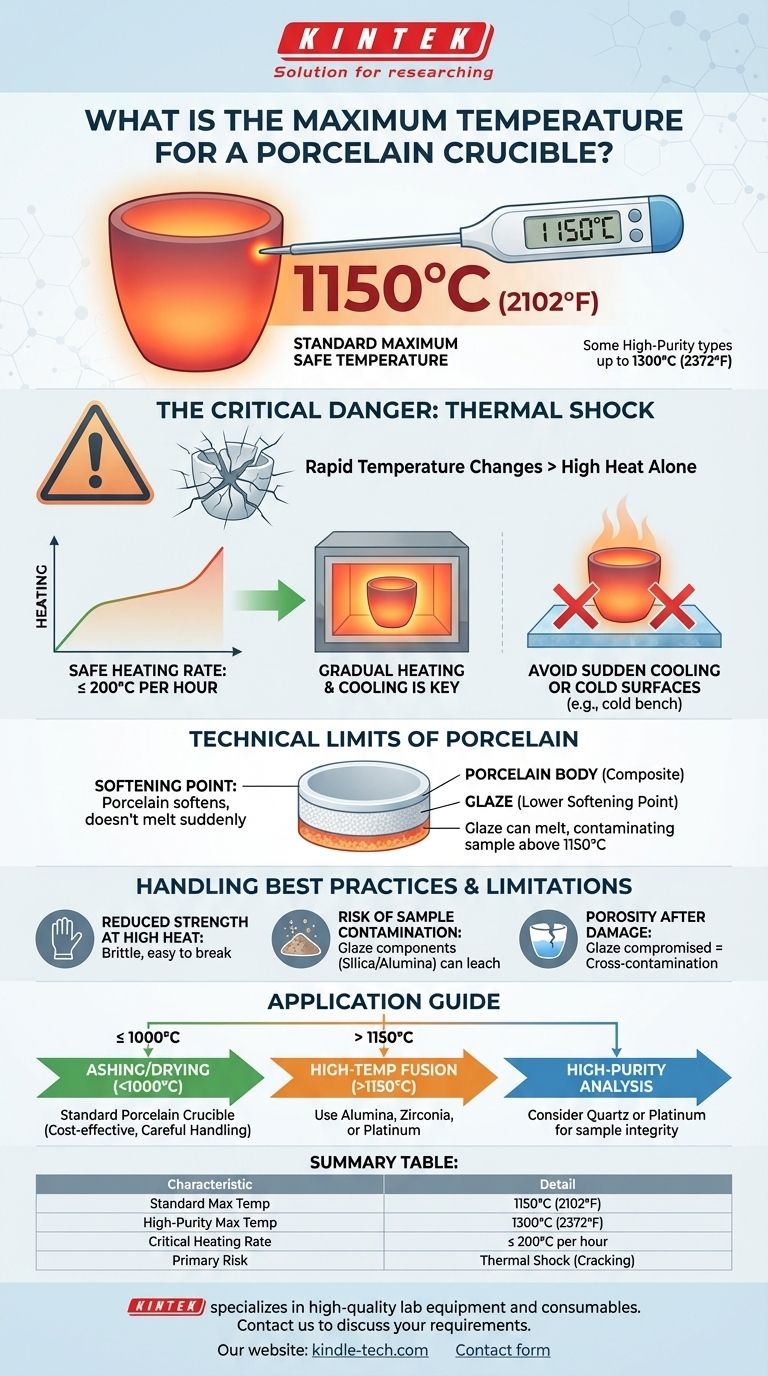
In short, most standard laboratory porcelain crucibles have a maximum safe working temperature of about 1150°C (2102°F). While some high-purity porcelain can be heated to 1300°C (2372°F), exceeding these limits risks deforming the crucible, melting its protective glaze, and compromising your sample. However, the absolute temperature is only half the story; how you get there is far more critical.
The single most important factor in using a porcelain crucible is not its maximum temperature, but its vulnerability to thermal shock. Abrupt changes in temperature will crack porcelain far more readily than high heat alone.

The Technical Limits of Porcelain
Porcelain is a ceramic material valued in the lab for its high resistance to heat and chemical attack. Understanding its composition helps clarify its physical limits.
The Softening Point
A porcelain crucible doesn't have a sharp, defined melting point like a pure metal. Instead, it has a softening point where it begins to lose its structural integrity.
