In short, the porosity of a sintered ceramic is not a fixed number. It is a highly variable and engineered property that is intentionally controlled during the manufacturing process. The final porosity is determined by the initial state of the ceramic powder and the specific temperature, duration, and pressure used during sintering.
The central takeaway is that porosity in ceramics is a design choice, not an inherent flaw. By carefully controlling the sintering process, manufacturers can tune the level of porosity to achieve specific performance characteristics, from maximum strength to controlled permeability.

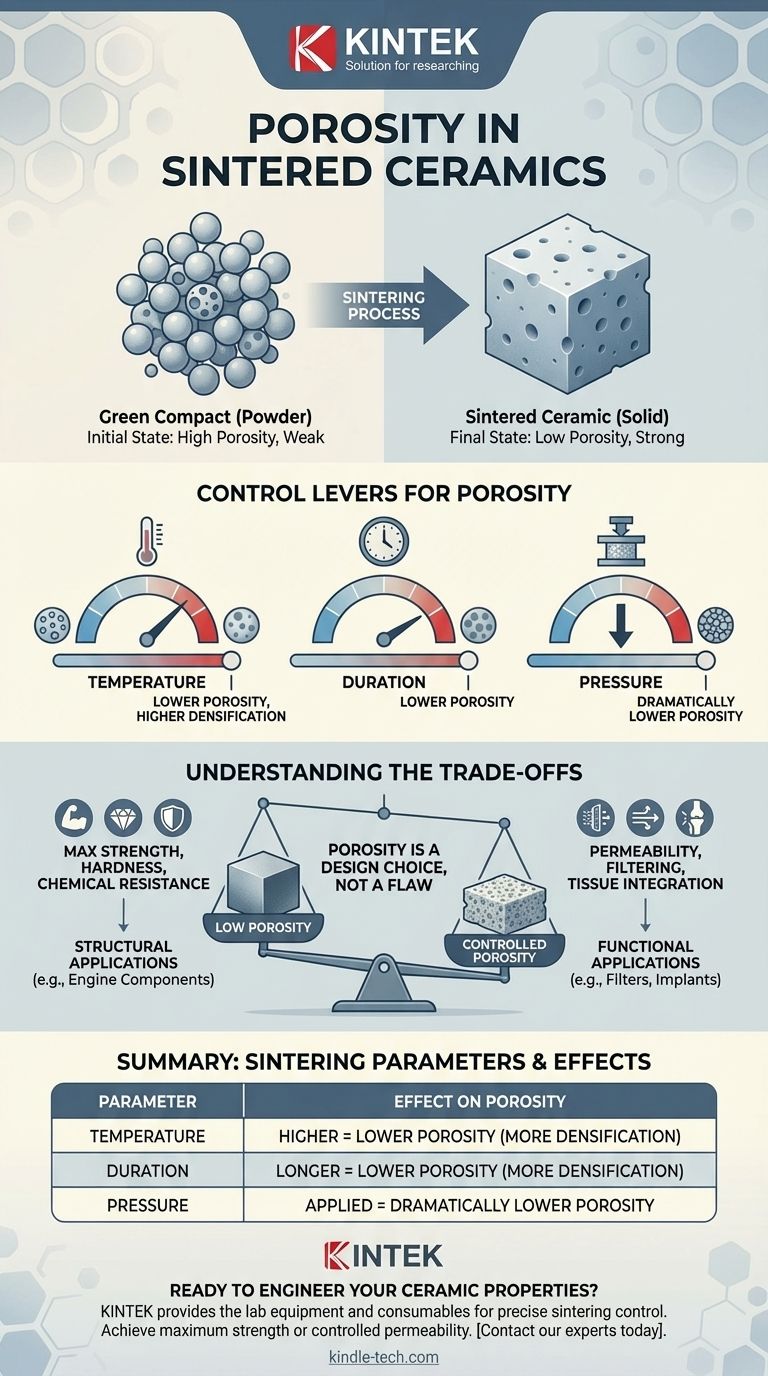
The Sintering Process: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is the cornerstone of modern ceramic manufacturing. It is the process that transforms a compacted powder, known as a "green compact," into a dense, solid object with useful mechanical properties.
