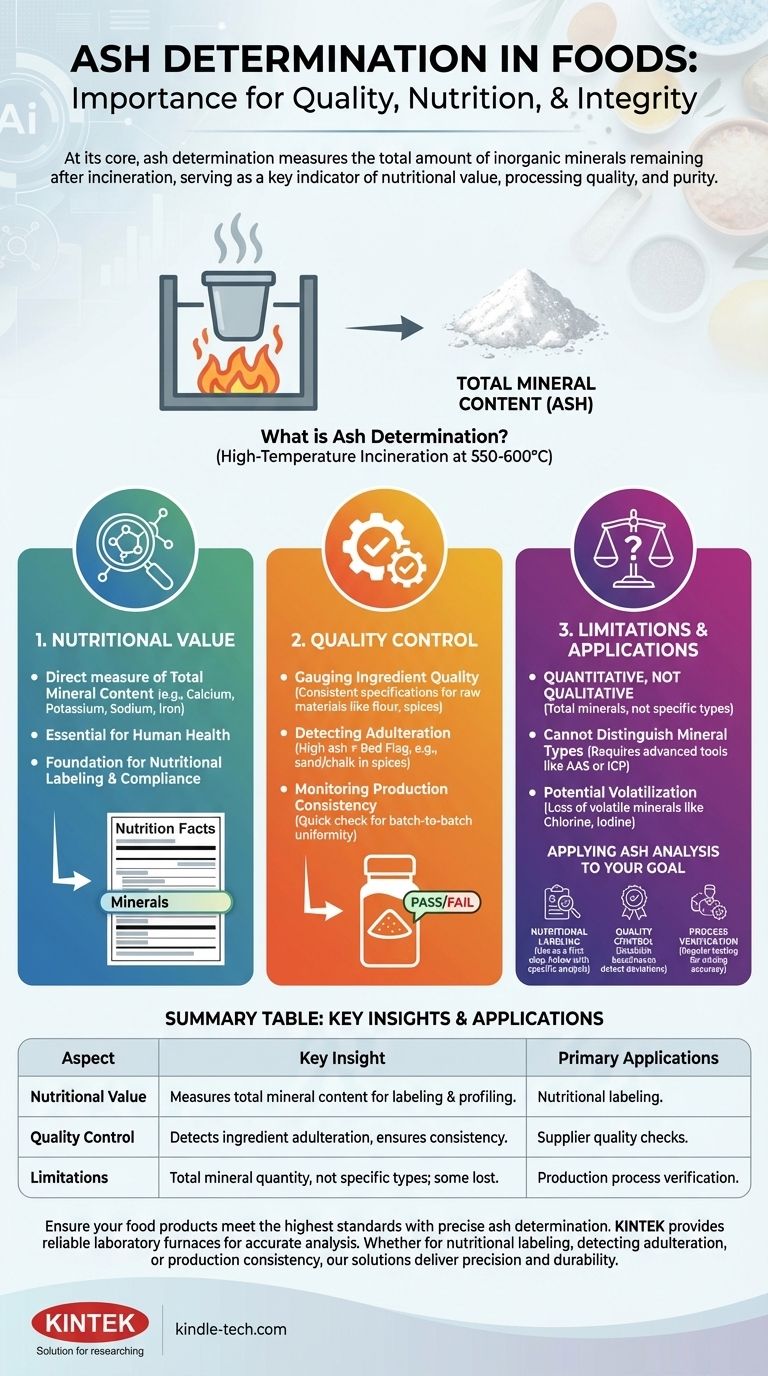
At its core, ash determination in food science is the process of measuring the total amount of inorganic minerals remaining after all organic matter has been burned away. This simple measurement serves as a fundamental indicator of a food's nutritional value, processing quality, and overall purity.
While ash determination provides a single number representing total mineral content, its true importance lies in what that number reveals about a food's nutritional profile, production integrity, and potential adulteration.

