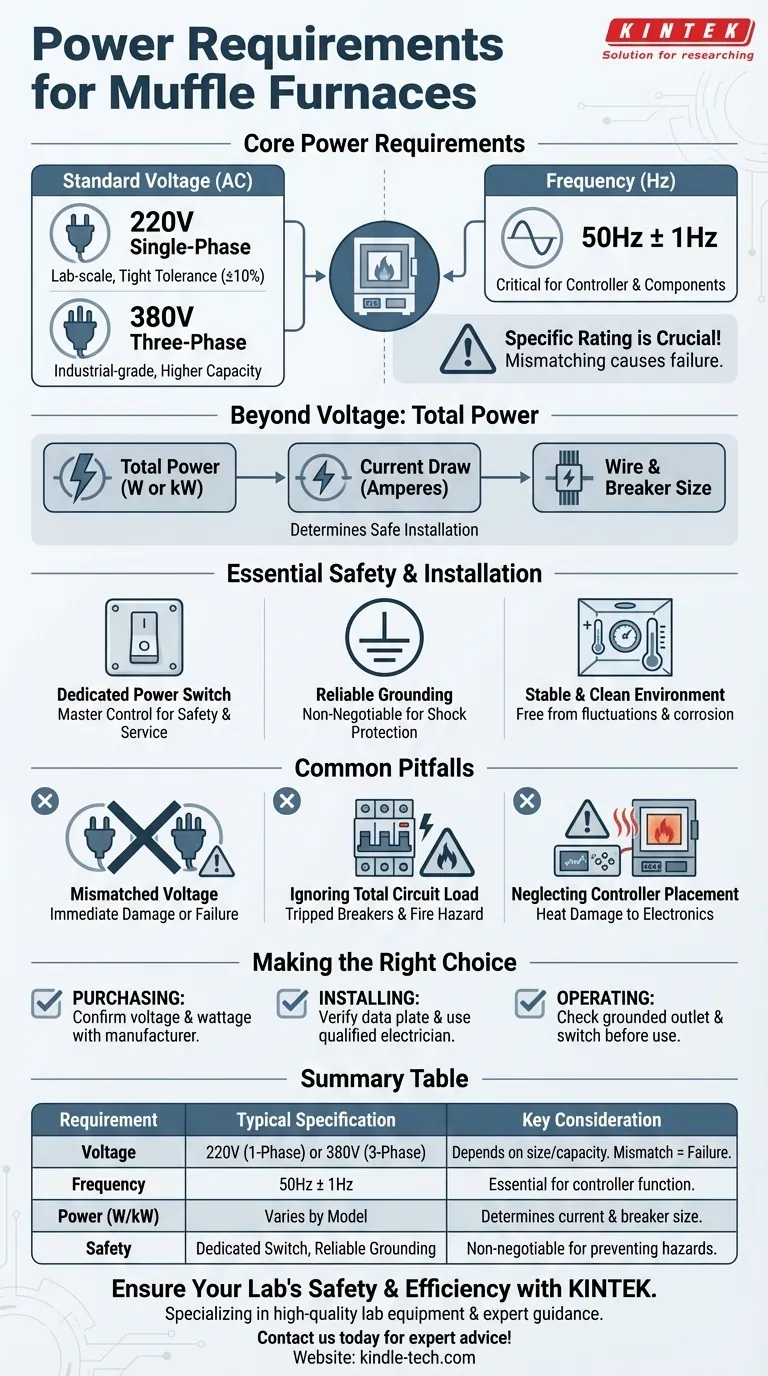
At its core, a muffle furnace typically operates on either a standard 220V single-phase or a more powerful 380V three-phase power supply. The specific requirement depends entirely on the furnace's size, heating capacity, and intended application. The provided alternating current (AC) must also be stable, with a standard frequency like 50Hz.
The most critical factor is not a universal standard, but the specific electrical rating of your particular furnace model. Mismatching the voltage or underestimating the power draw is a primary cause of equipment failure and a significant safety hazard.

Deconstructing the Power Requirement
To ensure safe and effective operation, you must look beyond a single voltage number. The complete electrical profile includes voltage, current, and the stability of the supply.
Standard Voltage Levels
Most laboratory-scale muffle furnaces are designed for a standard single-phase power supply, commonly AC 220V. The tolerance for this is usually tight, for example, within ±10% (22V) of the target.