The "Green Compact": Your Starting Point
Ceramic production begins with a fine powder that is pressed or formed into the desired shape. This initial object, the green compact, is weak and contains a significant amount of empty space, or pores, between its particles.
This initial porosity is the baseline that the sintering process aims to reduce.
How Sintering Reduces Porosity
Sintering involves heating the green compact to a high temperature, but one that is still below the material's melting point. At this temperature, atoms begin to diffuse across the boundaries of the particles.
This solid-state diffusion causes the individual particles to fuse together, eliminating the voids between them and causing the entire part to shrink and densify.
The Primary Goal: Densification
For most high-performance applications like cutting tools or electrical insulators, the primary goal of sintering is to achieve the highest possible density.
Reducing porosity increases the material's mechanical strength, hardness, and thermal stability, making the final product robust and reliable.
The Levers for Controlling Ceramic Porosity
Engineers have several key variables they can manipulate during the sintering process to achieve the desired final porosity.
Sintering Temperature
Higher temperatures accelerate the rate of atomic diffusion. This allows particles to bond more quickly and effectively, leading to greater densification and lower final porosity in a shorter amount of time.
Sintering Duration
Extending the time the ceramic is held at the sintering temperature allows the diffusion process to continue for longer. This gives the material more time to eliminate residual pores, further increasing its density.
Applied Pressure
In some advanced processes, external pressure is applied during heating. This physically forces the particles closer together, dramatically speeding up densification and making it possible to achieve exceptionally low levels of porosity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving a specific level of porosity is always a balance between desired performance and practical constraints. There is no single "best" level of porosity; it depends entirely on the application.
Low Porosity: The Path to Strength
For structural applications, lower porosity is almost always better. A dense, non-porous ceramic has superior mechanical strength, hardness, and resistance to chemical attack. This is critical for parts like engine components, cutting tools, and refractory materials.
When Porosity Is a Feature, Not a Flaw
However, some advanced applications require a specific, controlled level of porosity. Materials used for filters, catalyst supports, or biomedical implants are designed with an interconnected network of pores to allow fluids to pass through or to encourage tissue integration.
The Cost of Perfection
Achieving near-zero porosity requires aggressive sintering conditions—very high temperatures, long durations, or expensive pressure-assisted equipment. This increases energy consumption and manufacturing costs, which may not be justifiable for products like common ceramic tiles or sanitaryware.
Engineering Porosity for Your Application
The right level of porosity is determined by the end-use of the ceramic component. The manufacturing process must be tailored to meet that specific goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical strength and durability: You must minimize porosity by using high temperatures, sufficient time, and potentially pressure-assisted sintering.
- If your primary focus is creating a functional porous material: You must use carefully controlled, often lower, temperatures and specialized starting materials to create and preserve a desired pore structure.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost and general performance: You must optimize sintering parameters to achieve acceptable density and strength without incurring the high energy and time costs of full densification.
Ultimately, viewing porosity as a controllable design parameter is the key to unlocking the vast potential of ceramic materials.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Parameter | Effect on Porosity |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Higher temperature = Lower porosity (more densification) |
| Duration | Longer time = Lower porosity (more densification) |
| Pressure | Applied pressure = Dramatically lower porosity |
Ready to engineer the perfect ceramic properties for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed to precisely control the sintering process. Whether your goal is maximum strength or controlled permeability, our solutions help you achieve the exact porosity your project demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's ceramic manufacturing and research needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Aluminum Oxide Al2O3 Heat Sink for Insulation
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining
- What is a ceramic tube? A Guide to Extreme Environment Performance
- How do porcelain boats and quartz tubes function in CVD of BN? Optimize Your Boron Nitride Coating Efficiency
- Why is Boron Nitride used in RRDE? Enhance Precision with Superior Insulating and Protective Material
- What are ceramic tubes used for? Essential Components for Extreme Heat & Electrical Insulation



















