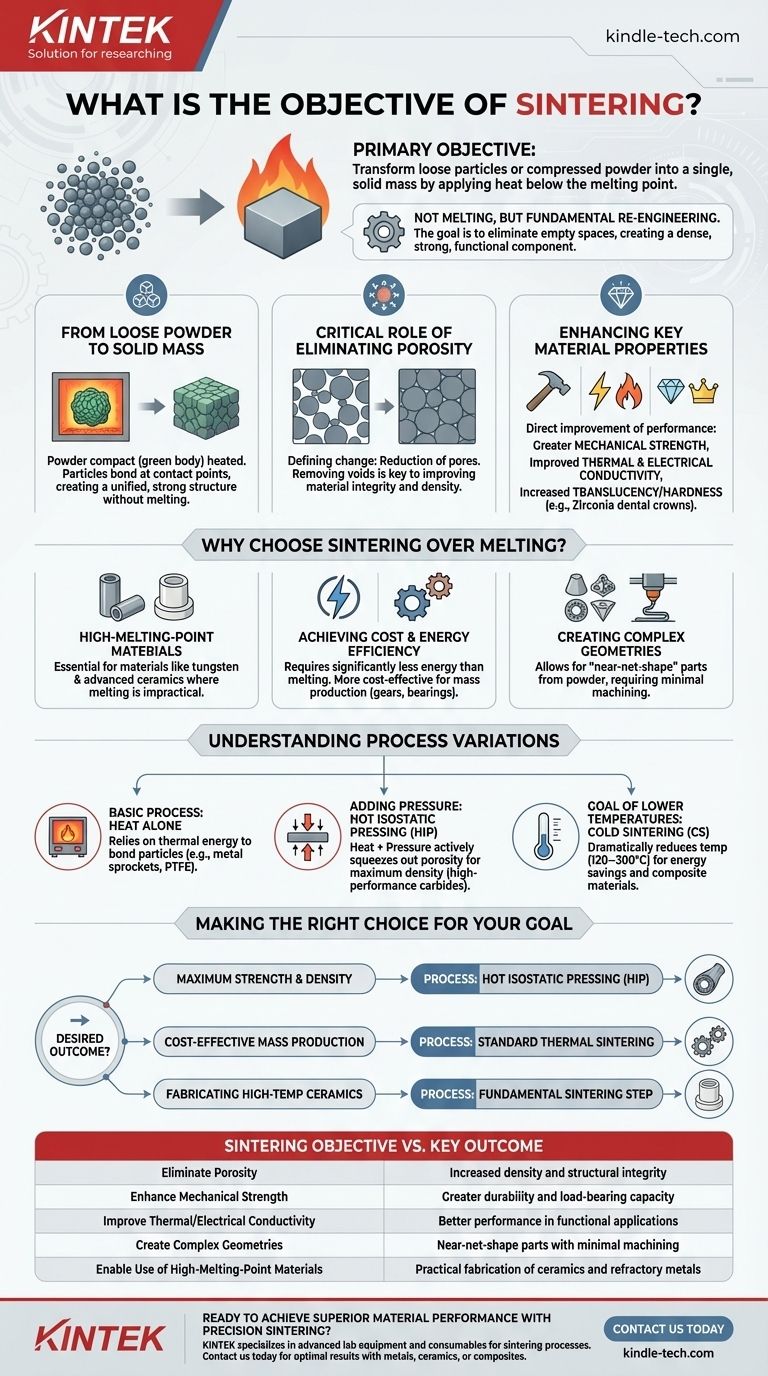
The primary objective of sintering is to transform a collection of loose particles or a compressed powder into a single, solid mass. This is accomplished by applying heat below the material's melting point, causing the particles to fuse together, which increases the material's strength, density, and overall performance.
Sintering is not about melting a material; it's about fundamentally re-engineering it. The core goal is to eliminate the empty spaces between powder particles, thereby creating a dense, strong, and functional component with enhanced properties like strength and conductivity.

