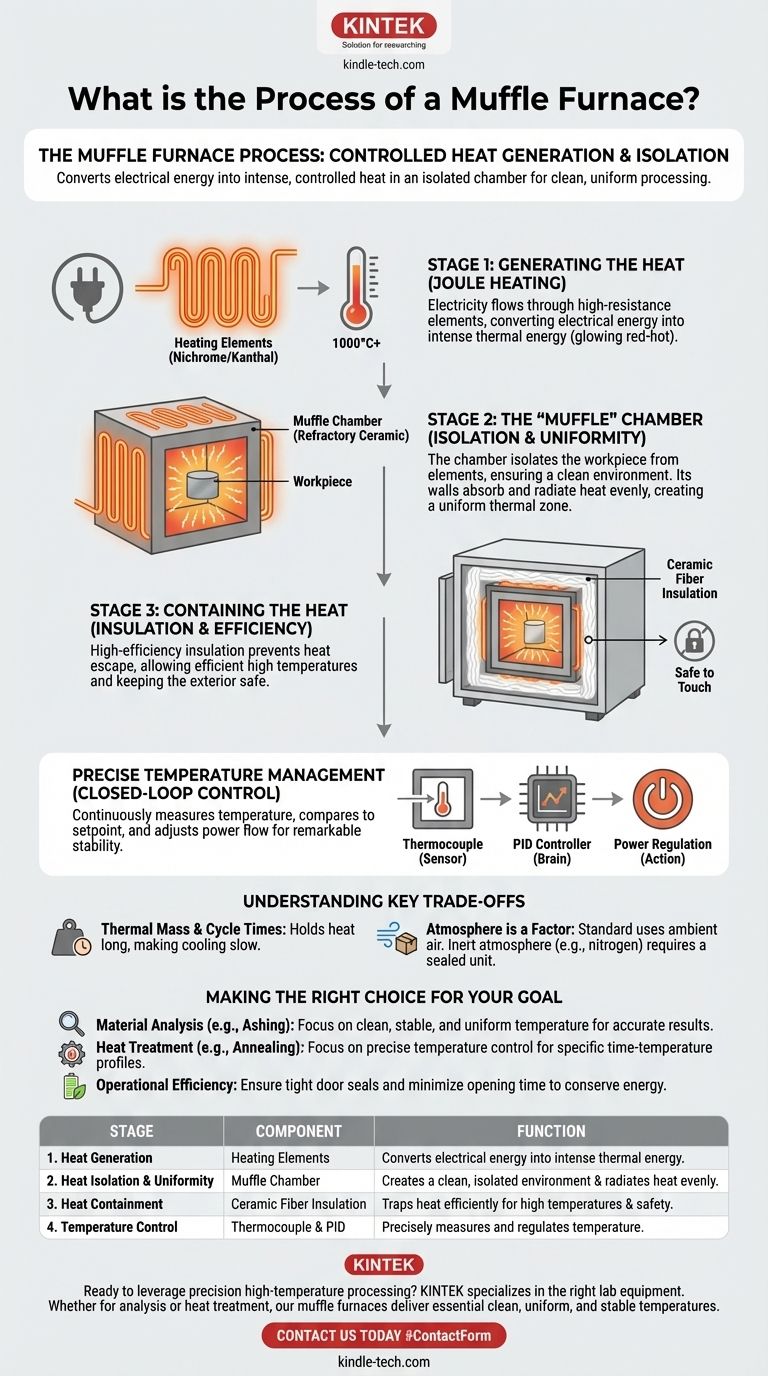
In essence, a muffle furnace operates by converting electrical energy into intense, controlled heat within a highly insulated chamber. It uses high-resistance heating elements to radiate thermal energy, heating a sample or workpiece without any direct contact, combustion byproducts, or flames.
The core principle is not just about generating extreme heat, but about creating an isolated and uniform thermal environment. A muffle furnace separates the item being heated from the raw heat source, ensuring clean, precise, and repeatable high-temperature processing.

The Core Principle: From Electricity to Controlled Heat
A muffle furnace's operation can be broken down into three fundamental stages: heat generation, heat isolation, and heat containment. Each stage relies on specific components working in concert.
Stage 1: Generating the Heat
The process begins with Joule heating, a basic principle of physics. An electric current is passed through specialized heating elements, typically made of a high-resistance material like Nichrome or Kanthal.
As electricity struggles to pass through this resistance, the electrical energy is converted directly into thermal energy, causing the elements to glow red-hot and reach temperatures well over 1000°C.
Stage 2: The "Muffle" Chamber
The heating elements are positioned around or embedded within the walls of an inner chamber. This chamber, made of dense, heat-resistant refractory ceramic, is the "muffle."
Its critical purpose is twofold:
- Isolation: It acts as a barrier, protecting the workpiece from direct contact with the glowing-hot elements. This ensures the sample is heated cleanly, without contamination.
