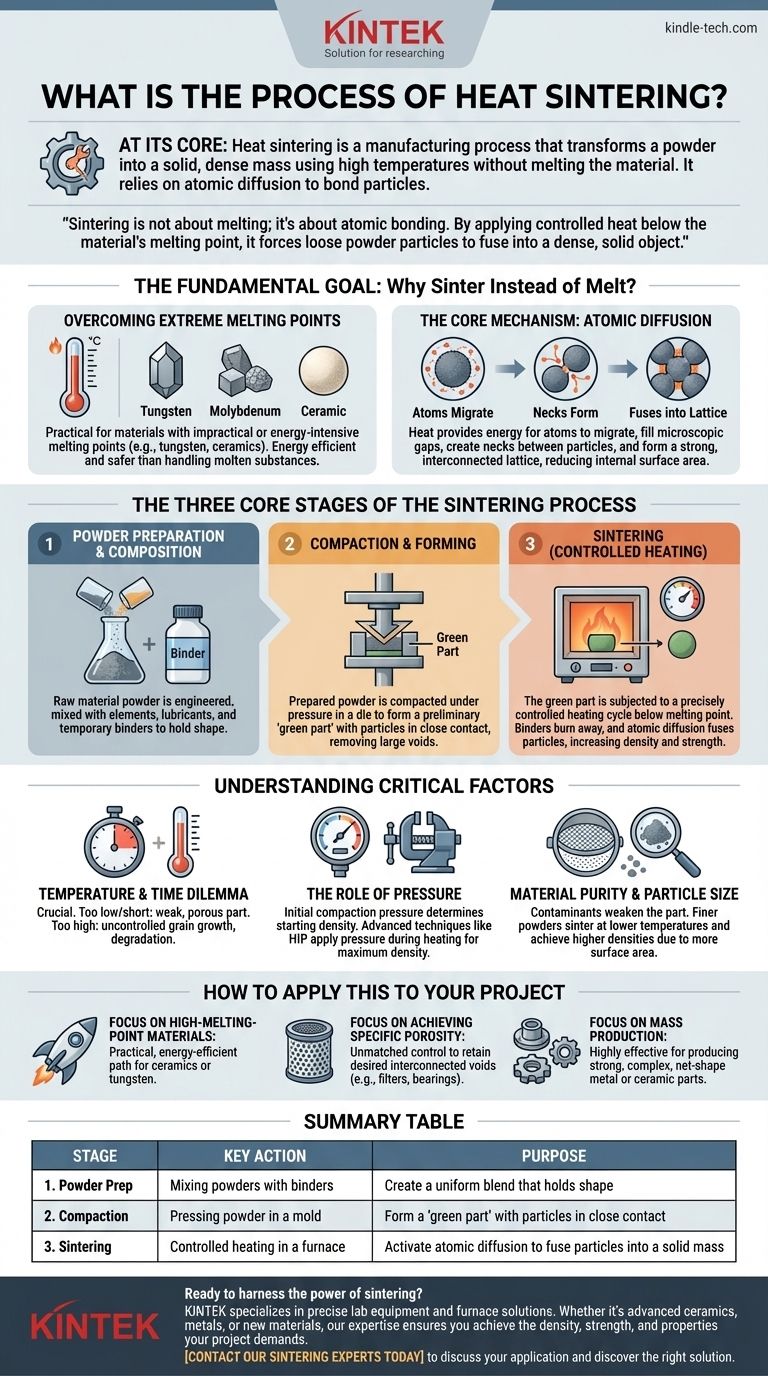
At its core, heat sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms a powder into a solid, dense mass using high temperatures. Critically, this is achieved without ever melting the material to a liquid state. Instead of liquefaction, the process relies on atomic diffusion, where the atoms of individual powder particles migrate and fuse together, bonding the particles into a strong, cohesive whole.
Sintering is not about melting; it's about atomic bonding. By applying controlled heat below the material's melting point, it forces loose powder particles to fuse into a dense, solid object, making it an essential technique for working with materials that have extremely high melting points.
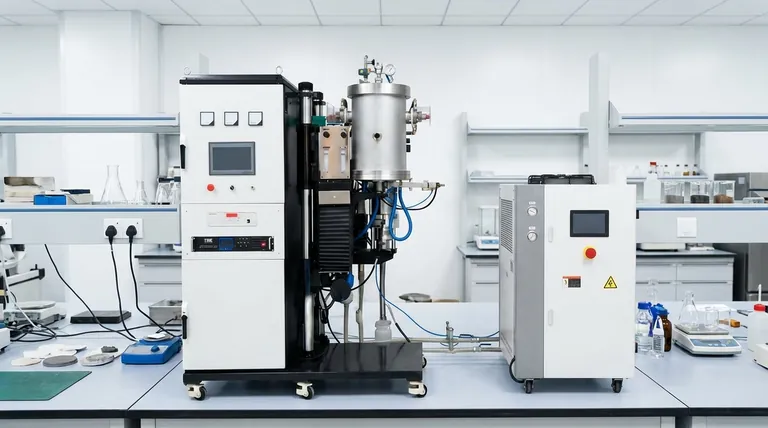

The Fundamental Goal: Why Sinter Instead of Melt?