This is because porcelain is a composite, typically made from kaolin, quartz, and feldspar. As it approaches its maximum temperature, it gradually softens and can deform under its own weight or the weight of its contents.
The Role of Glaze
Most porcelain labware is coated with a hard, non-porous glaze. This glaze is crucial, as it makes the crucible easy to clean and prevents the porous ceramic body from absorbing chemicals.
However, this glaze often has a lower softening temperature than the porcelain body itself. Pushing a crucible to its absolute limit can cause the glaze to melt, potentially contaminating your sample or fusing it to the crucible walls.
Why 1150°C is the Standard Guideline
The 1150°C (2102°F) guideline is a conservative, safe operating limit for general-purpose porcelain. It provides a buffer before the material begins to soften or the glaze begins to degrade, ensuring the crucible remains inert and structurally sound.
The Real Danger: Thermal Shock
A porcelain crucible can survive hours at 1000°C but shatter instantly under the wrong conditions. This failure is almost always due to thermal shock.
What is Thermal Shock?
Thermal shock occurs when different parts of the crucible expand or contract at different rates due to a rapid temperature change. This creates immense internal stress that overcomes the material's strength, resulting in cracks or complete failure.
Pouring cold liquid into a hot crucible or placing a hot crucible onto a cold lab bench are classic examples of inducing thermal shock.
The Critical Heating Rate
To prevent cracking, heating must be gradual. Placing a room-temperature crucible directly into a pre-heated high-temperature furnace is a guaranteed way to destroy it.
A common rule of thumb is to limit the heating rate to no more than 200°C per hour. This allows the temperature to distribute evenly throughout the material, minimizing internal stress.
The Cooling Down Process
Cooling is just as critical as heating. Never remove a glowing hot crucible from a furnace and place it on a cool surface.
The safest method is to allow the crucible to cool slowly inside the furnace. If it must be removed, it should be placed on a ceramic fiber insulation board or a similar surface that will not draw heat away too quickly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While excellent for many tasks, porcelain has clear limitations that you must respect to ensure accurate and safe work.
Reduced Mechanical Strength at High Heat
As a porcelain crucible approaches its maximum temperature, it becomes mechanically weaker and more brittle. It is much more susceptible to breaking from physical impact when hot.
Risk of Sample Contamination
Heating near the glaze's softening point increases the risk that components of the glaze (like silica or alumina) could leach into your sample. For high-purity analysis, this can compromise your results.
Porosity After Damage
If the glaze is compromised by thermal shock or chemical attack, the underlying ceramic becomes exposed. This porous body can absorb materials, leading to cross-contamination between experiments that is impossible to remove through cleaning.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of procedure should be guided by your specific analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is general ashing or drying below 1000°C: A standard porcelain crucible is a perfect, cost-effective tool, provided you always manage heating and cooling rates carefully.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature fusion or working above 1150°C: You must use a different material. Consider crucibles made of alumina, zirconia, or even platinum for these applications.
- If your primary focus is high-purity analysis: Be cautious when operating near the 1150°C limit of porcelain and consider if a higher-grade material like quartz or platinum would better protect your sample's integrity.
Mastering the proper handling of porcelain is about controlling the rate of temperature change, not just the peak temperature itself.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Detail |
|---|---|
| Standard Max Safe Temperature | 1150°C (2102°F) |
| High-Purity Max Temperature | Up to 1300°C (2372°F) |
| Critical Heating Rate | ≤ 200°C per hour |
| Primary Risk | Thermal Shock (Cracking) |
Ensure your lab work is precise and safe. Porcelain crucibles are excellent for many applications, but choosing the right lab equipment is critical for your results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including crucibles for a wide range of temperatures and applications. Our experts can help you select the perfect tools for your specific needs, from standard porcelain to high-temperature alumina or platinum.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and ensure the integrity of your samples. Get in touch via our contact form to learn more.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why must aluminum alloys be heated in alumina crucibles? Ensure Pure Results in Molten Corrosion Experiments
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- Why are high-purity alumina (Al2O3) crucibles necessary for liquid lead corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Data
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible required for LLTO calcination? Ensure Material Purity and Stoichiometry
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety



















