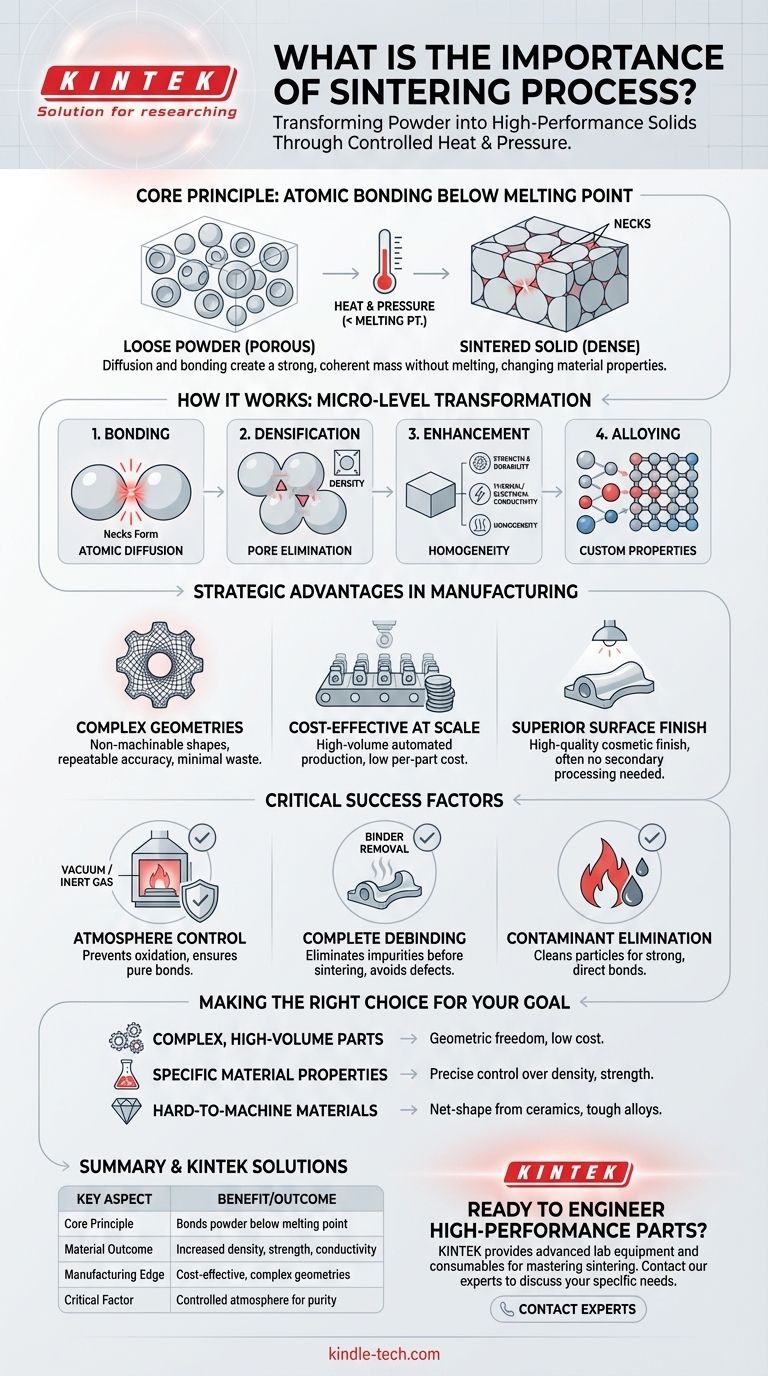
At its core, the importance of the sintering process is its unique ability to transform loose powders into a strong, dense, and solid mass without melting the material. This is achieved by applying heat and pressure, which causes the atoms of individual particles to bond, fundamentally changing the material's properties to achieve a desired engineering outcome.
Sintering is not merely a method for creating a solid object from powder. Its true significance lies in its power to precisely control and enhance a material's final characteristics—from mechanical strength and density to electrical conductivity and thermal performance.
