The induction furnace process in steel manufacturing uses a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field to melt metal. Instead of applying external heat, this process induces an electrical current directly within the steel charge itself, causing the metal to heat up and melt from the inside out due to its own electrical resistance.
The core principle is electromagnetic induction: the furnace acts as a large transformer, turning the raw steel scrap into its own efficient, self-contained heat source. This allows for a clean melting process with precise control over temperature and final alloy composition.
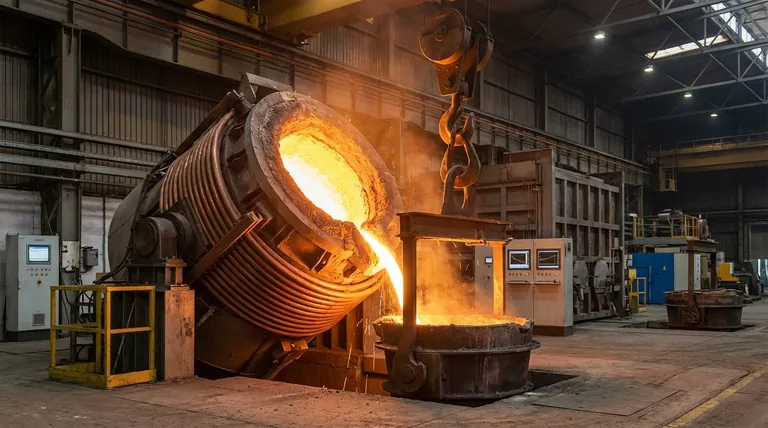

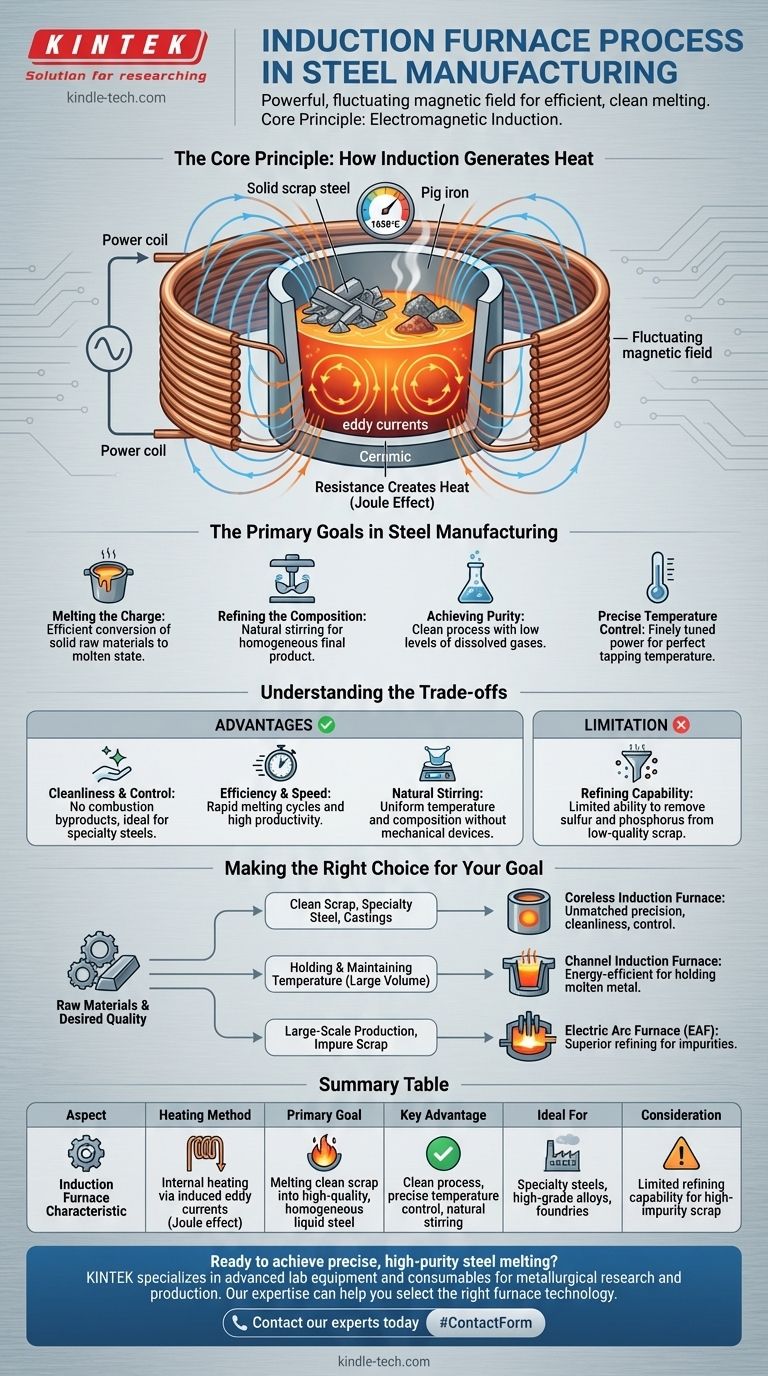
The Core Principle: How Induction Generates Heat
Understanding the induction furnace begins with the physics of electromagnetism. The process is remarkably efficient because it doesn't waste energy heating the furnace chamber; it heats the target metal directly.
