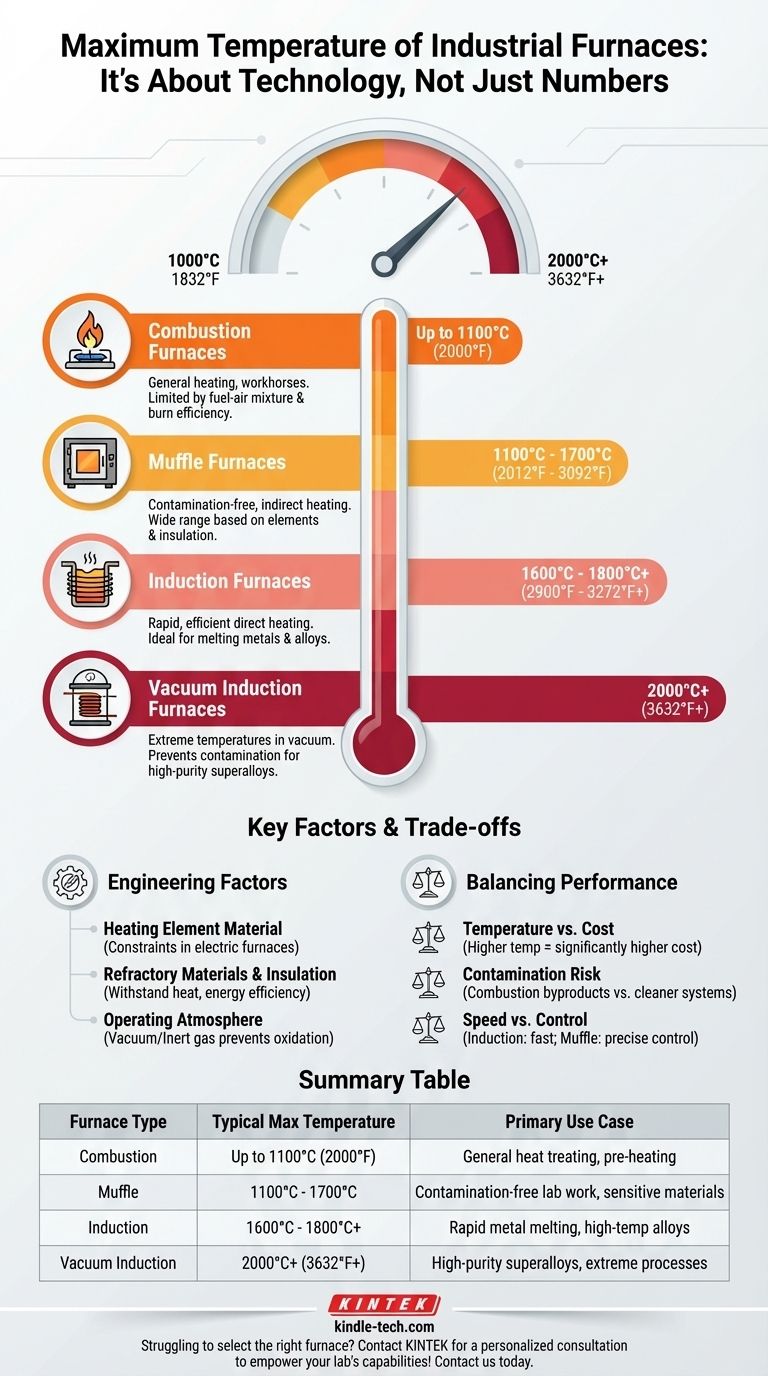
The maximum temperature of an industrial furnace is not a single value but is determined entirely by its design, heating method, and purpose. While common combustion furnaces operate around 1100°C (2000°F), highly specialized systems like vacuum induction furnaces can exceed 2000°C (3632°F).
The core takeaway is that furnace technology is a spectrum. The right question isn't "what is the absolute maximum temperature," but rather "which furnace technology can achieve the specific temperature my process requires?" The answer depends on a trade-off between heat source, material construction, and operational cost.
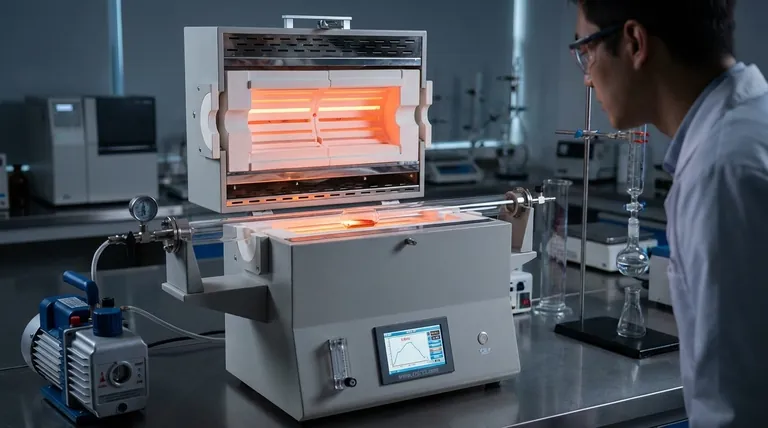

Furnace Capabilities by Heating Technology
The term "industrial furnace" covers a vast range of equipment, each engineered for a different task. The primary factor determining a furnace's maximum temperature is its method of generating heat.
