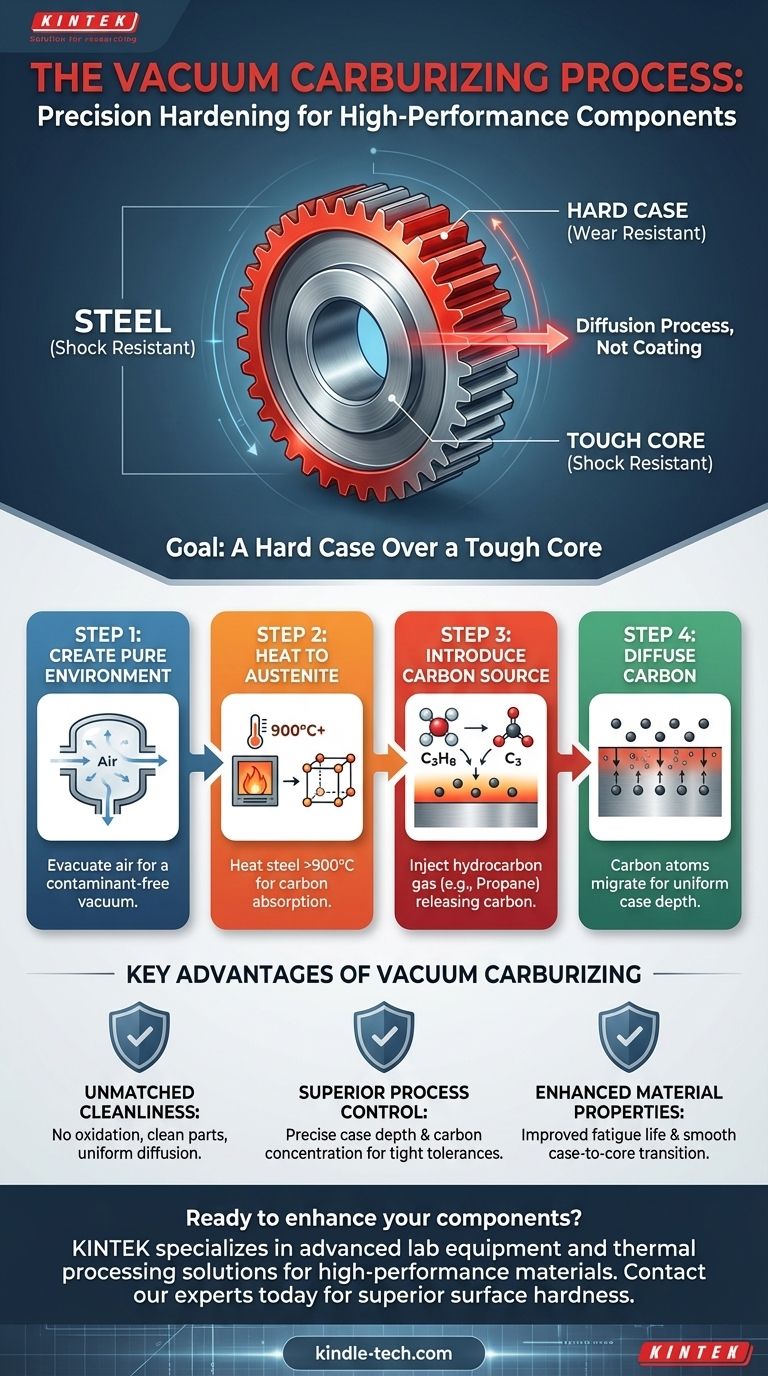
The process of vacuum carburizing is a highly controlled heat treatment used to harden the surface of steel components. It involves heating the steel in a vacuum, introducing a carbon-rich gas like propane, and allowing the heat to break the gas down, which infuses carbon atoms directly into the metal's surface layer. This diffusion of carbon creates an extremely hard, wear-resistant outer "case" while the inner "core" of the component remains tough and ductile.
