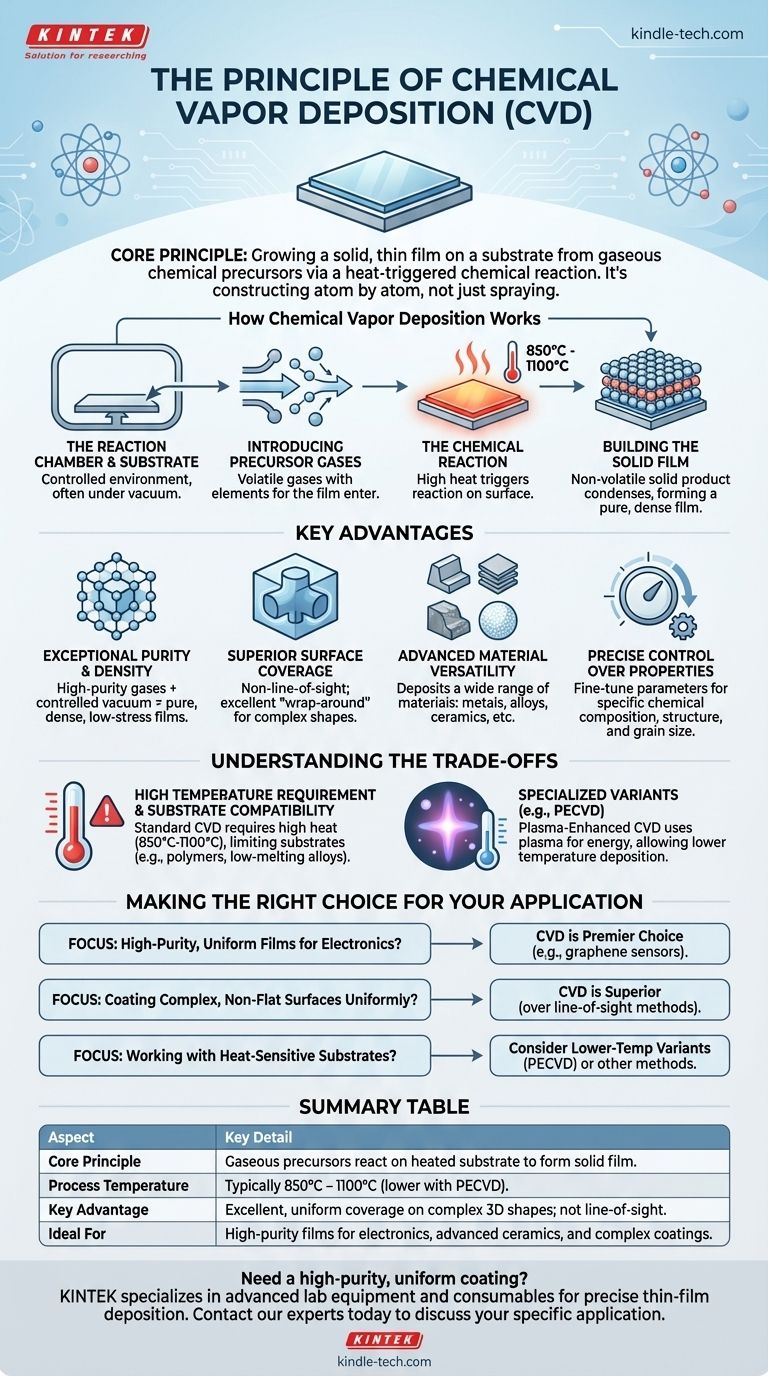
At its core, the principle of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a process where a solid, thin film is grown on a surface, known as a substrate, from gaseous chemical precursors. These gases are introduced into a reaction chamber where they undergo a chemical reaction triggered by heat. The product of this reaction is a solid material that deposits onto the substrate, building the desired film layer by layer.
The central idea of CVD is not to simply spray a coating onto a surface, but to construct it atom by atom from chemical reactions in a gaseous state. This provides exceptional control over the film's purity, structure, and properties, making it a cornerstone of high-technology manufacturing.
How Chemical Vapor Deposition Works
The CVD process, while highly sophisticated in its results, is based on a series of straightforward physical and chemical steps. It transforms volatile gases into a stable, high-performance solid film.
The Reaction Chamber and Substrate
First, the object to be coated (the substrate) is placed inside a sealed reaction chamber. This chamber is often operated under a vacuum to ensure a controlled environment free from contaminants.
Introducing Precursor Gases
Next, one or more volatile precursor gases are introduced into the chamber. These gases contain the chemical elements that will make up the final solid film.
The Chemical Reaction
The substrate is typically heated to a high temperature, generally between 850°C and 1100°C. This heat provides the energy needed to trigger a chemical reaction between the precursor gases on or near the substrate's surface.
Building the Solid Film
This chemical reaction produces a non-volatile solid product that condenses and deposits directly onto the heated substrate. Over time, this deposition builds up a thin, dense, and highly pure film with a strong bond to the underlying surface.
Key Advantages of the CVD Process
CVD is a leading manufacturing method because of the unique combination of quality and versatility it offers for producing advanced materials.
Exceptional Purity and Density
Because the process starts with highly pure gases in a controlled vacuum environment, the resulting films are exceptionally pure, dense, and have very low residual stress.
Superior Surface Coverage
CVD is not a line-of-sight process. The precursor gases surround the substrate, allowing the chemical reaction to occur on all exposed surfaces. This provides excellent "wrap-around" properties for coating complex, three-dimensional shapes uniformly.
Advanced Material Versatility
The process is incredibly flexible, capable of depositing a wide variety of materials. This includes metals, non-metal films like silicon nitride, multi-component alloys, and advanced ceramics.
Precise Control Over Film Properties
By carefully adjusting deposition parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas composition, engineers can precisely control the final film's chemical composition, crystal structure, and grain size.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD is not a universal solution. Its primary limitations stem directly from the core mechanism of using high heat to drive the chemical reaction.
The High Temperature Requirement
Standard CVD processes require very high temperatures. This high thermal budget can damage or deform many substrate materials, limiting which materials can be successfully coated.
Substrate Compatibility Issues
Materials with low melting points or those that are sensitive to thermal shock cannot be used as substrates in traditional high-temperature CVD processes.
Specialized Variants as a Solution
To overcome the heat limitation, specialized techniques like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) have been developed. These methods use a plasma to provide the energy for the chemical reaction, allowing deposition to occur at significantly lower temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a deposition method depends entirely on the required properties of the final film and the constraints of your substrate material.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity, uniform films for electronics: CVD is a premier choice, especially for advanced materials like the high-quality graphene sheets used in sensors.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-flat surfaces uniformly: CVD's excellent wrap-around capability makes it a superior choice over line-of-sight methods like sputtering.
- If you are working with heat-sensitive substrates like polymers or certain alloys: Standard high-temperature CVD is unsuitable, and you must consider lower-temperature variants like plasma-assisted CVD or entirely different coating methods.
Ultimately, chemical vapor deposition is a foundational tool for engineering materials at the atomic scale, enabling the creation of components that define modern technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Gaseous precursors react on a heated substrate to form a solid thin film. |
| Process Temperature | Typically 850°C - 1100°C (lower with Plasma-Enhanced CVD). |
| Key Advantage | Excellent, uniform coverage on complex 3D shapes; not line-of-sight. |
| Ideal For | High-purity films for electronics, advanced ceramics, and complex coatings. |
Need a high-purity, uniform coating for your lab's substrates? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise thin-film deposition. Whether you're developing new electronic components or require complex 3D coatings, our expertise in CVD and other deposition technologies can help you achieve superior material performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the ideal solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings



















