In chemistry, the melting point of a substance is one of its most fundamental and revealing physical properties. Determining this value is a rapid, inexpensive, and powerful technique used for two primary purposes: to help identify an unknown compound and, more importantly, to assess its purity. A pure crystalline solid will melt at a precise temperature over a very narrow range, while an impure substance will melt at a lower temperature and over a much broader range.
The core value of determining a melting point lies in what it tells you about a substance’s identity and integrity. A sharp, predictable melting point is a hallmark of purity, whereas a depressed and broad melting range is a clear indicator of impurities.
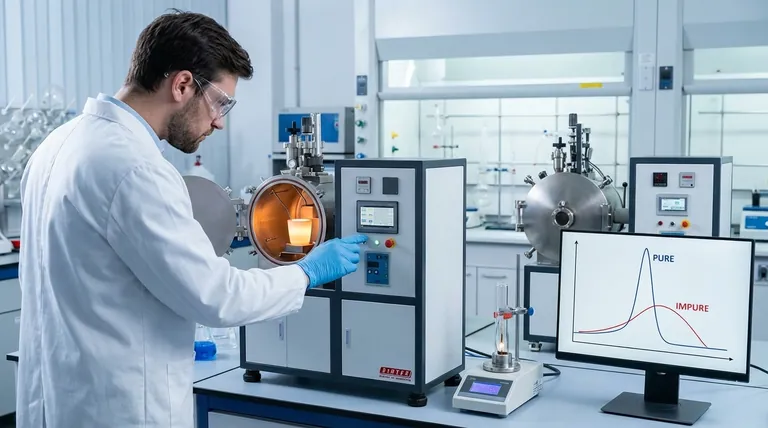

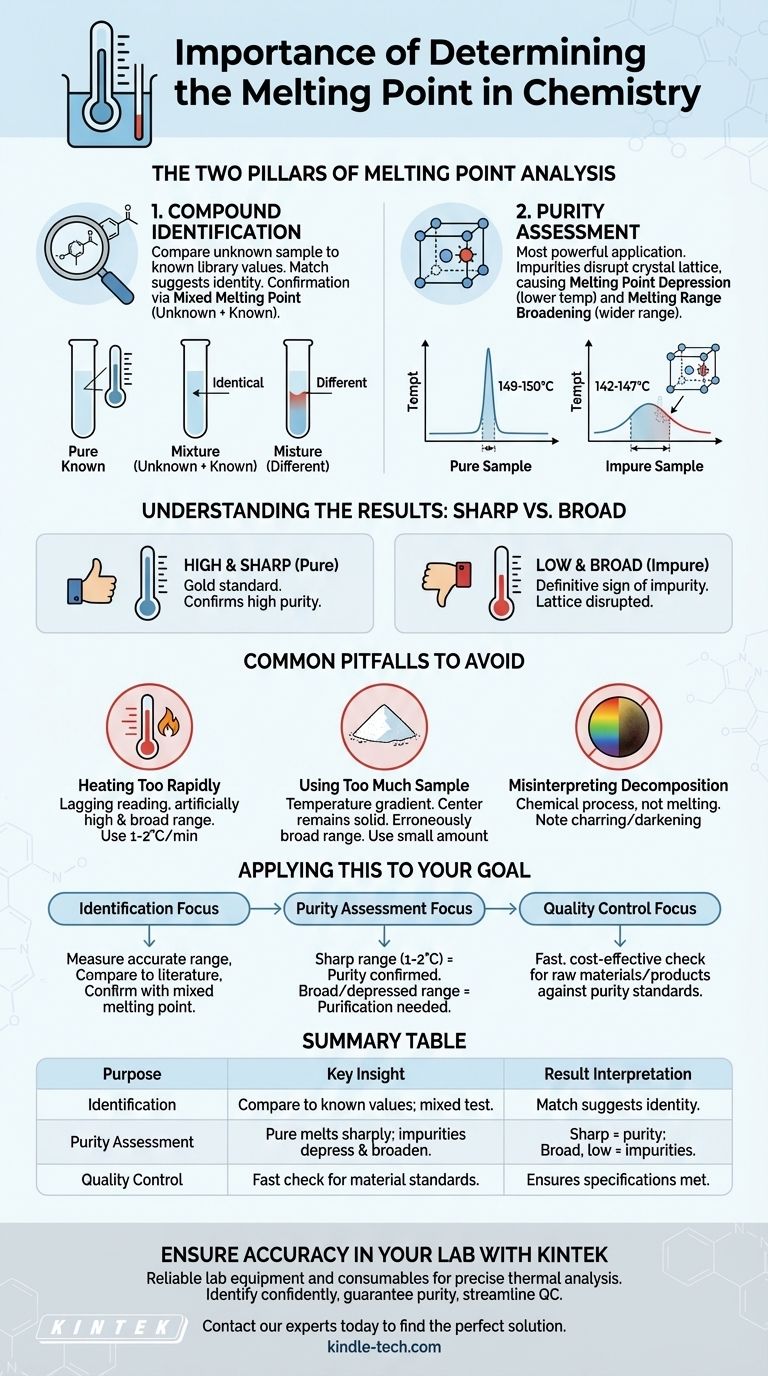
The Two Pillars of Melting Point Analysis
The melting point is the specific temperature at which a substance transitions from a solid to a liquid state. This temperature is a direct result of the energy required to break the forces holding the molecules together in a fixed, crystalline lattice.
