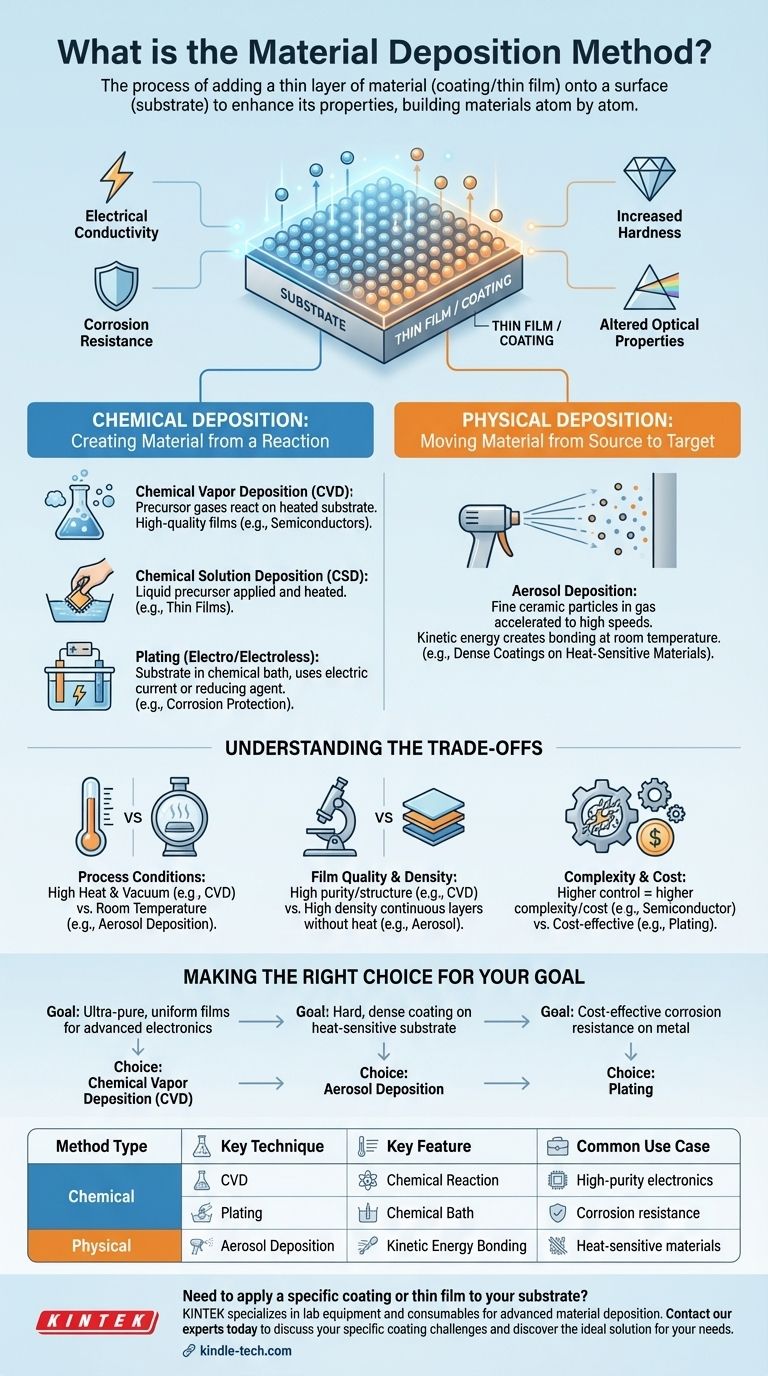
In essence, material deposition is any process where a thin layer of material is added, or "deposited," onto a surface, which is known as a substrate. This is a foundational technique in modern manufacturing, used to create everything from the anti-scratch coating on your glasses to the complex circuitry inside your phone. It's the art of building up materials, often atom by atom, to enhance an object's properties.
The core concept to grasp is that "material deposition" isn't a single method, but a broad category of techniques. The fundamental choice always comes down to two approaches: using a chemical reaction to create the new layer or physically moving material from a source to the target surface.

