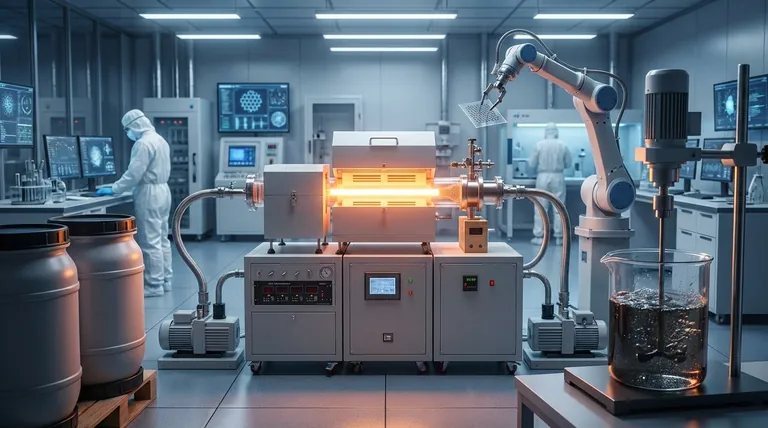
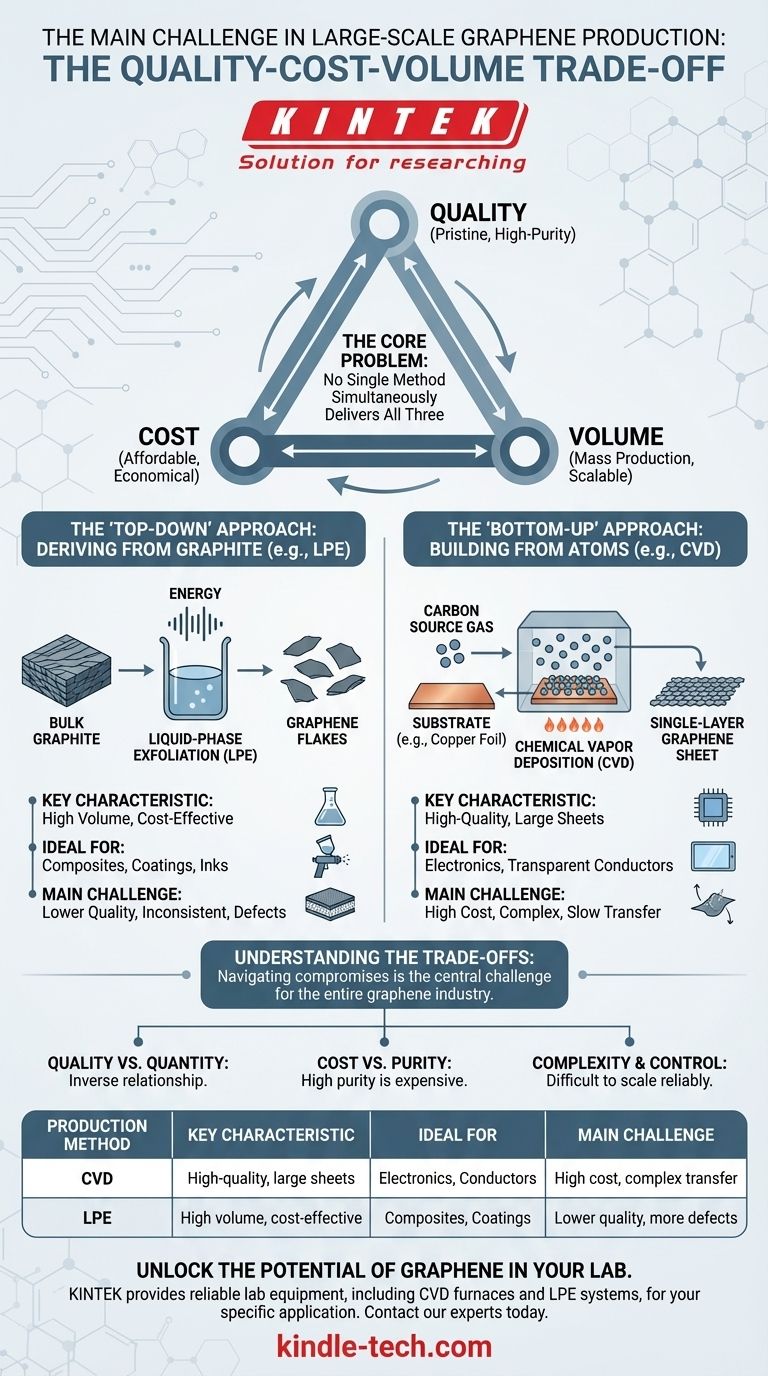
The main challenge in the large-scale production of graphene is the fundamental trade-off between quality, cost, and volume. Methods that produce high-quality, pristine graphene are currently too complex and expensive to scale for mass-market applications, while methods that can produce large quantities often yield a material with lower electrical quality and more defects.
