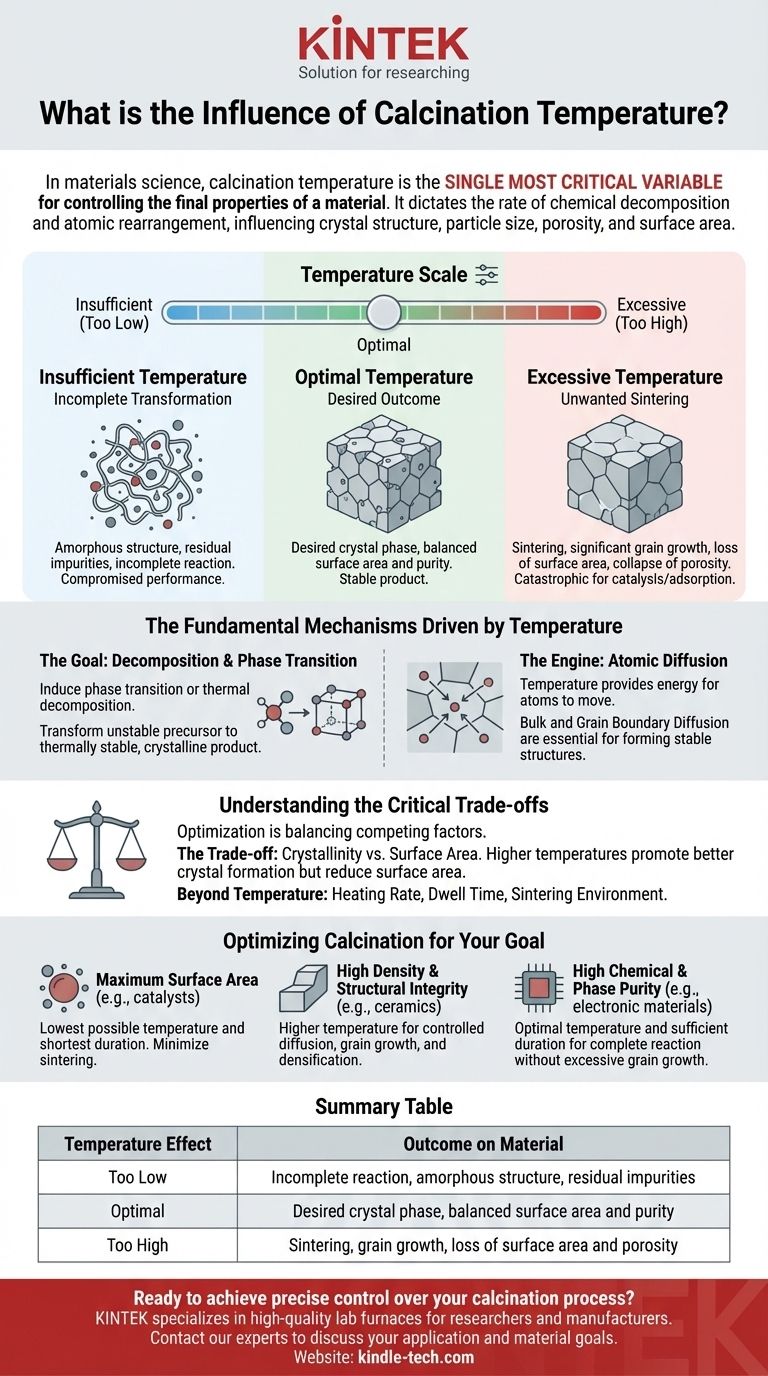
In materials science, calcination temperature is the single most critical variable for controlling the final properties of a material. It dictates the rate of chemical decomposition and atomic rearrangement, directly influencing the resulting crystal structure, particle size, porosity, and surface area of the final product.
The core function of calcination temperature is to provide the necessary thermal energy to drive specific chemical reactions and physical transformations. However, its influence is a delicate balance: too little heat results in an incomplete reaction, while too much heat causes unwanted particle fusion and loss of surface area, a process known as sintering.

