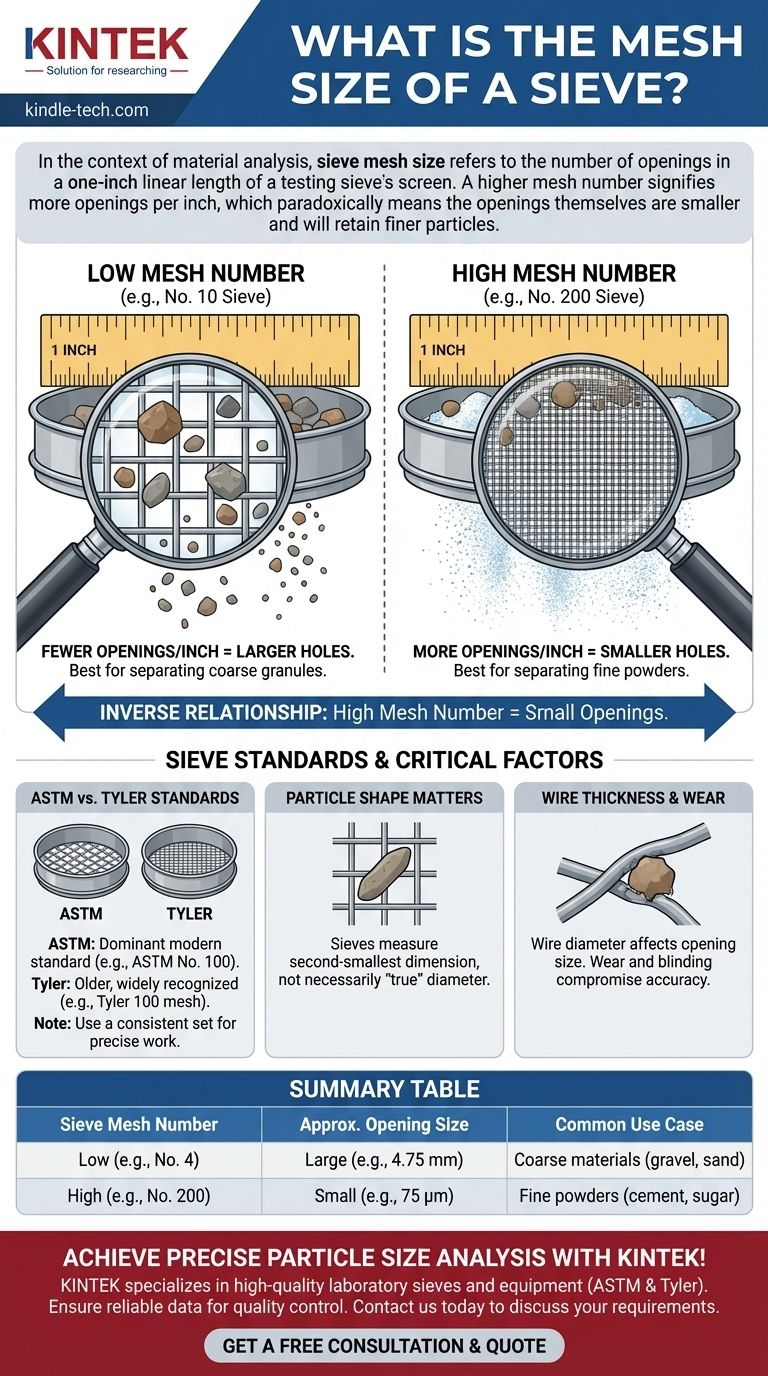
In the context of material analysis, sieve mesh size refers to the number of openings in a one-inch linear length of a testing sieve's screen. A higher mesh number signifies more openings per inch, which paradoxically means the openings themselves are smaller and will retain finer particles. For example, a No. 10 sieve has 10 openings per inch, while a much finer No. 200 sieve has 200 openings per inch.
Sieve mesh size is an inverse measure of particle size. The core principle to remember is that a high mesh number corresponds to small openings used to separate fine powders, while a low mesh number corresponds to large openings for separating coarse granules.

How Sieve Mesh Is Defined
To truly understand material separation, you must first grasp the simple but counterintuitive logic behind sieve mesh designations. The entire system is built on a physical count of wires within a specific area.
The Fundamental Principle: Openings Per Inch
The mesh number, or mesh count, is a straightforward measurement: the number of wires (or openings) that exist along one linear inch of the sieve screen.
This simple count gives the sieve its name, such as a "No. 35 Sieve," which has 35 openings per inch.
The Critical Inverse Relationship
This is the most common point of confusion. Because the mesh number is a count of openings within a fixed inch, more openings mean each individual opening must be smaller.