Ash as a Measure of Nutritional Value
Ash is what remains after a food sample is subjected to high temperatures (typically 550-600°C), a process called incineration. This residue is primarily composed of inorganic minerals.
The Link to Mineral Content
The ash content is a direct measure of the total mineral content in a food. These minerals, such as calcium, potassium, sodium, and iron, are essential nutrients for human health.
Foundation for Nutritional Labeling
For food manufacturers, determining ash content is a crucial first step in nutritional analysis. It provides the total mineral figure, which is a component of the overall nutritional profile required for labeling and compliance.
A Critical Tool for Quality Control
Beyond nutrition, ash measurement is a powerful and efficient tool for maintaining quality and safety standards throughout the food production chain.
Gauging Ingredient Quality
The ash content of raw materials like flour, spices, or juice concentrates should be consistent. A deviation from the established specification can indicate a lower quality ingredient or a problem with the supplier's process.
Detecting Adulteration
An abnormally high ash content is a classic red flag for adulteration. For example, ground spices with a higher-than-expected ash value may have been diluted with sand, chalk, or other cheap inorganic fillers.
Monitoring Production Consistency
For multi-ingredient products, a consistent ash value in the final product confirms that the formulation and mixing process are performing correctly. It is a quick check to ensure batch-to-batch uniformity.
Understanding the Limitations of Ash Analysis
While invaluable, it is critical to understand what ash determination does and does not tell you. Its power lies in its simplicity, but that is also its main limitation.
It's a Total, Not a Specific, Measurement
Ash analysis provides a quantitative, but not qualitative, result. It tells you the total amount of minerals present but does not identify which specific minerals are there or in what quantity.
It Cannot Distinguish Mineral Types
An ash test cannot differentiate between a nutritionally valuable mineral like calcium and a less desirable one like sodium. For that, more advanced and expensive techniques like Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) or Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) are required.
Potential for Volatilization
The high heat of incineration can cause some volatile minerals (such as chlorine, iodine, and selenium) to be lost. This can lead to a slight underestimation of the true total mineral content, a factor that must be understood when interpreting results.
Applying Ash Analysis to Your Objective
How you use ash data depends entirely on your goal. It is a versatile tool that can be applied in different ways to ensure product integrity.
- If your primary focus is nutritional labeling: Use total ash as a fundamental first step, but recognize it must be followed by specific mineral analysis for accurate claims on nutrients like calcium or iron.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Establish a baseline ash specification for your raw materials and finished products to quickly and cost-effectively detect deviations and potential adulteration.
- If your primary focus is process verification: Regularly test finished product ash content to ensure your batching and mixing systems are operating with consistent accuracy.
Ultimately, ash determination is a foundational, cost-effective analysis that provides a powerful snapshot of a food product's overall integrity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Nutritional Value | Measures total mineral content (e.g., calcium, potassium) for labeling and profiling. |
| Quality Control | Detects ingredient adulteration (e.g., sand in spices) and ensures batch consistency. |
| Limitations | Provides total mineral quantity, not specific types; volatile minerals may be lost during incineration. |
| Primary Applications | Nutritional labeling, supplier quality checks, and production process verification. |
Ensure your food products meet the highest standards of quality and safety with precise ash determination. KINTEK provides reliable laboratory furnaces and equipment essential for accurate ash content analysis. Whether you're focused on nutritional labeling, detecting adulteration, or maintaining production consistency, our solutions deliver the precision and durability your lab needs. Contact us today to learn how KINTEK can support your laboratory's quality control and analytical workflows!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the acceptance criteria for muffle furnace? Ensure Safety, Performance & Success
- How is a muffle furnace used for sample digestion? A Guide to Dry Ashing for Accurate Analysis
- How do you keep a sample in a muffle furnace? A Guide to Safe and Accurate Placement
- How hot does a muffle furnace get? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Lab
- How do you run a muffle furnace? Master the Step-by-Step Process for Safe, Precise Results



















