Technically, an induction furnace has no single "melting temperature" because its purpose is not to melt itself, but to generate controlled heat within a metallic charge. However, these systems are engineered to achieve extremely high temperatures, with most industrial induction furnaces capable of reaching up to 2000°C (3632°F), which is well above the melting point of common metals like steel.
An induction furnace doesn't possess its own melting point. Instead, it uses electromagnetic induction to heat a specific metal to its unique melting point with exceptional precision. The furnace's true value is its ability to deliver controlled, uniform, and efficient heating, not just its maximum temperature.
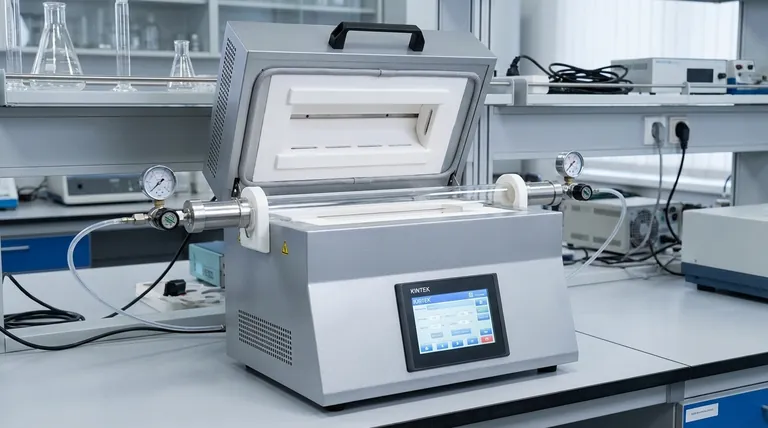

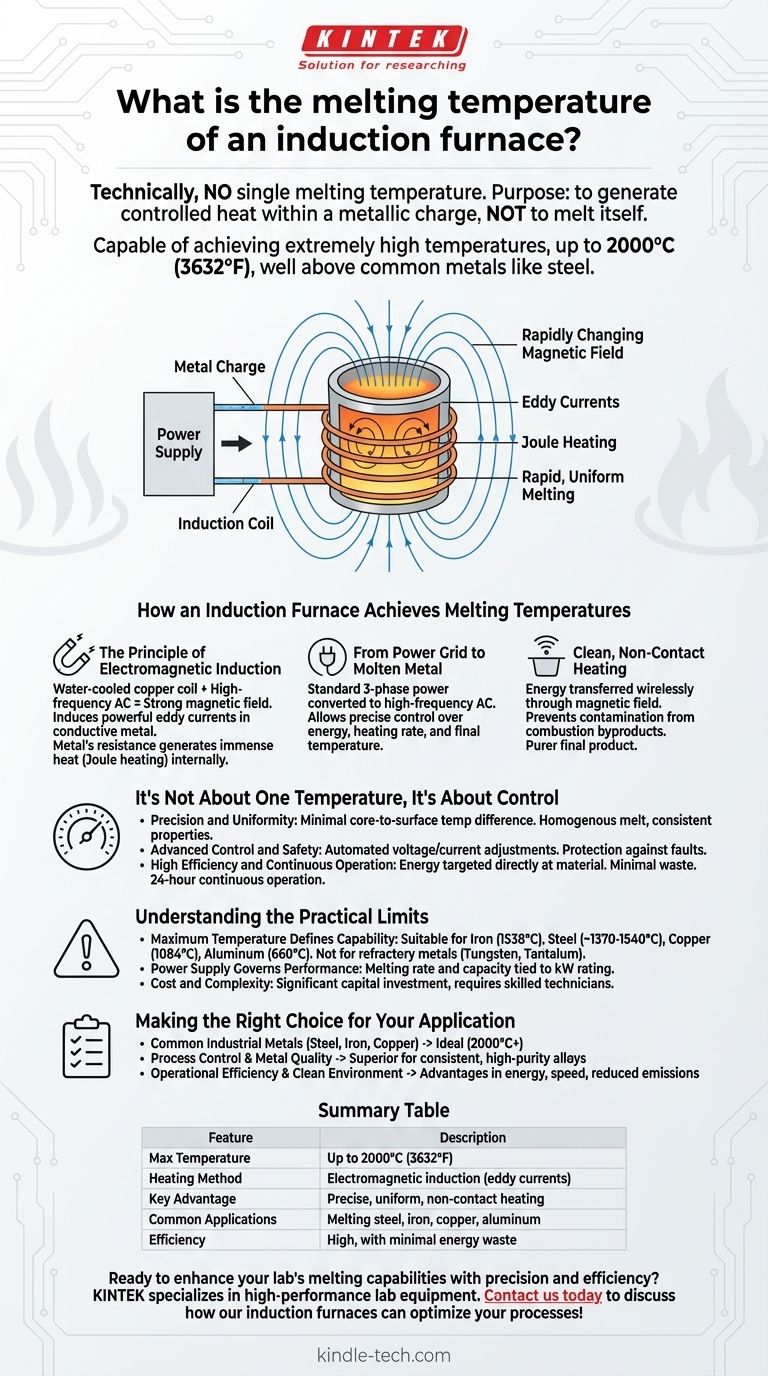
How an Induction Furnace Achieves Melting Temperatures
An induction furnace operates on a principle that is fundamentally different from a traditional fuel-fired furnace. It does not burn fuel to create heat; it uses electricity to induce heat directly within the target material.