Carburizing is not simply a coating; it is a diffusion process that fundamentally changes the chemistry of the steel's surface. Using a vacuum creates an ultra-clean environment, enabling precise control over the final hardness and depth of the hardened layer without the risk of surface contamination.

The Goal: A Hard Case Over a Tough Core
The primary objective of carburizing is to create a component with a dual nature: a surface that can withstand abrasion and wear, and a core that can absorb shock and resist fracture.
The Role of Carbon in Steel
In simple terms, more carbon makes steel harder. By introducing additional carbon into the crystalline structure of the steel's surface, we increase its hardness and wear resistance significantly.
Why Not Harden the Entire Part?
A component that is hardened all the way through becomes brittle. For parts like gears or bearings, this is a critical failure point. A tough, non-brittle core is essential for absorbing operational stress, while the hard case provides the durable surface needed for contact with other parts.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of Vacuum Carburizing
The process is a carefully orchestrated sequence of heating, gas injection, and diffusion, all performed within a specialized vacuum furnace.
Step 1: Creating a Pure Environment
The steel components are loaded into a furnace, and the air is pumped out to create a vacuum. This critical first step removes oxygen and other atmospheric contaminants that could react with the hot steel, ensuring the surface remains perfectly clean for optimal carbon absorption.
Step 2: Heating to the Right Temperature
The furnace heats the parts to a specific temperature, typically above 900°C (1650°F). At this temperature, the steel's crystalline structure changes to a phase called austenite, which is uniquely capable of dissolving a high concentration of carbon.
Step 3: Introducing the Carbon Source
Once the steel is at the correct temperature, a hydrocarbon gas—most commonly propane (C3H8)—is introduced into the furnace. The intense heat causes the propane molecules to break apart, releasing free carbon atoms onto the surface of the steel.
Step 4: The Diffusion of Carbon
These free carbon atoms then migrate, or diffuse, into the surface of the steel. The depth of this carbon-rich layer, known as the "case depth," is precisely controlled by the temperature and the amount of time the parts are exposed to the carbon-rich atmosphere.
Understanding the Key Advantages
While other carburizing methods exist, the use of a vacuum provides distinct and critical benefits, particularly for high-performance applications.
Unmatched Cleanliness and Purity
The vacuum environment prevents the formation of surface oxides. This results in cleaner parts that often do not require subsequent cleaning operations and guarantees that the carbon diffusion is uniform and predictable.
Superior Process Control
Vacuum carburizing offers exceptional control over the final carbon concentration and case depth. This precision is essential for manufacturing components with tight tolerances and demanding performance requirements, such as in the aerospace and high-performance automotive industries.
Enhanced Material Properties
Because the process is so clean and controlled, it can lead to improved fatigue life and overall performance of the component. The transition from the hard case to the tough core is smooth and consistent.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Vacuum carburizing is a premium process designed for applications where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is high-performance components: This process is the ideal choice for gears, bearings, and shafts that demand exceptional surface hardness and fatigue resistance.
- If your primary focus is process precision and repeatability: The controlled vacuum environment offers unparalleled control over case depth and material properties, eliminating the variability common in older atmospheric methods.
Ultimately, vacuum carburizing gives you the power to engineer the material properties of a component's surface with molecular-level precision.
Summary Table:
| Step | Process | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Creating a Pure Environment | Evacuate air to create a vacuum, removing contaminants. |
| 2 | Heating to the Right Temperature | Heat steel above 900°C to form austenite for carbon absorption. |
| 3 | Introducing the Carbon Source | Inject hydrocarbon gas (e.g., propane) to release carbon atoms. |
| 4 | The Diffusion of Carbon | Allow carbon to migrate into the steel surface to a controlled depth. |
Ready to enhance your components with precision vacuum carburizing?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and thermal processing solutions, serving industries that demand high-performance materials. Our expertise ensures your gears, bearings, and critical parts achieve superior surface hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue life.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory and manufacturing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- How is the greatest joint strength obtained in brazing? Master the 3 Keys to Superior Metallurgical Bonds
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project



















