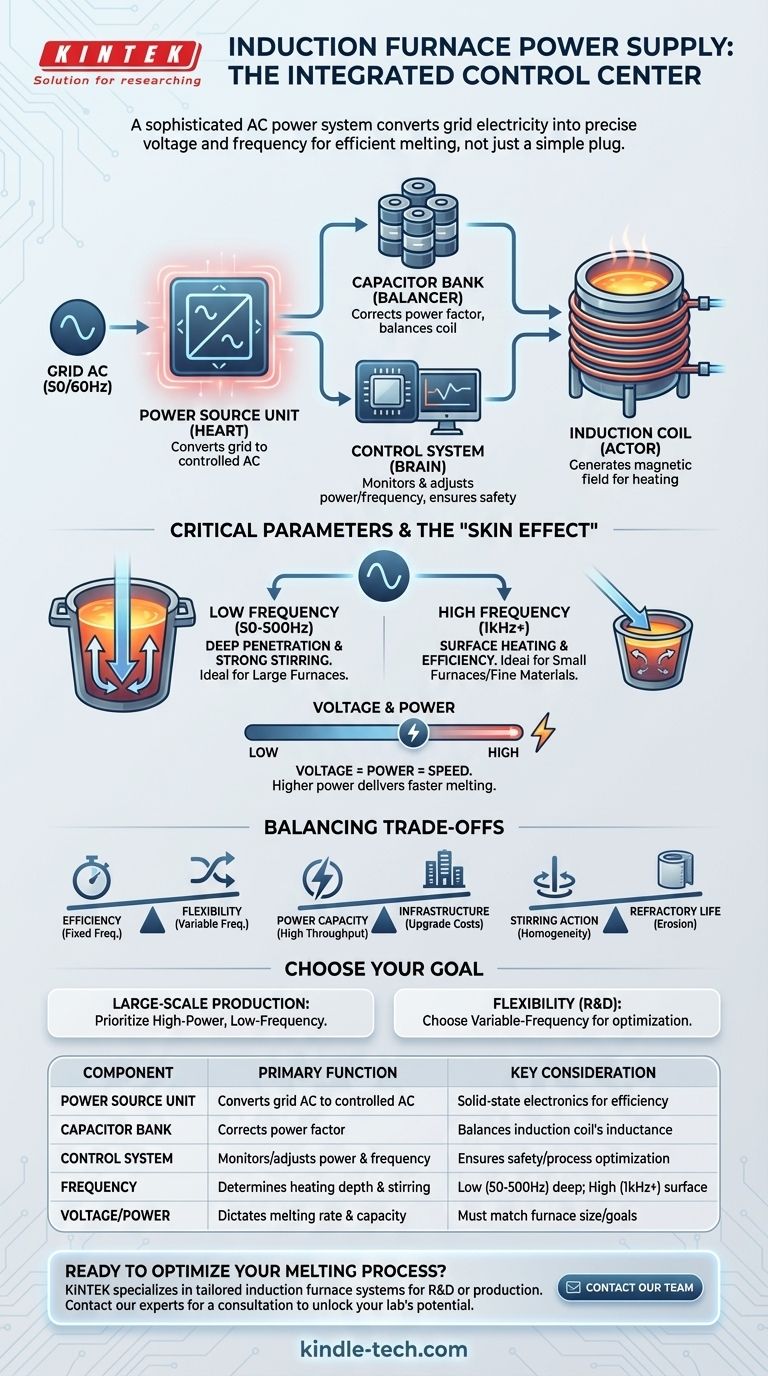
At its core, the power supply for an induction furnace is a specialized AC power system. It is not a simple connection to the electrical grid but a sophisticated unit designed to convert standard utility power into the precise voltage and frequency needed to melt metal. This system works in conjunction with capacitors and a control unit to generate powerful, oscillating magnetic fields within the furnace's induction coil, which in turn induces intense electrical currents directly within the material to be melted.
The power supply of an induction furnace is not merely a source of electricity; it is an integrated control system. Its primary function is to convert standard grid power into a high-current, precisely controlled frequency tailored to the furnace size and the material being melted.