The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
The core of the furnace is a water-cooled coil made of copper. A powerful, high-frequency alternating current is passed through this coil.
This current generates a strong and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil. When a conductive material like metal is placed inside this field (within a container called a crucible), the magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents, known as eddy currents, to flow within the metal itself.
Due to the metal's natural electrical resistance, these eddy currents generate immense heat through a process called Joule heating. The heat is created inside the metal, leading to rapid and uniform melting from the core outwards.
From Power Grid to Molten Metal
This process requires a sophisticated power supply. The system takes standard three-phase power from the grid and converts it into a high-frequency alternating current.
This conversion allows for precise control over the amount of energy delivered to the metal charge. By adjusting the frequency and current, operators can accurately manage the heating rate and final temperature.
Clean, Non-Contact Heating
A critical advantage of this method is that the induction coil never makes direct contact with the metal. The energy is transferred wirelessly through the magnetic field.
This prevents contamination of the molten metal by byproducts of combustion, which is a common issue in fuel-fired furnaces. The result is a purer final product.
It's Not About One Temperature, It's About Control
The maximum temperature of 2000°C is impressive, but the defining characteristic of an induction furnace is its precision. Sophisticated control systems make it a highly reliable industrial tool.
Precision and Uniformity
Because heat is generated throughout the metal charge, the temperature difference between the core and the surface is minimal. This ensures a homogenous melt with uniform chemical composition and temperature.
This level of control is crucial for producing high-quality alloys where specific properties must be consistently achieved.
Advanced Control and Safety
Modern induction furnaces feature highly integrated control systems. These systems automatically adjust voltage and current based on the amount of metal in the furnace, ensuring constant power delivery and efficient melting.
They also include comprehensive protection circuits that guard against over-voltage, over-current, and other faults, ensuring safe and reliable operation.
High Efficiency and Continuous Operation
Induction heating is remarkably efficient because the energy is targeted directly into the material being melted. Very little energy is wasted heating the furnace chamber or the surrounding air.
This efficiency, combined with robust engineering, allows many induction furnaces to operate continuously for 24 hours, maximizing production output.
Understanding the Practical Limits
While powerful, induction furnaces have operational boundaries and trade-offs that are important to understand.
Maximum Temperature Defines Capability
The typical 2000°C limit is more than sufficient for melting iron (1538°C), steel (around 1370-1540°C), copper (1084°C), and aluminum (660°C). However, it may not be suitable for melting refractory metals with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten (3422°C) or tantalum (3017°C), which require specialized vacuum arc or electron-beam furnaces.
Power Supply Governs Performance
The rate of melting and the total capacity of the furnace are directly tied to the kilowatt (kW) rating of its power supply. A smaller, lower-kW furnace is excellent for a laboratory or small foundry but cannot match the throughput of a large, high-power industrial unit.
Cost and Complexity
The sophisticated power supplies and control systems make induction furnaces a significant capital investment. Their complexity also requires skilled technicians for maintenance and repair, a factor to consider when comparing them to simpler, more traditional melting technologies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The suitability of an induction furnace depends entirely on your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is melting common industrial metals like steel, iron, or copper: An induction furnace is an ideal choice, as its typical maximum temperature of 2000°C far exceeds their melting points.
- If your primary focus is process control and metal quality: The precise temperature regulation and uniform, non-contact heating make an induction furnace superior for creating consistent, high-purity alloys.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency and a clean environment: The flameless, targeted heating method offers significant advantages in energy efficiency, speed, and reduced emissions compared to fossil-fuel furnaces.
Ultimately, understanding that an induction furnace is a precision tool for controlled heating—not just a source of raw heat—is the key to leveraging its full potential.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 2000°C (3632°F) |
| Heating Method | Electromagnetic induction (eddy currents) |
| Key Advantage | Precise, uniform, non-contact heating |
| Common Applications | Melting steel, iron, copper, aluminum |
| Efficiency | High, with minimal energy waste |
Ready to enhance your lab's melting capabilities with precision and efficiency? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for uniform heating and superior metal purity. Whether you're melting common alloys or need controlled environments for high-quality results, our solutions are tailored to meet your laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how our induction furnaces can optimize your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What is the principle of a tube furnace? Master Controlled Heating for Precise Lab Results
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















