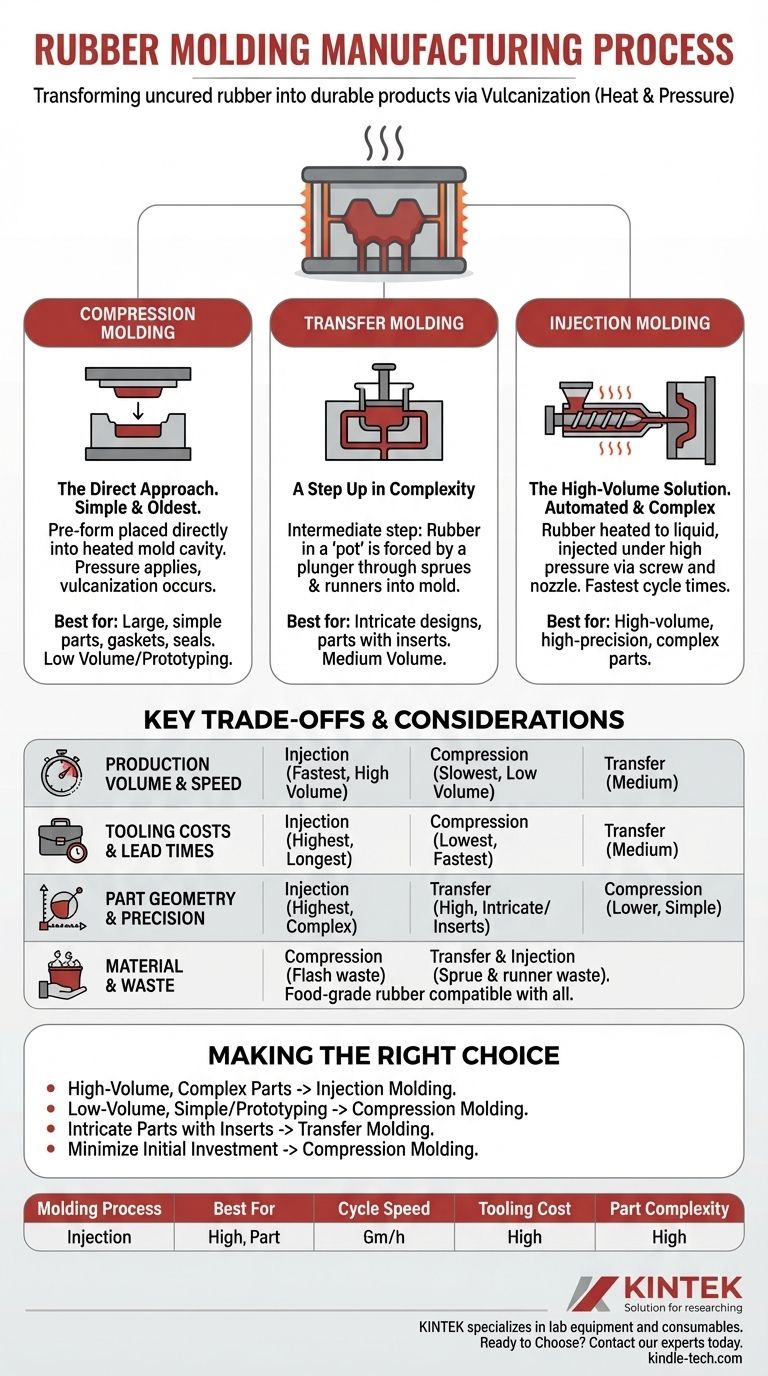
In manufacturing, rubber molding is the process of transforming uncured rubber into a durable, usable product. This is achieved by placing raw rubber material into a heated mold cavity, where a combination of heat and pressure cures the material—a process known as vulcanization—locking it into its final, permanent shape. The three principal methods for achieving this are injection, compression, and transfer molding.
The choice between injection, compression, and transfer molding is not about which method is "best," but which is the most effective for your specific goal. The decision hinges on a careful balance of part complexity, production volume, material type, and overall cost.

A Breakdown of Each Molding Process
Each of the three primary rubber molding techniques uses a different method to introduce the uncured rubber material into the mold cavity. This fundamental difference dictates the ideal applications for each process.