The Anatomy of an Induction Furnace Power System
To understand the furnace, you must first understand the components that drive it. The "power supply" is actually a system of interconnected parts working in harmony.
The Power Source Unit
This is the heart of the system. It takes standard three-phase AC power from the grid (typically at 50 or 60 Hz) and converts it. Modern systems use solid-state electronics to first rectify the AC to DC, and then invert it back to a single-phase AC at a new, precisely controlled frequency.
The Capacitor Bank
The induction coil in the furnace is a massive inductor. To operate efficiently, this inductance must be balanced. A bank of capacitors is connected in parallel with the coil to correct the power factor, ensuring that the maximum amount of energy is transferred to the metal and not wasted.
The Control System
This is the brain of the operation. The control system monitors the melting process and gives the operator precise control over the power level and frequency. It ensures the furnace operates safely and efficiently, adjusting output to match the specific requirements of the melt.
The Induction Coil
While technically part of the furnace body, the induction coil is the final component of the electrical circuit. This large, water-cooled copper coil receives the high-current, controlled-frequency power from the supply system. The current flowing through it generates the powerful magnetic field that is the basis of induction heating.
Why Frequency and Voltage Are Critical
The effectiveness of an induction furnace is defined by the characteristics of the power delivered to it. The voltage and frequency are not arbitrary; they are fundamental engineering parameters.
The Role of Frequency
The frequency of the AC power determines how the magnetic field interacts with the metal charge. This is known as the "skin effect," where higher frequencies concentrate the induced current near the surface of the material.
- Low Frequencies (e.g., 50 Hz - 500 Hz): This power penetrates deeper into the melt, creating strong stirring action. This is ideal for large furnaces melting large scrap pieces, as it promotes temperature and chemical uniformity.
- Medium to High Frequencies (e.g., 1 kHz - 10 kHz+): This power is more concentrated at the surface. It is highly efficient for smaller furnaces, melting finer materials, or applications where less stirring is desired.
The Importance of Voltage and Power
The voltage applied to the system determines the maximum power that can be delivered to the coil. A higher power level translates directly to a faster melting rate. Ensuring the power supply can meet the furnace's demand is essential for meeting production targets.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting or operating a power supply involves balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" solution, only the one that is right for the application.
Efficiency vs. Flexibility
A fixed-frequency power supply designed for a specific furnace and material can be highly efficient. However, a variable-frequency supply offers the flexibility to efficiently melt different batch sizes or material types, often at a higher initial cost and complexity.
Power Capacity vs. Infrastructure
A high-power furnace can dramatically increase throughput, but it places significant demands on a facility's electrical infrastructure. The cost of upgrading transformers, switchgear, and cabling must be factored into the decision to install a more powerful system.
Stirring Action vs. Refractory Life
The strong stirring action created by low-frequency power supplies is excellent for metallurgical homogeneity. However, this vigorous movement can also accelerate the erosion of the furnace's refractory lining, leading to increased maintenance costs and downtime.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational goals should dictate your power supply strategy.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, consistent production: Prioritize a high-power, lower-frequency system that is precisely matched to your furnace size for maximum melting rate and metallurgical stirring.
- If your primary focus is flexibility for R&D or specialty alloys: A variable-frequency power supply is the superior choice, as it allows you to optimize the heating and stirring for a wide range of materials and batch sizes.
Ultimately, viewing the power supply as the furnace's integrated control center—not just its plug—is the key to unlocking operational efficiency and quality.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source Unit | Converts grid AC to controlled AC | Solid-state electronics for efficiency |
| Capacitor Bank | Corrects power factor for efficiency | Balances the induction coil's inductance |
| Control System | Monitors and adjusts power & frequency | Ensures safety and process optimization |
| Frequency | Determines heating depth and stirring | Low (50-500Hz) for deep stirring; High (1kHz+) for surface heating |
| Voltage/Power | Dictates melting rate and capacity | Must match furnace size and production goals |
Ready to optimize your melting process? The right power supply is critical for efficiency, quality, and flexibility. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including induction furnace systems tailored to your specific R&D or production needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect system to achieve your metallurgical goals.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and unlock the full potential of your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab



