For larger, industrial-grade furnaces with higher temperature capabilities or larger chambers, a three-phase 380V supply is often necessary to deliver the required power efficiently.
The Role of Frequency (Hz)
The power supply frequency, specified as 50Hz ± 1Hz, is another critical parameter. The furnace's internal controller and electrical components are designed to operate at this specific frequency. Using an incorrect frequency can lead to erratic performance or damage.
Beyond Voltage: Verifying Total Power
Voltage is only one part of the equation. The furnace's total power consumption, measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW), determines how much electrical current it will draw, measured in amperes (A). This total power rating dictates the necessary wire gauge and circuit breaker size for safe installation.
Essential Electrical Safety and Installation
Proper setup is as important as the power supply itself. The environment and the electrical connections are foundational to safe operation.
The Dedicated Power Switch
A separate, main power switch must be installed at the power cord's entry point. This switch acts as a master control for the entire system, providing a clear and accessible way to de-energize the furnace completely in an emergency or for servicing.
Grounding is Non-Negotiable
Both the furnace body and its temperature controller must be reliably grounded. This is a critical safety feature that protects operators from electrical shock in the event of an internal fault where a live wire might contact the metal casing.
A Stable and Clean Environment
The furnace requires a stable power source free from significant fluctuations. It should also be placed in a clean, dry room on a solid surface, away from any flammable materials or corrosive gases that could degrade the wiring and electrical components over time.
Understanding the Common Pitfalls
Many operational issues stem from overlooking basic electrical requirements during the initial setup.
Mismatching the Voltage
The most severe mistake is connecting the furnace to the wrong voltage. Connecting a 220V furnace to a 380V supply will cause immediate and catastrophic damage to the heating elements and controller. Connecting a 380V furnace to a 220V supply will result in it failing to reach its target temperature, if it heats at all.
Ignoring the Total Circuit Load
Focusing only on voltage while ignoring the amperage draw is a common oversight. A furnace can draw significant current, and plugging it into a circuit that is not rated for that load will lead to tripped breakers or, in a worst-case scenario, overheating wires that create a fire hazard.
Neglecting the Controller's Placement
The temperature controller contains sensitive electronics. It should not be placed too close to the furnace, as the radiant heat can cause it to overheat and fail. It must also be kept free from excessive vibration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your approach should be dictated by whether you are purchasing, installing, or operating the equipment.
- If your primary focus is purchasing a new furnace: Confirm the required voltage (220V or 380V) and total wattage with the manufacturer before you buy to ensure it is compatible with your facility's electrical system.
- If your primary focus is installing a furnace: Locate the manufacturer's data plate on the unit to verify its exact power requirements, and have a qualified electrician install a dedicated, grounded circuit with an appropriate main switch.
- If your primary focus is daily operation: Always confirm that the unit is properly plugged into its designated, grounded outlet and that the main power switch is accessible before beginning any heating cycle.
Verifying the specific electrical needs of your muffle furnace is the first and most critical step toward safe, reliable, and effective operation.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | Typical Specification | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | 220V (Single-Phase) or 380V (Three-Phase) | Depends on furnace size and heating capacity. Mismatching causes failure. |
| Frequency | 50Hz ± 1Hz | Essential for the proper function of the controller and components. |
| Power (W/kW) | Varies by model | Determines the current draw (Amperes) and necessary circuit breaker size. |
| Safety | Dedicated switch, reliable grounding | A non-negotiable requirement to prevent electrical hazards and equipment damage. |
Ensure your lab's safety and efficiency with the right power setup for your muffle furnace.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including muffle furnaces, and provides expert guidance on installation and operation. Our team can help you verify your facility's compatibility and ensure a safe, dedicated circuit is in place.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let our expertise power your success. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of wet ashing? Key Safety & Contamination Risks
- What is commonly used during a dry ashing experiment? Essential Equipment for Accurate Ash Analysis
- Why is the metal melting temperature important? The Key to Manufacturing & Performance
- What are the advantages of dry ashing over wet ashing? Streamline Your Lab's Sample Prep
- What affects the rate of melting? Master the Key Factors for Precise Control



