- Uniformity: The chamber walls absorb the intense energy from the elements and radiate it evenly throughout the interior. This creates a uniform temperature zone, ensuring the entire workpiece is heated consistently.
Stage 3: Containing the Heat
The entire muffle chamber is housed within a larger cabinet filled with high-efficiency ceramic fiber insulation. This outer layer prevents the extreme heat from escaping.
This exceptional insulation is what allows the furnace to reach and maintain very high temperatures efficiently and keeps the exterior of the unit safe to touch.
How Temperature is Precisely Managed
A muffle furnace is more than just a hot box; it is a precision instrument. This precision comes from a closed-loop electronic control system.
The Sensor: Thermocouple
A thermocouple, a highly sensitive temperature probe, is placed inside the heating chamber. It constantly measures the internal temperature and sends this data back to the controller as a small voltage signal.
The Brain: PID Controller
The temperature controller (most commonly a PID controller) is the brain of the operation. It continuously compares the real-time temperature reading from the thermocouple to the target temperature set by the user.
The Action: Power Regulation
Based on the difference between the actual and setpoint temperatures, the controller precisely adjusts the amount of electricity flowing to the heating elements. It uses solid-state relays (SSRs) or contactors to cycle the power on and off rapidly, delivering just enough energy to maintain the target temperature with remarkable stability.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While powerful, the design of a muffle furnace comes with operational considerations that are important to understand.
The Origin of the "Muffle"
The term originates from older, fuel-fired furnaces. In those designs, a physical box (the muffle) was essential to shield the workpiece from the soot, ash, and gases produced by burning fuel. While modern electric furnaces don't have combustion byproducts, the term persists to describe the isolated heating chamber that ensures a clean processing environment.
Thermal Mass and Cycle Times
The dense refractory materials and thick insulation needed to handle high temperatures give the furnace significant thermal mass. This means that while it can heat up relatively quickly, it holds that heat for a very long time. Cooling down can be a slow process unless the model includes features for forced cooling.
Atmosphere is a Factor
A standard muffle furnace operates by heating the ambient air inside the chamber. This is suitable for most applications like ashing or general heat-treating. However, if a process requires an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent oxidation, a specialized, sealed furnace is necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the furnace's process allows you to leverage its capabilities for specific applications.
- If your primary focus is material analysis (e.g., ashing, gravimetrics): The key is the furnace's ability to provide a clean, stable, and uniform temperature, ensuring that your results are accurate and repeatable.
- If your primary focus is heat treatment (e.g., annealing, hardening): The precise temperature control of the PID system is your most critical tool, allowing you to execute specific time-temperature profiles to achieve desired material properties.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: Recognize that the process relies on superior insulation. Ensuring the door seal is tight and minimizing how long the door is open are crucial for maintaining temperature stability and conserving energy.
By understanding how these components work together, you can transform the muffle furnace from a simple oven into a precision instrument for advanced materials processing.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Component | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Heat Generation | Heating Elements (Nichrome/Kanthal) | Converts electrical energy into intense thermal energy via Joule heating. |
| 2. Heat Isolation & Uniformity | Muffle Chamber (Refractory Ceramic) | Creates a clean, isolated environment and radiates heat evenly. |
| 3. Heat Containment | Ceramic Fiber Insulation | Traps heat efficiently, enabling high temperatures and safe operation. |
| 4. Temperature Control | Thermocouple & PID Controller | Precisely measures and regulates temperature for stability and accuracy. |
Ready to leverage precision high-temperature processing in your lab?
Understanding the controlled process of a muffle furnace is the first step. KINTEK specializes in providing the right lab equipment to put that knowledge into practice.
Whether your focus is on material analysis (ashing, gravimetrics) or heat treatment (annealing, hardening), our muffle furnaces deliver the clean, uniform, and stable temperatures essential for accurate and repeatable results.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your specific application needs. Our experts will help you select the ideal furnace to enhance your lab's efficiency and capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of a laboratory oven in MnO2-GAC synthesis? Optimize Your Catalyst Preparation
- How is a high-temperature box furnace used for 500-hour oxidation testing? Simulate Real-World Superalloy Performance
- What is the function of an annealing furnace in Na3PS4 synthesis? Achieve High-Conductivity Cubic-Phase Electrolytes
- What is the role of high-temperature muffle furnaces in the synthesis of NASICON-structured LATP ceramic powder?
- What role does a high-temperature muffle furnace play in FM steel heat treatment? Expert Microstructure Engineering
- What is the difference between an oven and a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Thermal Equipment
- What is the use of muffle furnace in soil? Analyze Soil Composition with High-Temperature Precision
- What is the primary characteristic of a muffle furnace? Unlock Pure, Contamination-Free Heating



