Understanding sintering begins with knowing why it is often superior to conventional melting and casting. The decision to sinter is typically driven by material properties and the desired final characteristics of the part.
Overcoming Extreme Melting Points
Many advanced materials, such as tungsten, molybdenum, and technical ceramics, have melting points so high that melting them is impractical, energy-intensive, and difficult to control.
Sintering provides a pathway to form solid parts from these materials at temperatures significantly below their melting point, saving energy and avoiding the challenges of handling molten, high-temperature substances.
The Core Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion
Sintering works by creating the conditions for atoms to move. When the powdered material is heated, its atoms become more energetic.
At the points where particles touch, atoms migrate across the particle boundaries. This movement fills the microscopic gaps, creates "necks" between adjacent particles, and ultimately fuses them into a single, interconnected lattice.
This process reduces the internal surface area and minimizes the overall energy of the system, resulting in a denser and more stable structure.
The Three Core Stages of the Sintering Process
While specifics vary by material, the sintering process follows a consistent, three-stage framework from powder to final product.
Stage 1: Powder Preparation and Composition
The process begins with the raw material in powder form. This is not simply a pile of dust; it is often a carefully engineered mix.
Depending on the application, primary material powders may be mixed with other elements, lubricants, or temporary binders. These binders help the powder hold its shape in the next stage.
Stage 2: Compaction and Forming
The prepared powder is placed into a die or mold and compacted under pressure. This step forms the material into its desired preliminary shape, often called a "green part."
Compaction is critical because it forces the powder particles into close contact, which is a prerequisite for the atomic diffusion that will occur during heating. This initial pressing removes large voids and establishes a uniform starting density.
Stage 3: Sintering (Controlled Heating)
The green part is placed into a sintering furnace or kiln where it is subjected to a precisely controlled heating cycle. The temperature is raised to a point below the material's melting point but high enough to activate atomic diffusion.
During this stage, two key events happen: the binders used in the preparation stage burn away, and the primary material particles begin to fuse. The part shrinks and becomes significantly denser and stronger as the voids between particles are eliminated.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Sintering is a powerful process, but its success depends on carefully managing a few critical variables. Mismanagement of these factors can lead to weak, defective, or unusable parts.
The Temperature and Time Dilemma
The sintering temperature and the duration of the heating cycle are the most critical parameters.
If the temperature is too low or the time too short, diffusion will be incomplete, resulting in a weak and porous part. If the temperature is too high, you risk uncontrolled grain growth or even partial melting, which can degrade the material's mechanical properties.
The Role of Pressure
While most of the work is done by heat, pressure remains a key factor. The initial compaction pressure determines the starting density and the proximity of the particles.
In some advanced techniques like hot isostatic pressing (HIP), pressure is applied during the heating cycle to achieve maximum density, often close to 100% of the solid material's theoretical density.
Material Purity and Particle Size
The characteristics of the starting powder have a profound impact on the final product. Contaminants can interfere with the diffusion process and weaken the final part.
Particle size is also crucial. Finer powders generally have more surface area and more contact points, allowing them to sinter at lower temperatures and achieve higher final densities.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your approach to sintering should be guided by the specific outcome you need to achieve for your material and application.
- If your primary focus is creating parts from high-melting-point materials: Sintering is your most practical and energy-efficient path, allowing you to bypass the extreme challenges of liquefying materials like ceramics or tungsten.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific porosity (e.g., for filters or self-lubricating bearings): Sintering offers unmatched control, enabling you to deliberately halt the process to retain a desired level of interconnected voids.
- If your primary focus is mass production of complex metal or ceramic parts: Powder metallurgy, which relies on sintering, is a highly effective and economical manufacturing route for producing strong, net-shape components.
By mastering the interplay between powder, pressure, and heat, you can leverage sintering to create high-performance components that are impossible to achieve through other means.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Powder Prep | Mixing powders with binders | Create a uniform blend that holds shape |
| 2. Compaction | Pressing powder in a mold | Form a 'green part' with particles in close contact |
| 3. Sintering | Controlled heating in a furnace | Activate atomic diffusion to fuse particles into a solid mass |
Ready to harness the power of sintering for your high-performance materials? KINTEK specializes in the precise lab equipment and furnace solutions needed to master this critical process. Whether you're working with advanced ceramics, metals, or developing new materials, our expertise ensures you achieve the density, strength, and properties your project demands. Contact our sintering experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the right solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness



