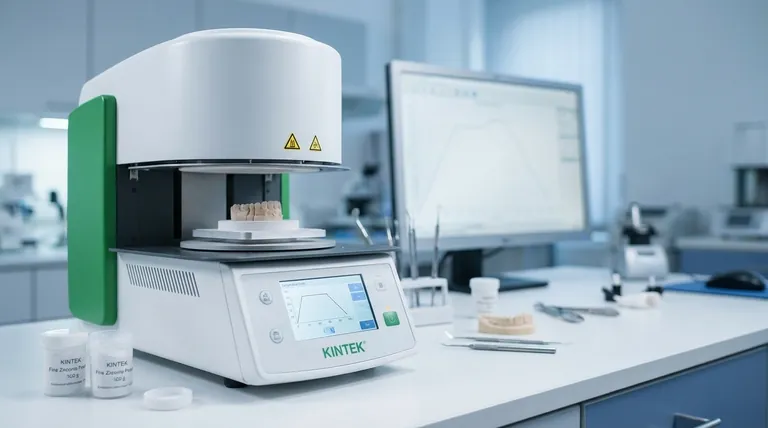

How Sintering Fundamentally Transforms Materials
Sintering works on a microscopic level to build a robust final part. The process involves more than just compaction; it's a carefully controlled thermal treatment that re-engineers the material's internal structure.
The Principle: Bonding Below the Melting Point
The process uses heat that is high enough to excite atoms and encourage diffusion but remains below the material's melting point. This energy allows atoms on the surfaces of adjacent powder particles to move and create solid bonds, or "necks," where they touch. As these necks grow, the individual particles merge into a coherent, solid structure.
From Porous to Dense
A key outcome of sintering is the dramatic reduction of porosity. The initial compacted powder is full of voids. During sintering, these pores shrink and can be eliminated, resulting in a dense, stronger final part. This increase in density is directly linked to improvements in nearly every physical property.
Enhancing Material Properties
By closing these internal voids, sintering significantly enhances key characteristics. Properties like mechanical strength, durability, thermal conductivity, and electrical conductivity all improve as the material becomes denser and more homogenous.
Alloying and Material Customization
Sintering also provides an opportunity to create alloys. By mixing different elemental powders (like graphite, nickel, or copper with iron), the process facilitates the diffusion of these elements into the primary material, creating a custom alloy with specific properties that are consistent throughout the part.
The Strategic Advantages in Manufacturing
Beyond its effect on materials, sintering offers tangible benefits that make it a cornerstone of modern, high-volume production.
Mass Production of Complex Geometries
Sintering excels at producing parts with non-machinable geometries or intricate internal features. Because the part is formed in a die, complex shapes can be created repeatably and accurately, bypassing the limitations and waste of subtractive manufacturing.
Cost-Effectiveness at Scale
While initial tooling can be an investment, sintering is extremely cost-effective for large production volumes. The process is highly automated, fast, and generates minimal material waste, leading to a low per-part cost.
Superior Surface Finish
Parts often emerge from the sintering furnace with a high-quality cosmetic finish that may not require secondary finishing processes. This further reduces production time and cost.
Understanding the Critical Process Factors
Achieving these benefits is not automatic. The success of sintering depends on precise control over several critical variables, and failure to manage them can lead to defective parts.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
The sintering atmosphere is one of the most critical factors. Using a vacuum or a controlled gas environment prevents oxidation and contamination of the material at high temperatures. An inert atmosphere ensures that strong, pure atomic bonds can form, leading to a high-density product with superior mechanical properties.
The Risk of Poor Debinding
Many powder metallurgy processes use a binder to hold the powder in its "green" state after compaction. Debinding is the crucial step of removing this binder before sintering begins. If debinding is incomplete, the leftover impurities can contaminate the furnace, cause surface blistering, or create internal pores that cannot be removed during sintering, compromising the part's integrity.
Eliminating Contaminants
The heat of the sintering process also serves to burn off contaminants like lubricants used during compaction and to reduce surface oxides on the powder particles. This cleaning action is essential for creating the strong, direct bonds that give a sintered part its strength.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sintering is a powerful tool when applied to the right problem. Your specific goal will determine if it is the optimal manufacturing process for your project.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, high-volume parts: Sintering offers unmatched geometric freedom and repeatability at a low per-unit cost.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific material properties: The process allows for precise control over density, strength, and conductivity by managing powder composition and furnace atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is working with hard-to-machine materials: Sintering is an essential method for creating net-shape parts from ceramics or tough metal alloys that are difficult to process otherwise.
Ultimately, understanding sintering empowers you to move beyond traditional manufacturing constraints and build parts with precisely engineered performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Benefit/Outcome |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Bonds powder particles below melting point |
| Material Outcome | Increased density, strength, and conductivity |
| Manufacturing Edge | Cost-effective production of complex geometries |
| Critical Factor | Controlled atmosphere for purity and strength |
Ready to engineer high-performance parts with precision sintering?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables essential for mastering the sintering process. Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up production, our solutions help you achieve superior density, strength, and complex geometries.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific sintering and material science needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability



