The Fundamental Mechanisms Driven by Temperature
To properly control calcination, you must first understand the atomic-level processes that temperature governs. The process isn't just about heating; it's about managing energy to guide specific physical changes.
The Goal: Decomposition and Phase Transition
Calcination is a thermal treatment process designed to induce a phase transition or thermal decomposition. This typically involves removing volatile components, such as water or carbon dioxide, from a precursor material.
The ultimate goal is to transform an unstable precursor into a thermally stable, often crystalline, final product with a well-defined structure.
The Engine: Atomic Diffusion
Temperature provides the energy for atoms to move, a process known as diffusion. The rate of diffusion is highly dependent on temperature.
The two primary types are bulk diffusion, where atoms move through the crystal lattice itself, and grain boundary diffusion, where atoms move along the interfaces between individual crystals. Both are essential for forming a stable, crystalline structure.
The Direct Consequences of Temperature Selection
The temperature you choose has a direct and predictable impact on the material. Setting the right temperature is a function of the specific material system and the desired outcome.
Insufficient Temperature: Incomplete Transformation
If the calcination temperature is too low, the material will not receive enough energy to complete its chemical and structural transformation.
This can result in an amorphous (non-crystalline) structure, the presence of residual impurities, or an incomplete reaction, all of which compromise the final material's performance.
Excessive Temperature: Unwanted Sintering
If the temperature is too high, diffusion becomes excessively rapid. Instead of simply forming stable crystals, individual particles begin to fuse together.
This process, known as sintering, causes significant grain growth, a drastic reduction in surface area, and the collapse of porous structures. For applications like catalysis or adsorption, where high surface area is critical, this is a catastrophic failure.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Optimizing calcination temperature is rarely about finding a single "perfect" number. It is about balancing competing factors to achieve the best possible outcome for a specific application.
The Trade-off: Crystallinity vs. Surface Area
There is often an inverse relationship between crystallinity and surface area. Higher temperatures promote better crystal formation and purity but simultaneously encourage grain growth that reduces surface area.
Choosing the right temperature means finding the sweet spot where the desired crystal phase is achieved with the minimum possible loss of surface area.
Beyond Temperature: Rate and Environment
The peak temperature is not the only factor. The heating rate (how fast you reach the target temperature) and the dwell time (how long you hold it there) also play crucial roles.
Furthermore, the composition of the furnace atmosphere, referred to as the sintering environment, can significantly influence the chemical reactions taking place.
Optimizing Calcination for Your Goal
The ideal calcination temperature is entirely dependent on the intended application of the material. Your strategy must be aligned with your primary performance metric.
- If your primary focus is maximum surface area (e.g., for catalysts or adsorbents): Use the lowest possible temperature and shortest duration required to achieve the necessary phase transformation, minimizing any chance of sintering.
- If your primary focus is high density and structural integrity (e.g., for structural ceramics): Utilize a higher temperature to intentionally promote controlled diffusion, grain growth, and densification of the material.
- If your primary focus is high chemical and phase purity (e.g., for electronic materials): Focus on an optimal temperature held for a sufficient duration to ensure the reaction fully completes without triggering excessive and detrimental grain growth.
Ultimately, mastering calcination temperature is the key to transforming raw precursors into high-performance materials with predictable and reliable properties.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Effect | Outcome on Material |
|---|---|
| Too Low | Incomplete reaction, amorphous structure, residual impurities |
| Optimal | Desired crystal phase, balanced surface area and purity |
| Too High | Sintering, grain growth, loss of surface area and porosity |
Ready to achieve precise control over your calcination process? The right lab furnace is critical for replicating these results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed for researchers and manufacturers who demand accuracy and reliability. Whether you are developing new catalysts, ceramics, or electronic materials, our solutions help you hit the perfect temperature profile every time. Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your specific application and material goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of a laboratory muffle furnace? Find the Right Model for Your Application
- What is the working principle of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is the construction of a muffle furnace? A Deep Dive into Its Core Systems
- What are muffle furnaces used for? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- How do you cool down a muffle furnace? Ensure Longevity and Safety with the Correct Procedure



