Compression Molding: The Direct Approach
Compression molding is the simplest and oldest method. A pre-measured amount of uncured rubber, called a pre-form, is placed directly into the heated lower mold cavity.
The top half of the mold is then closed, applying immense pressure. This action forces the rubber to fill the entire cavity, and the sustained heat and pressure trigger the vulcanization process.
This method is highly effective for large, relatively simple parts, gaskets, and seals.
Transfer Molding: A Step Up in Complexity
Transfer molding shares similarities with compression molding but adds an intermediate step. The rubber pre-form is placed in a "pot" located between the top plate and a plunger.
When the mold closes, the plunger forces the heated, softened rubber through channels, known as sprues and runners, into the closed mold cavities.
This process is better suited for more intricate designs and for parts where metal or plastic inserts are molded directly into the rubber component.
Injection Molding: The High-Volume Solution
Injection molding is the most automated and complex of the three. Rubber is heated to a liquid state and then injected under high pressure into a closed mold.
An extruder screw forces the material through a nozzle into the mold's runner system, which distributes it to the individual cavities. The process is extremely fast and repeatable.
This method is the standard for high-volume production runs of complex, high-precision parts, as it offers the fastest cycle times.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing the right process requires a clear understanding of the trade-offs between cost, speed, and precision. No single method excels in all areas.
Production Volume and Speed
Injection molding offers the fastest cycle times, making it the undisputed choice for high-volume orders where per-part cost is a key driver.
Compression molding is significantly slower, with longer cycle times due to the manual loading of pre-forms and longer curing periods. It is best for prototypes and low-volume production.
Transfer molding sits in the middle, offering faster cycle times than compression but slower than injection.
Tooling Costs and Lead Times
The simplicity of compression molding tools makes them the least expensive and fastest to produce.
Transfer molding tools are more complex due to the addition of the transfer pot and plunger, leading to higher costs.
Injection molding requires the most complex and precisely engineered molds, resulting in the highest initial tooling investment and the longest lead times.
Part Geometry and Precision
Injection molding provides the highest level of dimensional tolerance and is ideal for complex geometries with very fine details.
Transfer molding also produces highly precise parts and is excellent for creating sharp edges and accommodating inserts.
Compression molding is less suited for intricate designs and has lower dimensional consistency compared to the other two methods.
Material Considerations and Waste
Each process handles materials differently. For example, specific compounds like food-grade natural rubber can be used in any of the three processes, but the choice might be influenced by factors like curing time and potential for material waste.
Compression molding often produces a significant amount of overflow material, known as flash, which must be trimmed. Transfer and injection molding offer better control over flash but create waste in the form of sprues and runners.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your project's specific requirements will point you to the optimal molding process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex parts: Injection molding is the most efficient and cost-effective choice in the long run.
- If your primary focus is low-volume runs or prototyping simple parts: Compression molding offers the lowest tooling cost and is ideal for getting started.
- If your primary focus is intricate parts with inserts at medium volume: Transfer molding provides a balance of precision and moderate production speed.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial investment on a simple part: Compression molding's low-cost tooling makes it the clear winner.
Ultimately, understanding these core processes empowers you to make an informed decision that aligns your manufacturing method with your design intent and business goals.
Summary Table:
| Molding Process | Best For | Cycle Speed | Tooling Cost | Part Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | High-volume, complex parts | Fastest | Highest | High |
| Compression Molding | Low-volume, simple parts, prototyping | Slowest | Lowest | Low |
| Transfer Molding | Medium-volume, intricate parts with inserts | Medium | Medium | High |
Ready to Choose the Right Rubber Molding Process for Your Project?
Navigating the trade-offs between injection, compression, and transfer molding can be complex. The ideal method depends on your specific part design, material, production volume, and budget.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our expertise can help you select the perfect molding solution to ensure precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for your rubber components.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how we can support your manufacturing success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Ring Press Mold for Lab Applications
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between injection molding and pressure molding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process
- What is short capacity of injection Moulding machine? Optimize Your Shot Size for Flawless Parts
- What is molding technique? A Guide to High-Volume, Complex Part Manufacturing
- What are the three 3 differences between compression molding and injection molding? Choose the Right Process for Your Project
- What can you make with an injection moulding machine? Mass-Produce High-Quality Plastic Parts Efficiently



