The Core Principle: Building a Surface Layer by Layer
At its heart, material deposition is about controlled addition. You start with a base material, the substrate, and systematically apply a new material onto it, creating what is often called a thin film or coating.
Why Deposit a Material?
The goal is to give the substrate new properties it doesn't naturally possess. This could include adding electrical conductivity, improving corrosion resistance, increasing hardness, or altering its optical properties.
The Two Fundamental Approaches
Nearly all deposition methods fall into one of two major categories. The distinction is how the new layer is formed on the substrate.
Chemical Deposition: Creating Material from a Reaction
In these methods, the material of the new layer isn't just moved—it's created directly on the substrate's surface through a chemical reaction. Precursor gases or solutions are introduced, which then react under specific conditions to form the desired solid film.
Common chemical methods include:
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Precursor gases are passed over a heated substrate, causing them to react and decompose, leaving behind a high-quality solid film. This is a cornerstone of the semiconductor industry.
- Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD): A liquid solution containing the desired material precursors is applied to the substrate, often by spinning or dipping, and then heated to initiate a chemical reaction that forms the film.
- Plating (Electroplating/Electroless): A substrate is submerged in a chemical bath, and either an electric current (electroplating) or a chemical reducing agent (electroless plating) causes dissolved metal ions to deposit onto the surface.
Physical Deposition: Moving Material from Source to Target
In physical deposition, the material for the new layer already exists in its final chemical form. The process involves physically dislodging it from a source (or "target") and transporting it to the substrate, where it condenses to form a film.
A key example of this approach is:
- Aerosol Deposition: In this innovative method, very fine ceramic particles are mixed into a gas to form an aerosol. This mixture is then accelerated to high speeds through a nozzle and aimed at the substrate.
- The key mechanism is the conversion of kinetic energy into binding energy. When the particles impact the substrate at room temperature, their sheer velocity is enough to cause them to fracture and bond tightly to the surface and to each other. This creates a dense coating without needing high-temperature treatments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition method is a matter of balancing competing priorities. No single technique is best for every application.
Process Conditions: Heat and Vacuum
Many CVD processes require very high temperatures and vacuum chambers to work correctly. This limits the types of substrates that can be used and increases equipment cost. In contrast, methods like aerosol deposition can operate at room temperature, making them suitable for coating heat-sensitive materials like plastics.
Film Quality and Density
High-temperature, vacuum-based methods like CVD often produce films with exceptional purity and structural perfection. However, newer methods like aerosol deposition are capable of producing surprisingly high-density continuous layers without the need for additional heat treatment.
Complexity and Cost
Generally, the more control you have over the film's properties (like thickness and purity), the more complex and expensive the equipment becomes. Simple methods like plating are highly cost-effective for corrosion protection, while semiconductor fabrication requires far more sophisticated systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal deposition method is entirely dependent on your end goal, your materials, and your budget.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-pure, uniform films for advanced electronics: A technique like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is likely necessary for its atomic-level control.
- If your primary focus is applying a hard, dense coating onto a heat-sensitive substrate: A room-temperature process like Aerosol Deposition offers a unique advantage.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective corrosion resistance on a metal part: A simpler and more established method like electroplating is often the most practical choice.
Ultimately, understanding material deposition is about seeing it as a versatile toolkit for engineering the precise surface properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Method Type | Key Technique | Key Feature | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Creates film via chemical reaction | High-purity electronics, semiconductors |
| Chemical | Plating (Electro/Electroless) | Uses chemical bath | Corrosion resistance, decorative coatings |
| Physical | Aerosol Deposition | Room-temperature, kinetic energy bonding | Dense coatings on heat-sensitive materials |
Need to apply a specific coating or thin film to your substrate?
The right deposition method is critical for achieving the surface properties—like hardness, conductivity, or corrosion resistance—that your project demands. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material deposition processes. Our expertise can help you select the perfect technique for your materials and budget, ensuring optimal results for your laboratory's research and development.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific coating challenges and discover the ideal solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