The Power Coil
The heart of the furnace is a hollow copper coil. A high-frequency alternating electrical current (AC) from a dedicated power unit is passed through this coil.
The Magnetic Field
As the AC current flows and rapidly changes direction, it generates a powerful and fluctuating magnetic field inside the furnace, passing through the crucible where the metal charge (like scrap steel or pig iron) is placed.
Inducing Eddy Currents
This intense magnetic field induces smaller, circular electrical currents within the conductive metal charge. These are known as eddy currents.
Resistance Creates Heat
The metal has a natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents. This resistance generates immense heat—known as the Joule effect—rapidly raising the metal's temperature past its melting point, typically to around 1650°C.
The Primary Goals in Steel Manufacturing
An induction furnace is not just a melter; it's a tool for creating high-quality liquid steel with specific properties.
Melting the Charge
The first and most obvious goal is to efficiently convert solid raw materials, such as scrap steel and pig iron, into a completely molten state.
Refining the Composition
Once the steel is molten, operators can introduce various alloying elements. The electromagnetic forces that generate heat also create a natural stirring action, ensuring these elements are mixed thoroughly for a perfectly homogeneous final product.
Achieving Purity
Because the heat is generated internally without any combustion, the process is inherently clean. This results in molten steel with very low levels of dissolved gases, which is critical for high-performance applications.
Precise Temperature Control
The power supplied to the coil can be finely tuned, giving operators precise control over the temperature of the molten bath. This ensures the steel is at the perfect temperature for being tapped into a ladle and sent for casting.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful and precise, the induction furnace is not the universal solution for all steelmaking scenarios. Understanding its advantages and limitations is key.
Advantage: Cleanliness and Control
With no electrodes or burning fuel, there are no byproducts of combustion to contaminate the melt. This makes induction furnaces ideal for producing specialty steels and high-grade alloys where purity is paramount.
Advantage: Efficiency and Speed
Generating heat directly within the metal is very energy-efficient. This leads to rapid melting cycles and high productivity, especially for foundries and smaller-scale mills.
Advantage: Natural Stirring
The inherent electromagnetic stirring of the molten bath ensures uniform temperature and chemical composition without the need for mechanical stirrers.
Limitation: Refining Capability
The induction furnace excels at melting clean scrap but has limited capability to refine out impurities like sulfur and phosphorus. Large-scale operations that rely on lower-quality scrap often require furnaces with more aggressive refining technologies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a furnace technology depends entirely on the raw materials available and the desired quality of the final product.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality specialty steels or castings from clean scrap: The coreless induction furnace offers unmatched precision, cleanliness, and control.
- If your primary focus is holding and maintaining the temperature of a large volume of already-molten metal: The channel induction furnace, which operates like a true transformer, is a more energy-efficient choice for this specific task.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production using a wide variety of scrap qualities: An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is often more suitable due to its superior ability to handle and refine impurities from the charge.
Ultimately, the induction furnace is a cornerstone of modern metallurgy for its ability to deliver exceptionally clean, precisely controlled molten steel through the elegant principle of direct electromagnetic heating.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Furnace Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Internal heating via induced eddy currents (Joule effect) |
| Primary Goal | Melting clean scrap into high-quality, homogeneous liquid steel |
| Key Advantage | Clean process, precise temperature control, natural stirring |
| Ideal For | Specialty steels, high-grade alloys, foundries |
| Consideration | Limited refining capability for high-impurity scrap |
Ready to achieve precise, high-purity steel melting? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for metallurgical research and production. Our expertise can help you select the right furnace technology for your specific steel manufacturing goals. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What type of lining is needed for induction furnace? Choose the Right Refractory for Your Metal
- What are the benefits of using plasma melting equipment? Maximize Metal Recovery & Safety
- What is the primary purpose of using a high-temperature melting furnace for Chromel-TaC? Achieve Superior Homogeneity
- What is the induction furnace used for? Master Efficient Metal Melting & Heating
- Which furnace is used to melt aluminum? Induction vs. Combustion for Your Needs
- What is the main frequency of an induction furnace? A Guide to Optimizing Melting & Heating
- What are the factors to be considered for inductor design in induction heating? Optimize Your Heating Process
- What role do high-frequency induction furnaces and cold-wall Hukin crucibles play in U-Zr-Si crystal growth?



