How Sintering Fundamentally Transforms Materials
Sintering is a critical step in powder metallurgy and ceramics processing. It takes a fragile, loosely-bound shape and turns it into a robust, finished part.
From Loose Powder to Solid Mass
The process begins with a powder compact, often called a "green body," which is held together loosely. By heating this compact in a furnace, the particles bond at their contact points, creating a strong, unified structure without ever becoming fully liquid.
This method is highly effective for turning fragmented materials into a solid object with desirable characteristics.
The Critical Role of Eliminating Porosity
The defining change during sintering is the reduction or elimination of pores—the tiny empty spaces between the initial powder particles. Removing these voids is the key to improving the material's integrity.
As the particles fuse, these pores shrink and close, making the final object much denser than the initial powder compact.
Enhancing Key Material Properties
By eliminating porosity and increasing density, sintering directly improves a material's performance characteristics. This is the ultimate objective.
Key enhancements include greater mechanical strength, improved thermal and electrical conductivity, and in some ceramics, increased translucency or hardness. This is why sintered zirconia is used for durable dental crowns.
Why Choose Sintering Over Melting?
While melting and casting can also create solid objects, sintering offers unique advantages that make it the superior or only choice for many applications.
Working with High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering is essential for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten and many advanced ceramics. Melting these materials is often impractical or prohibitively expensive, making sintering the only viable method to form them into useful shapes.
Achieving Cost and Energy Efficiency
Because sintering occurs below the melting point, it requires significantly less energy than melting and casting processes. This makes it a more cost-effective and efficient method for the mass production of components like gears, bearings, and electrical contacts.
Creating Complex Geometries
The process starts with a powder that can be pressed into intricate shapes. This allows for the creation of complex, "near-net-shape" parts that require minimal follow-up machining, saving both time and material.
Understanding the Process Variations
Not all sintering is the same. The process can be adapted to achieve specific outcomes, often by introducing additional variables like pressure.
The Basic Process: Heat Alone
The most common form of sintering relies solely on thermal energy applied in a furnace to bond particles together. This is sufficient for a vast range of applications, from producing metal sprockets to PTFE (Teflon) components.
Adding Pressure for Maximum Density
For applications demanding the highest possible performance, pressure is applied simultaneously with heat. This process, known as Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), actively squeezes out remaining porosity to create an exceptionally dense and strong final product, which is vital for high-performance carbides.
The Goal of Lower Temperatures
Advanced methods like Cold Sintering (CS) aim to dramatically reduce the required temperature (down to 120–300°C). The objective here is to further reduce energy consumption and enable the synthesis of new composite materials that would be damaged by high heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific objective of sintering depends entirely on the desired outcome for the final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and density: A process that combines heat and pressure, like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP), is the ideal path for performance-critical parts.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: Standard thermal sintering of pressed powder is the most efficient method for creating components like gears and bearings.
- If your primary focus is fabricating high-temperature ceramics: Sintering is not just an option but a necessary and fundamental step to achieve the required hardness and durability.
Ultimately, sintering provides a powerful and versatile method to engineer a material's final properties from the particle level upwards.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Objective | Key Outcome |
|---|---|
| Eliminate Porosity | Increased density and structural integrity |
| Enhance Mechanical Strength | Greater durability and load-bearing capacity |
| Improve Thermal/Electrical Conductivity | Better performance in functional applications |
| Create Complex Geometries | Near-net-shape parts with minimal machining |
| Enable Use of High-Melting-Point Materials | Practical fabrication of ceramics and refractory metals |
Ready to achieve superior material performance with precision sintering? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for sintering processes, helping you create stronger, denser, and more reliable components. Whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or composites, our solutions ensure optimal results. Contact us today to discuss your specific sintering needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- What conditions does a vacuum hot press provide for Al2O3/ZrO2 sintering? Achieve 1550°C and 30 MPa Densification
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.



