Pillar 1: Compound Identification
Every pure crystalline compound has a characteristic and reproducible melting point. This value is a physical constant, much like its boiling point or density.
Scientists can measure the melting point of an unknown sample and compare it to a vast library of known values. A match suggests a possible identity for the compound.
For confirmation, a technique called mixed melting point is often used. The unknown substance is mixed with a small amount of a pure, known sample. If the two are identical, the melting point of the mixture will be sharp and unchanged. If they are different, the mixture will exhibit melting point depression.
Pillar 2: Purity Assessment
This is the most common and powerful application of melting point analysis. The presence of even small amounts of an impurity can significantly alter a substance's melting behavior.
This phenomenon is known as melting point depression. Impurities disrupt the uniform crystal lattice of the solid. This weakened, disorganized structure requires less thermal energy to break apart, causing the substance to begin melting at a lower temperature than its pure form.
Furthermore, impurities cause the melting to occur over a wider temperature range, a phenomenon called melting range broadening. A pure substance typically melts over a very sharp range (often just 1-2°C), while an impure sample might melt over a range of 5°C, 10°C, or even more.
Understanding the Results: Sharp vs. Broad
The data from a melting point apparatus provides immediate insight into the nature of your sample.
A High and Sharp Melting Point
This is the gold standard and indicates a high degree of purity. For example, if you expect a compound to melt at 150°C and it melts cleanly over a range of 149-150°C, you can be confident in its purity.
A Low and Broad Melting Point
This is a definitive sign of impurity. If that same compound melts over a range of 142-147°C, it is clearly contaminated. The lower temperature and wider range are direct consequences of impurities disrupting the crystal lattice.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While the technique is straightforward, inaccurate results can arise from poor procedure. These are the most common errors.
Heating Too Rapidly
If the sample is heated too quickly, the thermometer reading will lag behind the actual temperature of the sample. This will result in an observed melting range that is artificially high and broad, potentially leading you to misinterpret a pure sample as impure. A slow, controlled heating rate (1-2°C per minute) is critical for accuracy.
Using Too Much Sample
A large sample creates a temperature gradient within the substance itself. The part of the sample closest to the heat source will melt first, while the center remains solid. This leads to an erroneously broad melting range. Only a small, tightly packed amount of material should be used.
Misinterpreting Decomposition
Some compounds do not melt but instead decompose upon heating. This is often indicated by a color change (like charring or darkening) and is a distinct chemical process, not a physical phase change. It's important to note decomposition rather than recording it as a melting point.
Applying This to Your Goal
Your reason for measuring the melting point dictates how you interpret the result.
- If your primary focus is identifying an unknown compound: Measure its melting range accurately and compare it to literature values, then confirm the identity using a mixed melting point test with a known standard.
- If your primary focus is assessing the purity of a product: A sharp melting range (1-2°C) that matches the expected value confirms purity, while a broad and depressed range signals that purification is necessary.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Use melting point as a fast and cost-effective check to ensure incoming raw materials or final products meet established purity standards before they are used in a larger process.
Ultimately, measuring a melting point is a foundational technique that transforms a simple temperature reading into a profound statement about a substance's chemical identity and purity.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Insight | Result Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Identification | Compare to known values; use mixed melting point test. | A match suggests a possible identity. |
| Purity Assessment | Pure substances melt sharply; impurities depress and broaden the range. | A sharp range indicates purity; a broad, low range indicates impurities. |
| Quality Control | A fast, cost-effective check for material standards. | Ensures raw materials or products meet purity specifications. |
Ensure Accuracy in Your Lab with KINTEK
Accurate melting point determination is fundamental to your research and quality control. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables to support precise thermal analysis.
We help you:
- Identify Unknowns Confidently: With the right equipment, you can accurately compare your samples to known standards.
- Guarantee Purity: Ensure your compounds and products meet the highest standards with consistent, reliable results.
- Streamline Quality Control: Implement fast, cost-effective checks into your workflow.
Ready to enhance your analytical capabilities? Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What are some additional advantages of using Ultra-Low Temperature freezers in laboratories? Boost Lab Efficiency and Cut Costs
- What role does an industrial Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) system play? Mastering ODS Steel Consolidation
- Can aluminum be sputtered? Master the Process for High-Quality Thin Films
- How does a benchtop orbital shaker facilitate the production of reducing sugars? Boost Cellulose Hydrolysis Yields
- Why is a laboratory ultrasonic homogenizer necessary? Ensure Accurate Silver-Silica Nanocomposite Analysis
- What are the limitations of the IR spectroscopy? Understanding Its Boundaries for Accurate Analysis
- Why do intrinsic self-healing polymers require heating? Unlock Repeatable Repair with Thermal Activation
- Which is better carbon or graphite? Choose the Right Material for Your Application



