Therefore, the relationship between mesh number and particle size is always inverse:
- High Mesh Number = More Wires/Openings = Smaller Holes = Retains Finer Particles
- Low Mesh Number = Fewer Wires/Openings = Larger Holes = Retains Coarser Particles
From Mesh Number to Particle Size (Microns)
While the mesh number is a convenient label, the critical technical specification is the actual size of the openings, typically measured in micrometers (µm) or millimeters (mm).
Every standardized sieve has a defined opening size. For instance, an ASTM No. 200 sieve, which has 200 wires per inch, is defined as having openings of 75 µm (or 0.075 mm). Any particle larger than 75 µm will be retained on this sieve screen.
Sieve Standards: ASTM vs. Tyler
To ensure results are repeatable and comparable across different labs and industries, standardized sieve series were created. The two most common are ASTM and Tyler.
The ASTM Standard
The ASTM International (American Society for Testing and Materials) standard is the dominant modern standard, particularly in the United States. Its designations are written as "ASTM No. X" (e.g., ASTM No. 100).
This standard precisely specifies the nominal opening dimension, allowable variations, and the diameter of the wire used to weave the mesh.
The Tyler Standard
The Tyler Standard Sieve Series is an older but still widely recognized system. Its designations are often written as "Tyler X mesh" (e.g., Tyler 100 mesh).
The basis for the Tyler series is the No. 200 sieve with an opening of 74 microns. Each successively coarser sieve in the series has an opening size that is approximately 1.414 (the square root of 2) times larger than the one before it.
Why the Distinction Matters
While many ASTM and Tyler sieve sizes are very close and sometimes used interchangeably, they are not identical. For precise scientific or quality control work, it is critical to use a consistent set of sieves from a single standard.
Mixing standards within a single test stack will introduce errors and make the resulting particle size distribution data unreliable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Sieve analysis is a powerful technique, but it is a mechanical process with inherent limitations that every professional must understand to interpret results correctly.
It's Not a Perfect Sphere
Sieve analysis measures a particle's size based on its ability to pass through a square opening. Elongated or irregularly shaped particles may pass through an opening end-on or diagonally, even if their longest dimension is larger than the opening size.
The result is a measurement of the particle's second-smallest dimension, not necessarily its "true" diameter.
Wire Thickness Affects Opening Size
The mesh number only tells you the number of wires per inch. The actual open space available for particles to pass through also depends on the diameter of the wire itself.
This is why standards are so crucial. ASTM E11 specifies the required wire diameter for each mesh size to guarantee a consistent nominal opening. Using non-standard or worn sieves can lead to inaccurate results.
Wear, Damage, and Blinding
Over time, sieve mesh can stretch, wires can break, or the frame can be damaged. This changes the effective opening size and compromises test accuracy.
Furthermore, a phenomenon called blinding occurs when particles become lodged in the mesh openings, preventing other particles from passing through. Regular inspection and proper cleaning are essential for maintaining sieve integrity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of sieves is dictated entirely by the material you are analyzing and the data you need to collect. A stack of sieves is used to determine the "particle size distribution" of a sample.
- If your primary focus is coarse material (like gravel or sand): You will use sieves with low mesh numbers and large openings, such as No. 4 (4.75 mm) to No. 40 (425 µm).
- If your primary focus is fine powders (like cement or powdered sugar): You will need sieves with high mesh numbers and small openings, such as No. 100 (150 µm) to No. 400 (38 µm).
- If you need a full particle size distribution: You will use a standardized stack of sieves with progressively smaller openings (higher mesh numbers) to characterize the full range of particle sizes within your sample.
Ultimately, understanding sieve mesh size transforms it from an abstract number into a powerful tool for precisely controlling and characterizing your materials.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Mesh Number | Approx. Opening Size | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Low (e.g., No. 4) | Large (e.g., 4.75 mm) | Coarse materials (gravel, sand) |
| High (e.g., No. 200) | Small (e.g., 75 µm) | Fine powders (cement, sugar) |
Achieve precise particle size analysis with the right sieves from KINTEK!
Accurate sieve analysis is critical for quality control in industries like pharmaceuticals, construction, and food processing. KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory sieves and equipment, including full ASTM and Tyler standard sieve sets, to ensure your particle size distribution data is reliable and reproducible.
Our experts can help you select the perfect sieves for your specific material and application needs. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Get a Free Consultation & Quote
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- Why is a laboratory sieving system required for bentonite in coatings? Ensure Flawless Surface Performance
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- How do high-precision sieving systems benefit zeolite preparation? Maximize Adsorption for Wastewater Treatment



















