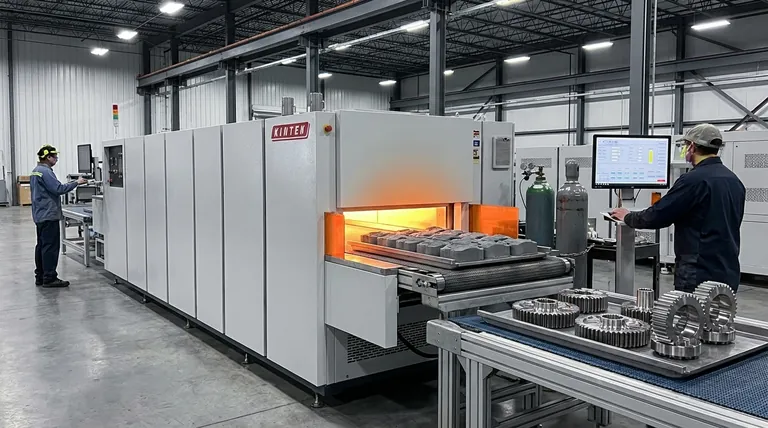
At its core, sintering is a transformative process that turns a collection of loose powder into a solid, high-performance object. Its primary importance lies in its ability to dramatically increase a material's strength, density, and conductivity using heat below the material's melting point, enabling the creation of parts that would be difficult or impossible to make through other means.
Sintering is not just about making a material solid; it is a precise engineering tool for controlling a part's final properties. It unlocks the ability to manufacture strong, complex components from high-performance materials in a repeatable and cost-effective way.

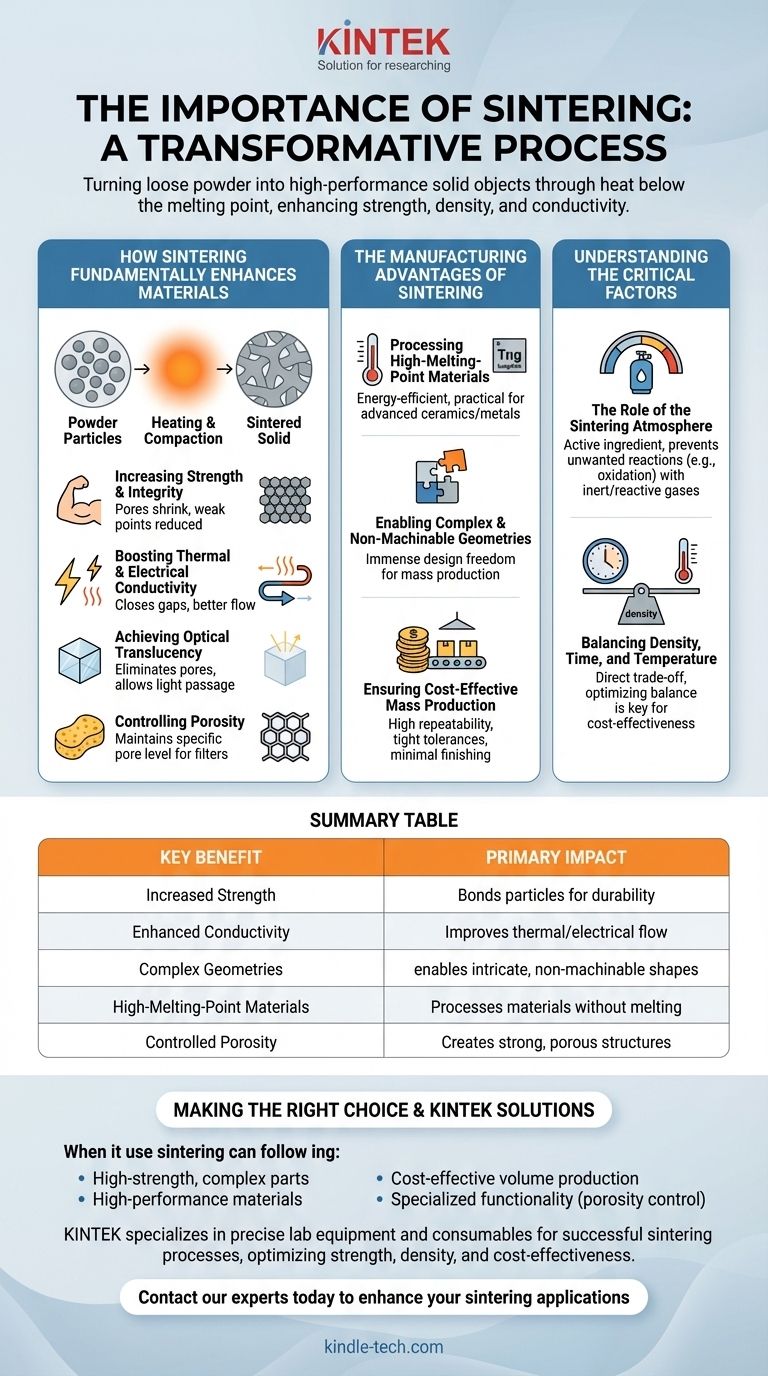
How Sintering Fundamentally Enhances Materials
Sintering creates a microscopic transformation within the material. By heating a compacted powder, the individual particles begin to bond, or "neck," at their contact points. This atomic diffusion fundamentally alters the material's structure and properties.