The core problem is that no single production method currently exists that can simultaneously deliver the high-purity graphene needed for advanced electronics at the massive scale and low cost required for industrial adoption.

The Two Paths to Graphene Production
Understanding the production challenge requires looking at the two fundamental approaches for creating graphene: starting big and going small ("top-down"), or starting small and building up ("bottom-up").
The 'Top-Down' Approach: Deriving from Graphite
This method involves taking bulk graphite and breaking it down until you isolate single layers of graphene.
Liquid-Phase Exfoliation (LPE) is the most common top-down technique for mass production. It involves suspending graphite in a liquid and using energy (like sonication) to shear off graphene flakes.
While LPE is excellent for producing large volumes of graphene flakes cheaply, the material quality is inconsistent. The process often results in multi-layered flakes, structural defects, and impurities, making it unsuitable for high-performance electronics but acceptable for applications like composites, coatings, and conductive inks.
The 'Bottom-Up' Approach: Building from Atoms
This strategy involves assembling graphene atom-by-atom on a substrate from carbon-containing sources.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the most promising bottom-up technique. It involves heating a substrate (typically a copper foil) in a vacuum chamber and introducing a carbon-containing gas. The gas decomposes, and the carbon atoms arrange themselves into a single, continuous layer of graphene on the substrate surface.
CVD can produce very large sheets of high-quality graphene, which is ideal for electronics. However, the process is complex, requires high temperatures and vacuum conditions, and is therefore slow and expensive. Furthermore, transferring the fragile, single-atom-thick film from its growth substrate to a final target (like a silicon wafer) without introducing tears or wrinkles remains a significant engineering hurdle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of production method is dictated by a series of compromises. Navigating these trade-offs is the central challenge for the entire graphene industry.
Quality vs. Quantity
There is an inverse relationship between the quality of graphene and the quantity that can be produced economically.
CVD yields near-perfect, single-layer sheets ideal for sensitive electronic components, but the process is meticulous and slow. LPE can generate kilograms of graphene flakes quickly, but the average quality is much lower.
Cost vs. Purity
Achieving high purity and structural perfection comes at a high price.
Methods like the sublimation of silicon carbide can produce exceptionally high-quality graphene directly on an insulating substrate, but the cost is prohibitive for all but the most specialized research applications. CVD is less expensive but still requires significant capital investment in vacuum equipment and high-purity materials.
Complexity and Control
Industrial-scale manufacturing demands processes that are repeatable, reliable, and controllable.
Both CVD and LPE involve complex processes with many variables. Maintaining precise control over temperature, pressure, gas flow, and chemical precursors at a large scale is a major engineering challenge that directly impacts the final product's consistency and performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" graphene production method depends entirely on the final application. There is no one-size-fits-all solution.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or transparent conductors: CVD is the leading candidate, as its ability to produce large, high-quality sheets is essential.
- If your primary focus is bulk materials like composites, inks, or coatings: Liquid-phase exfoliation offers a cost-effective and scalable pathway where pristine quality is not the main requirement.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Mechanical exfoliation (the "Scotch tape" method) remains a valid technique for producing tiny, flawless samples for scientific study.
Ultimately, unlocking graphene's full potential hinges on developing a new method or refining an existing one to break the current compromise between quality, cost, and scale.
Summary Table:
| Production Method | Key Characteristic | Ideal For | Main Challenge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | High-quality, large sheets | Electronics, Transparent Conductors | High cost, complex transfer process |
| Liquid-Phase Exfoliation (LPE) | High volume, cost-effective | Composites, Coatings, Inks | Lower quality, more defects |
Unlock the Potential of Graphene in Your Lab
Navigating the complexities of graphene production requires the right equipment. Whether your research demands the high-quality sheets from CVD furnaces or the cost-effective volumes from LPE systems, KINTEK provides the reliable lab equipment and consumables you need to succeed.
Let's discuss your specific application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's graphene challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method



