Combustion Furnaces
Combustion furnaces, such as those powered by natural gas, generate heat by burning fuel.
Their temperature is limited by the fuel-air mixture and the efficiency of the burn. They are workhorses for general heating applications.
Maximum Temperature: Typically up to 1100°C (2000°F).
Muffle Furnaces
A muffle furnace is an oven where the material being heated is isolated from the heating elements and any combustion byproducts.
This indirect heating provides a clean, controlled environment, ideal for laboratory work or processes sensitive to contamination. Their temperature range varies significantly based on the quality of their heating elements and insulation.
Maximum Temperature: Varies widely from 1100°C to 1700°C (2012°F to 3092°F).
Induction Furnaces
Induction furnaces use powerful electromagnets to generate heat directly within the target material itself, assuming it's electrically conductive.
This method is exceptionally fast and efficient, capable of reaching very high temperatures for melting metals and creating specialized alloys.
Maximum Temperature: Generally 1600°C to 1800°C (2900°F to 3272°F), with some models exceeding this.
Specialized High-Temperature Furnaces
For the most demanding applications, specialized designs are required.
A vacuum induction furnace, for example, operates in a vacuum to prevent contamination and heat loss. This allows it to reach extreme temperatures for producing high-purity superalloys and materials.
Maximum Temperature: Can reach or exceed 2000°C (3632°F).
Key Factors That Define a Furnace's Limit
Beyond the heating method, several engineering factors dictate the ultimate temperature a furnace can safely and reliably achieve.
The Heating Element Material
In electric furnaces (like muffle furnaces), the material of the heating element is a primary constraint. Different materials have different maximum operating temperatures before they degrade or fail.
Refractory Materials and Insulation
The furnace chamber must be lined with refractory materials—like specialized ceramics and firebricks—that can withstand the internal heat without melting. The quality of this insulation dictates both the maximum temperature and the furnace's energy efficiency.
Operating Atmosphere
Heating materials in a vacuum or a controlled inert gas atmosphere can prevent chemical reactions (like oxidation) that occur at high temperatures in normal air. This enables cleaner processes and can help achieve higher effective temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace is not just about finding the highest temperature. It involves balancing performance with practical constraints.
Temperature vs. Cost
There is a direct and steep correlation between a furnace's maximum temperature and its cost. The specialized materials, power systems, and control electronics required for high-temperature operation are significantly more expensive.
Contamination Risk
Direct-fired combustion furnaces can introduce byproducts from the fuel into the heating chamber. For high-purity applications, the cleaner (and more expensive) environments of muffle, induction, or vacuum furnaces are necessary.
Speed vs. Control
Induction furnaces are incredibly fast at heating but may be less suitable for processes that require slow, precise temperature ramping. Muffle and resistance furnaces often provide more granular temperature control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching the technology to the specific requirements of your process.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating or pre-heating below 1100°C: A standard natural gas or electric resistance furnace is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is a contamination-free environment for lab work or sensitive materials up to 1700°C: A muffle furnace provides the necessary isolation and control.
- If your primary focus is rapidly melting metals or achieving extreme temperatures above 1600°C: An induction furnace is the required technology, with vacuum models representing the peak of performance.
Ultimately, matching the furnace's capabilities to your specific temperature, material, and purity needs is the key to achieving efficient and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Maximum Temperature | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Combustion Furnace | Up to 1100°C (2000°F) | General heat treating, pre-heating |
| Muffle Furnace | 1100°C - 1700°C (2012°F - 3092°F) | Contamination-free lab work, sensitive materials |
| Induction Furnace | 1600°C - 1800°C+ (2900°F - 3272°F+) | Rapid metal melting, high-temperature alloys |
| Vacuum Induction Furnace | 2000°C+ (3632°F+) | High-purity superalloys, extreme temperature processes |
Struggling to select the right furnace for your specific temperature and purity requirements?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between cost, contamination risk, and performance to identify the ideal furnace technology—whether it's a standard combustion furnace, a clean muffle furnace, or a high-performance induction system.
We provide reliable, efficient solutions tailored to your thermal processing goals. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let KINTEK empower your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary advantage of using a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature and Atmosphere Control
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