Increasing Strength and Integrity
The most critical benefit of sintering is the dramatic increase in mechanical strength. As particles bond and grow together, the pores and voids between them shrink or are eliminated entirely.
This process reduces the internal weak points, creating a dense, coherent mass that is significantly stronger and more durable than the original compacted powder.
Boosting Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
The voids between loose powder particles act as insulators, hindering the flow of heat or electricity.
Sintering closes these gaps, creating a more continuous path through the material. This directly improves both thermal and electrical conductivity, which is critical for applications in electronics and heat management.
Achieving Optical Translucency
In the field of advanced ceramics, sintering is used to achieve transparency or translucency.
By eliminating the microscopic pores that scatter light, sintering can turn an opaque ceramic powder into a solid object that allows light to pass through, essential for applications like transparent armor or high-intensity lamp envelopes.
Controlling Porosity for Specific Applications
While sintering is typically used to reduce porosity, it can also be precisely controlled to maintain a specific level of it.
This is vital for products like filters or catalysts, where a high surface area and gas absorbency are required. The process creates a strong, self-supporting structure while preserving the necessary porous network.
The Manufacturing Advantages of Sintering
Beyond improving material properties, sintering offers significant advantages from a production standpoint, making it a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Processing High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering allows for the processing of materials like tungsten, molybdenum, and advanced ceramics without having to reach their extremely high melting points.
This makes it more energy-efficient and practical than melting and casting, enabling the use of high-performance materials that would otherwise be unworkable.
Enabling Complex and Non-Machinable Geometries
The process excels at creating parts with intricate or complex shapes that are difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional machining.
Because the part is formed from a powder in a mold (a "green compact"), it opens up immense design freedom for mass production, a technique known as powder metallurgy.
Ensuring Cost-Effective Mass Production
For large production volumes, sintering is highly cost-effective. The process is highly repeatable, ensuring that each part is nearly identical with tight tolerances.
This consistency often produces parts with a great cosmetic finish, minimizing the need for expensive secondary finishing operations.
Understanding the Critical Factors
Achieving successful results with sintering requires careful control over the process variables. Mismanaging these factors can lead to subpar parts or outright failure.
The Role of the Sintering Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the furnace is not passive; it is an active ingredient in the process. It must be carefully selected to prevent unwanted chemical reactions, such as oxidation.
Common atmospheres include inert gases (like argon), reactive gases (like hydrogen to reduce surface oxides), or a vacuum. The wrong atmosphere can compromise the material's final properties and integrity.
Balancing Density, Time, and Temperature
There is a direct trade-off between the final density of the part and the energy required to achieve it. Higher temperatures or longer sintering times will generally result in a denser part but also increase production costs and energy consumption.
Optimizing this balance is key to creating a cost-effective and high-performing component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use sintering depends entirely on your specific material, geometry, and production requirements.
- If your primary focus is creating high-strength, complex parts: Sintering is ideal for mass-producing non-machinable geometries with excellent repeatability.
- If your primary focus is working with high-performance materials: The process allows you to form parts from materials with extremely high melting points, like tungsten or ceramics, without the energy cost and difficulty of melting.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective volume production: Sintering provides a highly accurate and repeatable method for creating net-shape parts at scale, often with a great cosmetic finish that reduces post-processing.
- If your primary focus is specialized functionality: The process offers precise control over porosity, making it perfect for creating engineered components like filters and catalysts.
Understanding when and how to apply sintering is a key enabler for advanced material design and efficient manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Primary Impact |
|---|---|
| Increased Strength | Bonds particles to create a strong, durable solid. |
| Enhanced Conductivity | Improves thermal and electrical flow by closing gaps. |
| Complex Geometries | Enables production of intricate, non-machinable shapes. |
| High-Melting-Point Materials | Processes materials like tungsten without melting them. |
| Controlled Porosity | Creates strong, porous structures for filters or catalysts. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your advanced materials or manufacturing needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables required for successful sintering processes. Whether you are developing new materials, manufacturing complex components, or need to optimize your production line, our expertise can help you achieve superior results in strength, density, and cost-effectiveness.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your sintering applications and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a tube atmosphere furnace in Li2MnSiO4 synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Battery Materials
- What advantages does a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace offer for UO2? Precision Fuel Densification
- How does an atmosphere furnace ensure quality in BN nanotube synthesis? Precision Control for Cup-Stacked Structures
- What is the core function of a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace in the fabrication of Ni-Al2O3-TiO2 composites?
- Why is a high-precision atmosphere furnace essential for high-nickel cathode sintering? Unlock Battery Performance



















